
(a)
Interpretation:
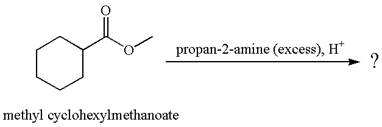
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
Concept introduction:
The esters in acidic condition undergo hydrolysis and form the corresponding
Answer to Problem 21.53P
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
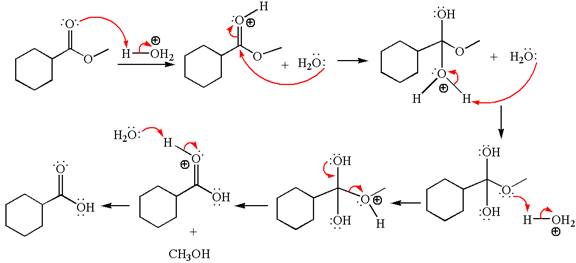
Explanation of Solution
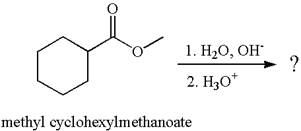
The equation for the reaction of methyl cyclohexylmethanoate with
The methyl cyclohexylmethanoate is an ester; in an acidic condition, it undergoes hydrolysis to form carboxylic acid and alcohol. The ester is activated by protonation of carbonyl oxygen. The water molecule acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carbonyl carbon of protonated ester and removes methanol as the leaving group. The product with detailed mechanism is as follows:
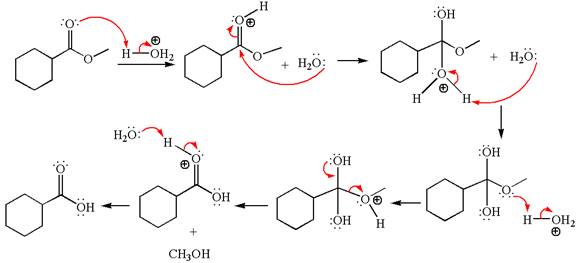
The product with detailed mechanism for the given reaction is drawn based on the reactivity of ester in an acidic condition.
(b)
Interpretation:
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
Concept introduction:
The ester can be hydrolyzed in basic condition and forms corresponding carboxylic acid and alcohol. As hydrolysis occurs in basic condition, it deprotonates carboxylic acid to carboxylate ion. Thus, to recover, it must then be treated with an acid.
Answer to Problem 21.53P
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
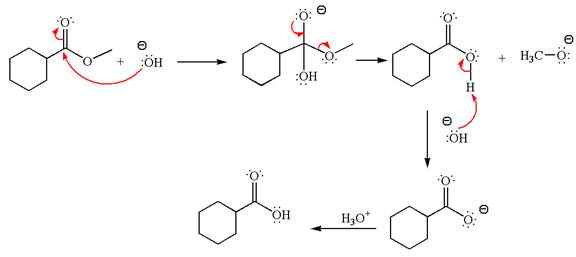
Explanation of Solution
The equation for the reaction of methyl cyclohexylmethanoate with
The methyl cyclohexylmethanoate is an ester; in a basic condition, it undergoes hydrolysis to form carboxylic acid and alcohol. The hydroxide ion acts as a nucleophile and attacks ester carbonyl to form an intermediate having negatively charged oxygen. The intermediate undergoes elimination of methoxide by delocalization of lone pair of negatively charged oxygen and forms carboxylic acid. The carboxylic acid further undergoes deprotonated to carboxylate ion due to basic reaction condition. Therefore, the carboxylic acid is recovered by addition of
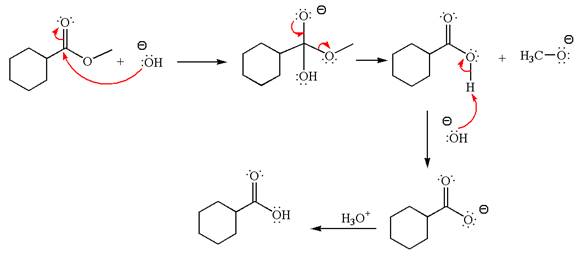
The product with detailed mechanism for the given reaction is drawn based on the reactivity of ester in a basic condition.
(c)
Interpretation:
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
Concept introduction:
The alcohols are weak nucleophiles and thus cannot react with an ester under normal condition. Thus, on addition of base, the alcohol is converted to alkoxide ion, which acts as a good nucleophile and undergoes transesterification when reacted with an ester.
