
Concept explainers
Draw enol tautomer(s) for each compound. Ignore stereoisomers.
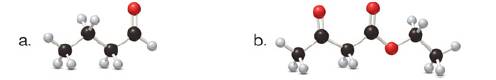
(a)
Interpretation: Enol tautomer(s) of the given compound is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: Tautomers are the isomers which differ only in the position of the hydrogens and electrons of electronegative element, generally oxygen. There is no change in the carbon skeleton of the compound. This phenomenon which involves simple proton transfer in an intramolecular fashion is known as tautomerism.
The very common example of tautomerism is Keto-enol tautomerism. It can be acid or base catalysed.
Answer to Problem 30P
. The enol tautomer of this compound is shown below:
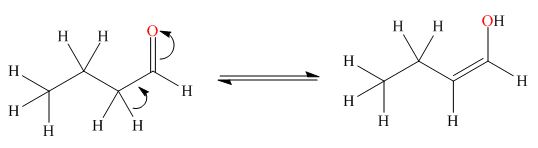
Explanation of Solution
Tautomers are isomers which differ only in the position of the protons and electrons of the compound. There is no change in the carbon skeleton of the compound. The ball and stick model as shown in Figure 1.
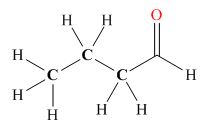
Figure 1
The enol tautomer of this compound is shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2
The tautomer of the given compound is showed in Figure 2.
(b)
Interpretation: Enol tautomer(s) of the given compound is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Tautomers are the isomers which differ only in the position of the hydrogens and electrons of electronegative element, generally oxygen. There is no change in the carbon skeleton of the compound. This phenomenon which involves simple proton transfer in an intramolecular fashion is known as tautomerism.
The very common example of tautomerism is Keto-enol tautomerism. It can be acid or base catalysed.
Answer to Problem 30P
. The enol tautomer of this compound is shown below:
Explanation of Solution
Tautomers are isomers which differ only in the position of the protons and electrons of the compound. There is no change in the carbon skeleton of the compound. The ball and stick model as shown in Figure 3.
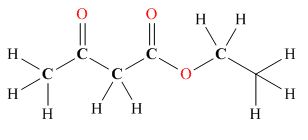
Figure 3
The enol tautomer of this compound is shown in Figure 4.

Figure 4
The tautomer of the given compound is showed in Figure 4.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-ACCESS
- Please correct answer and don't use hand ratingarrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardDraw Newman projects for each of the following molecules with 3 different rotational angles from carbon 2 to carbon 3. Rank your structures from lowest to highest energy. What causes the energy differences? Label the overlap. a. b. Br OH C. Br Brarrow_forward
- Draw the stereoisomers of 3,5-diethylcylopentane. Identify the different relationships between each molecules (diasteromers, enantiomers, meso compounds, etc.)arrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't use hand ratingarrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't use hand rating and don't use Ai solutionarrow_forward
- Show work....don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forwardIs it possible to do the following reduction in one step? If so, add the necessary reagents and catalysts to the reaction arrow. If not, check the box under the drawing area. T G टे 13arrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't use hand ratingarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
