
(a)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of carbinoxamine has to be shown.
Concept introduction:
The Grignard reaction:
Alkyl, vinyl, or aryl-magnesium halides (
Grignard reagent is reaction with carbonyl compound such as
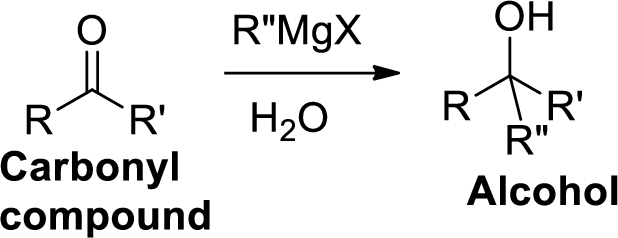
(b)
Interpretation:
The chirality of Carbinoxamine is to be identified and the possible stereoisomers has to be identified in the given synthesis.
Concept introduction:
Chiral:
A molecule is non superimposable on its mirror image is called chiral molecule.
Four different atoms attached to a carbon atom is called chiral molecule.
Isomer:
A molecule having the same molecular formula but with different chemical structure is called isomer.
Stereoisomers:
Stereoisomers are molecules that have the same molecular formula and they differ only in arrangement of atom in three-dimensional space.
Enantiomers:
A compound which is non-superimposable mirror image is called enantiomers.
Diastereomers:
A compound which is non-superimposable and non-mirror image is called diastereomers.
Racemic mixture:
A racemic mixture is simply a mixture containing an equal amount of each enantiomer.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 21 Solutions
Organic Chemistry, Loose-leaf Version
- What would be the major product of the following reaction? Please include a detailed explanation of what is happening in this question. Include steps and a drawing to show this reaction proceeds and how the final product is formed. The correct answer is B. I put answer D and I don't really understand what is going on in the question.arrow_forwardWhat is the product of the following reaction? Please explain what is happening in this question. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how the reagent is reacting with the catalysts to product the correct product. The correct answer is B.arrow_forwardWhat is the missing intermediate 1 and the final product 2. Please include a detailed explanation explaining the steps of malonic ester synthesis. Please include drawings of the intermediate and how it occurs and how the final product is former.arrow_forward
- What would be the reagents and conditions above and below the arrow that will complete the proposed acetoacetic ester synthesis? If it cannot be done efficiently, then I will choose that answer. There could be 2 or 4 reagents involved. Please provide a detailed explanation and drawings showing how it would proceed with the correct reagents.arrow_forwardFor benzene, the ∆H° of vaporization is 30.72 kJ/mol and the ∆S° of vaporization is 86.97 J/mol・K. At 1.00 atm and 228.0 K, what is the ∆G° of vaporization for benzene, in kJ/mol?arrow_forwardThe reaction Q(g) + R(g) → Z(l) is shown to be exothermic. Which of the following is true concerning the reaction. it is spontaneous only at High T, it is spontaneous at low T it is nonspontaneous at all T it is spontanrous at all T. it is non spontaneous only at low T.arrow_forward
- The reaction Q(g) + R(g) → Z(l) is shown to be exothermic. Which of the following is true concerning the reactionarrow_forwardWhich of the following has the largest standard molar entropy, S° (298.15 K) He H2 NaCl KBr Hgarrow_forwardWhich of the following is true for a particular reaction if ∆G° is -40.0 kJ/mol at 290 K and –20.0 kJ/mol at 390 K?arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning


