
A sample of a monatomic ideal gas occupies 5.00 L at atmospheric pressure and 300 K (point A in Fig. P21.65). It is warmed at constant volume to 3.00 atm (point B). Then it is allowed to expand isothermally to 1.00 atm (point C) and at last compressed isobarically to its original state, (a) Find the number of moles in the sample.
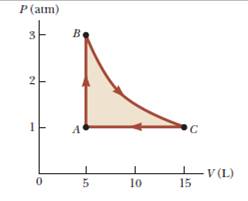
Find (b) the temperature at point B, (c) the temperature at point C, and (d) the volume at point C. (e) Now consider the processes A → B, B→ C, and C → A. Describe how to carry out each process experimentally, (f) Find Q, W, and ΔEint for each of the processes, (g) For the whole cycle A→ B→ C→ A, find Q, W, and ΔEint.
(a)
The number of moles in the sample.
Answer to Problem 21.65AP
The number of moles in the sample is
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The volume of the monatomic ideal gas is
The number of moles in the ideal gas equation is,
Here,
The value of the ideal gas constant is
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the number of moles in the sample is
(b)
The temperature at point
Answer to Problem 21.65AP
The temperature at point
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The volume of the monatomic ideal gas is
In the process from point
The expression for the process from point
Here,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the temperature at point
(c)
The temperature at point
Answer to Problem 21.65AP
The temperature at point
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The volume of the monatomic ideal gas is
In the process from point
So, the temperature at point
Conclusion:
Therefore, the temperature at point
(d)
The volume at point
Answer to Problem 21.65AP
The volume at point
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The volume of the monatomic ideal gas is
In the process from point
The expression for the process from point
Here,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the volume at point
(e)
The experimental methods to carry out the process
Answer to Problem 21.65AP
The experimental method to carry out the process
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The volume of the monatomic ideal gas is
In the process from point
The volume does not change. The temperature varies from
In the process from point
The temperature does not change. The pressure varies from
In the process from point
The pressure does not change. The temperature varies from
Conclusion:
Therefore, the experimental method to carry out the process
(f)
The heat
Answer to Problem 21.65AP
The heat
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The volume of the monatomic ideal gas is
For the process from point
The volume of gas does not change.
The work done is,
The change in internal energy is equal to the heat.
The expression for the change in internal energy is,
Here,
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, change in internal energy in process from point
For the process from point
The temperature does not change.
The change in internal energy is,
The expression of the work done is,
Substitute
Thus the change in internal energy in process from point
For the process from point
The formula of work done is,
Substitute
Thus, the work done for the point
The formula for the change in kinetic energy is,
Substitute
The heat obtain in this process is,
Conclusion:
Therefore, the heat
(g)
The heat
Answer to Problem 21.65AP
For the whole cycle
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The volume of the monatomic ideal gas is
The expression for the heat in complete cycle is,
Substitute
Thus, the heat in cycle is
The expression for the work done in complete cycle is,
Substitute
Thus, the total work done is
As the process is cyclic, the change in internal energy will be zero.
Conclusion:
Therefore, For the whole cycle
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology Update (No access codes included)
- An ideal gas in a sealed container starts out at a pressure of 8900 N/m2 and a volume of 5.7 m3. If the gas expands to a volume of 6.3 m3 while the pressure is held constant (still at 8900 N/m2), how much work is done by the gas? Give your answer as the number of Joules.arrow_forwardThe outside temperature is 25 °C. A heat engine operates in the environment (Tc = 25 °C) at 50% efficiency. How hot does it need to get the high temperature up to in Celsius?arrow_forwardGas is compressed in a cylinder creating 31 Joules of work on the gas during the isothermal process. How much heat flows from the gas into the cylinder in Joules?arrow_forward
- The heat engine gives 1100 Joules of energy of high temperature from the burning gasoline by exhausting 750 Joules to low-temperature . What is the efficiency of this heat engine in a percentage?arrow_forwardL₁ D₁ L₂ D2 Aluminum has a resistivity of p = 2.65 × 10 8 2. m. An aluminum wire is L = 2.00 m long and has a circular cross section that is not constant. The diameter of the wire is D₁ = 0.17 mm for a length of L₁ = 0.500 m and a diameter of D2 = 0.24 mm for the rest of the length. a) What is the resistance of this wire? R = Hint A potential difference of AV = 1.40 V is applied across the wire. b) What is the magnitude of the current density in the thin part of the wire? Hint J1 = c) What is the magnitude of the current density in the thick part of the wire? J₂ = d) What is the magnitude of the electric field in the thin part of the wire? E1 = Hint e) What is the magnitude of the electric field in the thick part of the wire? E2 =arrow_forwardplease helparrow_forward
- A cheetah spots a gazelle in the distance and begins to sprint from rest, accelerating uniformly at a rate of 8.00 m/s^2 for 5 seconds. After 5 seconds, the cheetah sees that the gazelle has escaped to safety, so it begins to decelerate uniformly at 6.00 m/s^2 until it comes to a stop.arrow_forwardA projectile is fired with an initial speed of 40.2 m/s at an angle of 35.0 degree above the horizontal on a long flat firing range. Determine. please help and show work for them so i can understand.arrow_forwardpls helparrow_forward
- J K L The graph in the figure shows the position of an object as a function of time. The letters H-L represent particular moments of time. At which moments shown (H, I, etc.) is the speed of the object the greatest? + Position H I K Timearrow_forward1. Two pendula of slightly different length oscillate next to each other. The short one oscillates with frequency 0.52 Hz and the longer one with frequency 0.50 Hz. If they start of in phase determine their phase difference after 75 s.arrow_forwardA mass is connect to a vertical revolving axle by two strings of length L, each making an angle of 45 degrees with the axle, as shown. Both the axle and mass are revolving with angular velocity w, Gravity is directed downward. The tension in the upper string is T_upper and the tension in the lower string is T_lower.Draw a clear free body diagram for mass m. Please include real forces only.Find the tensions in the upper and lower strings, T_upper and T_lowerarrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