Answer to Problem 21.53P
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
Explanation of Solution
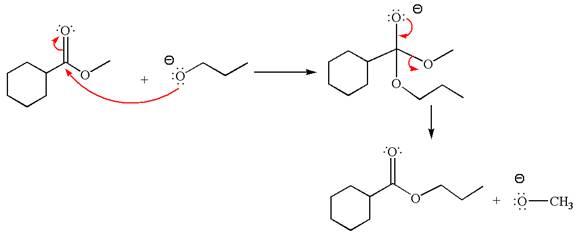
The equation for the reaction of methyl cyclohexylmethanoate with
The methyl cyclohexylmethanoate is an ester; on reaction with
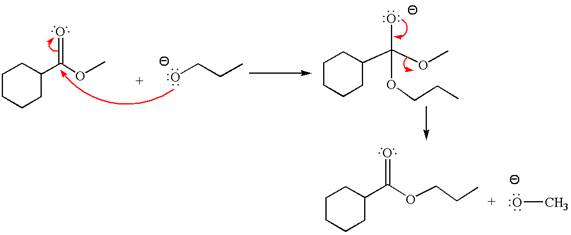
The product with detailed mechanism for the given reaction is drawn based on the reactivity of ester with alkoxide ion.
(d)
Interpretation:
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
Concept introduction:
Alcohols are weak nucleophiles and cannot react with an ester under normal condition. Thus, for the reaction to carry out, it can be catalyzed by addition of an acid. The ester, on acid-catalyzed reaction with alcohol, undergoes transesterification, called acid-catalyzed transesterification.
Answer to Problem 21.53P
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
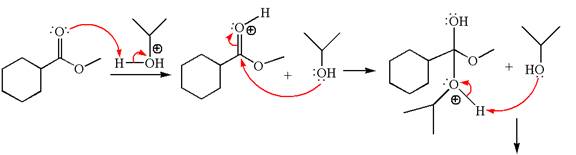
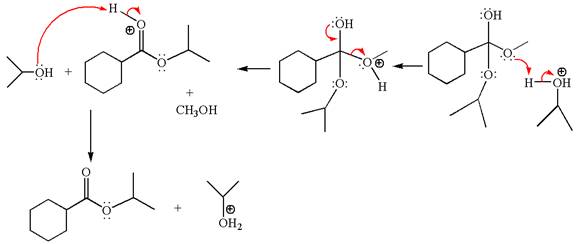
Explanation of Solution
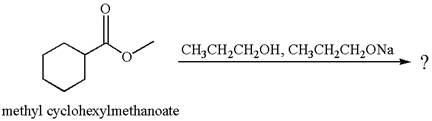
The equation for the reaction of methyl cyclohexylmethanoate with
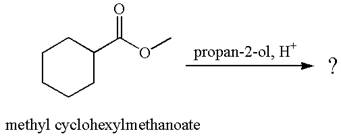
The methyl cyclohexylmethanoate is an ester; on reaction with


The product with detailed mechanism for the given reaction is drawn based on the reactivity of ester with alcohol in an acidic condition.
(e)
Interpretation:
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
Concept introduction:
The ester, on reaction with an excess of
Answer to Problem 21.53P
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
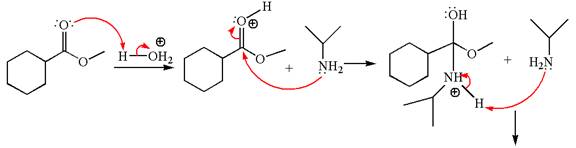
Explanation of Solution
The equation for the reaction of methyl cyclohexylmethanoate with
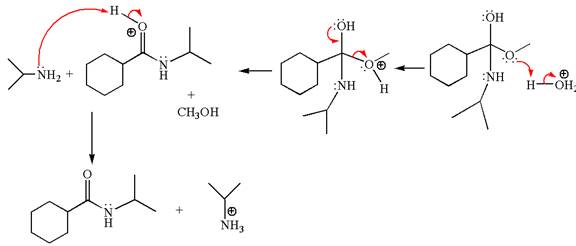
The methyl cyclohexylmethanoate is an ester; in an acidic condition, it undergoes aminolysis to form amide and alcohol. The ester is activated by protonation of carbonyl oxygen. The amine molecule acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carbonyl carbon of protonated ester and removes methanol as the leaving group. The product with detailed mechanism is as follows:

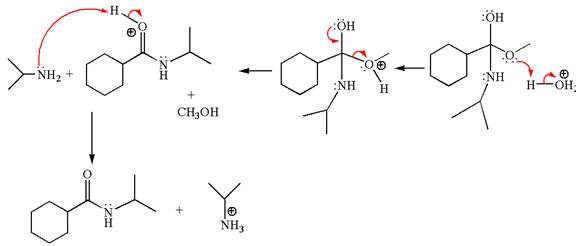
The product with detailed mechanism for the given reaction is drawn based on the reactivity of ester with amine in an acidic condition.
(f)
Interpretation:
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
Concept introduction:
The alcohols are weak nucleophiles; in an acidic or basic condition, they undergo transesterification with an ester, but under normal condition, the reaction does not occur.
Answer to Problem 21.53P
No reaction takes place between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
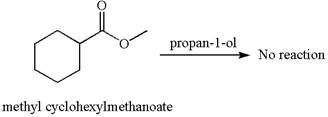
Explanation of Solution
The equation for the reaction of methyl cyclohexylmethanoate with
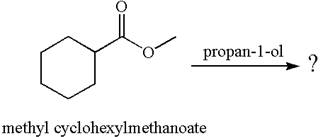
The methyl cyclohexylmethanoate is an ester, and the given reagent
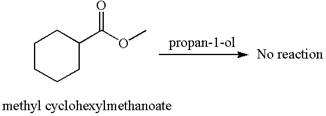
It is determined that there is no reaction between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles And Mechanisms: Study Guide/solutions Manual (second)
- Complete combustion of a 0.6250 g sample of the unknown crystal with excess O2 produced 1.8546 g of CO2 and 0.5243 g of H2O. A separate analysis of a 0.8500 g sample of the blue crystal was found to produce 0.0465 g NH3. The molar mass of the substance was found to be about 310 g/mol. What is the molecular formula of the unknown crystal?arrow_forward4. C6H100 5 I peak 3 2 PPM Integration values: 1.79ppm (2), 4.43ppm (1.33) Ipeakarrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
- 3. Consider the compounds below and determine if they are aromatic, antiaromatic, or non-aromatic. In case of aromatic or anti-aromatic, please indicate number of I electrons in the respective systems. (Hint: 1. Not all lone pair electrons were explicitly drawn and you should be able to tell that the bonding electrons and lone pair electrons should reside in which hybridized atomic orbital 2. You should consider ring strain- flexibility and steric repulsion that facilitates adoption of aromaticity or avoidance of anti- aromaticity) H H N N: NH2 N Aromaticity (Circle) Aromatic Aromatic Aromatic Aromatic Aromatic Antiaromatic Antiaromatic Antiaromatic Antiaromatic Antiaromatic nonaromatic nonaromatic nonaromatic nonaromatic nonaromatic aromatic TT electrons Me H Me Aromaticity (Circle) Aromatic Aromatic Aromatic Aromatic Aromatic Antiaromatic Antiaromatic Antiaromatic Antiaromatic Antiaromatic nonaromatic nonaromatic nonaromatic nonaromatic nonaromatic aromatic πT electrons H HH…arrow_forwardA chemistry graduate student is studying the rate of this reaction: 2 HI (g) →H2(g) +12(g) She fills a reaction vessel with HI and measures its concentration as the reaction proceeds: time (minutes) [IH] 0 0.800M 1.0 0.301 M 2.0 0.185 M 3.0 0.134M 4.0 0.105 M Use this data to answer the following questions. Write the rate law for this reaction. rate = 0 Calculate the value of the rate constant k. k = Round your answer to 2 significant digits. Also be sure your answer has the correct unit symbol.arrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
- in which spectral range of EMR, atomic and ionic lines of metal liesarrow_forwardQ2: Label the following molecules as chiral or achiral, and label each stereocenter as R or S. CI CH3 CH3 NH2 C CH3 CH3 Br CH3 X &p Bra 'CH 3 "CH3 X Br CH3 Me - N OMe O DuckDuckarrow_forward1. For the four structures provided, Please answer the following questions in the table below. a. Please draw π molecular orbital diagram (use the polygon-and-circle method if appropriate) and fill electrons in each molecular orbital b. Please indicate the number of π electrons c. Please indicate if each molecule provided is anti-aromatic, aromatic, or non- aromatic TT MO diagram Number of π e- Aromaticity Evaluation (X choose one) Non-aromatic Aromatic Anti-aromatic || ||| + IVarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





