
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
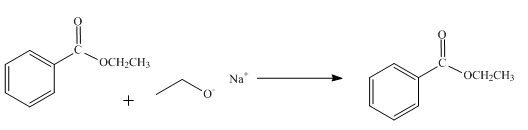
The product obtained from the reaction of ethyl benzoate and
Concept introduction:
An ester is a derivative of carboxylic which is obtained by replacing the
Answer to Problem 21.32AP
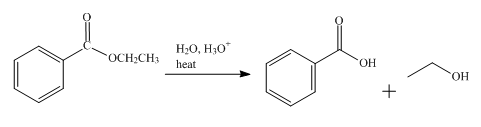
The product obtained from the reaction of ethyl benzoate and
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of ethyl benzoate in presence

Figure 1
The product obtained from the reaction of ethyl benzoate and
(b)
Interpretation:
The product obtained from the reaction of ethyl benzoate and
Concept introduction:
An ester is a derivative of carboxylic which is obtained by replacing the
Answer to Problem 21.32AP
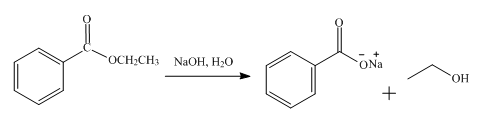
The product obtained from the reaction of ethyl benzoate and
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of ethyl benzoate in the presence of

Figure 2
The product obtained from the reaction of ethyl benzoate and
(c)
Interpretation:
The product obtained from the reaction of ethyl benzoate and aqueous
Concept introduction:
An ester is a derivative of carboxylic which is obtained by replacing the
Answer to Problem 21.32AP
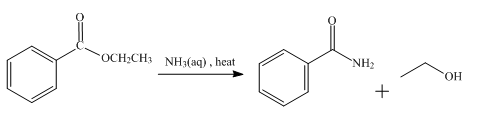
The product obtained from the reaction of ethyl benzoate and aqueous
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of ethyl benzoate in the presence of aqueous

Figure 3
The product obtained from the reaction of ethyl benzoate and aqueous
(d)
Interpretation:
The product obtained from the reaction of ethyl benzoate and
Concept introduction:
An ester is a derivative of carboxylic which is obtained by replacing the
Answer to Problem 21.32AP
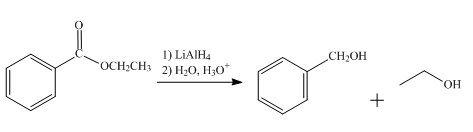
The product obtained from the reaction of ethyl benzoate and
Explanation of Solution
The reduction reaction of ethyl benzoate takes place in the presence of

Figure 4
The product obtained from the reaction of ethyl benzoate and
(e)
Interpretation:
The product obtained from the reaction of ethyl benzoate and excess
Concept introduction:
An ester is a derivative of carboxylic which is obtained by replacing the
Answer to Problem 21.32AP
The product obtained from the reaction of ethyl benzoate and excess
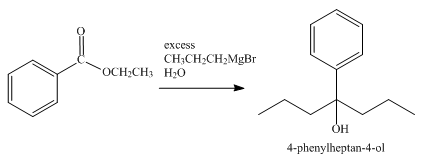
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of ethyl benzoate with an excess of Grignard reagent

Figure 5
The product obtained from the reaction of ethyl benzoate and excess
(f)
Interpretation:
The product obtained from the reaction of the product of part (e) and acetyl chloride, pyridine at
Concept introduction:
An ester is a derivative of carboxylic which is obtained by replacing the
Answer to Problem 21.32AP
The product obtained from the reaction of the product of part (e) and acetyl chloride, pyridine, at
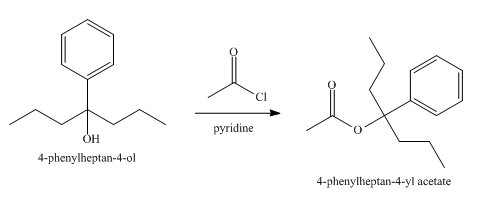
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of the product of part (e) and acetyl chloride, pyridine at

Figure 6
The product obtained from the reaction of the product of part (e) and acetyl chloride, pyridine, at
(g)
Interpretation:
The product obtained from the reaction of the product of part (e) and benzenesulfonyl chloride is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
An ester is a derivative of carboxylic which is obtained by replacing the
Answer to Problem 21.32AP
The product obtained from the reaction of the product of part (e) and benzenesulfonyl chloride is shown below.
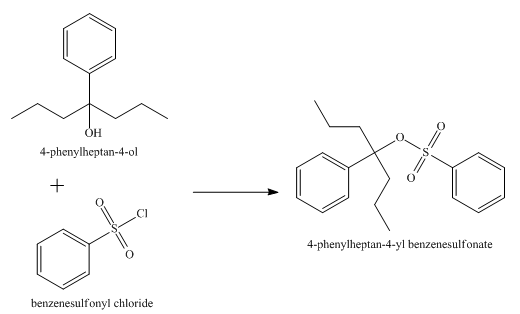
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of the product of part (e) and benzenesulphonyl chloride undergoes substitution reaction. It results in the formation of

Figure 7
The product obtained from the reaction of the product of part (e) and benzenesulfonyl chloride is shown in Figure 7.
(h)
Interpretation:
The product obtained from the reaction of ethyl benzoate and
Concept introduction:
An ester is a derivative of carboxylic which is obtained by replacing the
Answer to Problem 21.32AP
The product obtained from the reaction of ethyl benzoate and
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of ethyl benzoate with

Figure 8
The product obtained from the reaction of ethyl benzoate and
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY SAPLING ACCESS + ETEX
- Refer to the monosaccharides below to answer each of the following questions: CH2OH CHO CH₂OH CHZOH 0 H OH 0 0 HO H H OH HO H HO H H OH HO H CHZOH H OH HO H HO H CHZOH CHZOH CH3 a Sorbose b. Rhamnose c. Erythrulose d. Xylulose Classify each sugar by type; for example, glucose is an aldohexose. A. Xylulose is B. Erythrulose is C. Sorbose is D. Rhamnose isarrow_forwardRefer to the sugars below to answer the following questions. Choose the sugar that best fits each escription and place the letter of the sugar in the blank to the left of the description. There is only one orrect answer for each question, but sugars may be used more than once. CH₂OH 0 CHO HO H CHO CH₂OH HO H HO H HO H H OH HH OH OH H OH H OH HO H CH₂OH H OH CH₂OH CH₂OH CH₂OH a (-)-tagatose b. (+) gulose c. (-)-erythrose d (-)-n bulos A. ARCD a D-ketohexose B. C. D. oxidizes to an optically inactive aldaric acid a dextrorotary hexose a ketose with two chirality centersarrow_forwardDraw the structure of the aldol, self condensation product for each of the following compounds if a compound does not undergo aldol self condensation explain why it does notarrow_forward
- Show how each of the following transformations might be best accomplished. More than one step may required. Show all reagents and all intermediate structures. [4 only] CH3 A. CH CH2 C Br CH3 B OH only source of carbon CH3 CH CH2 C NHz CH 3 Harrow_forward. Choose a structure from the list provided below that best fits each of the following escriptions. Place the letter of the structure in the blank to the left of the description. There is nly one correct answer for each question. starch HO CH₂OH b. cellulose d. CH₂OH HO OH HO HO OH OH OH f. sucrose CH₂OH OH OH HO OCH₂ OH a monosaccharide that gives a negative Benedict's Test. a ẞ-1,4'-glycoside a disaccharidearrow_forwardShow how each of the following transformations might be best accomplished. More than one step may required. Show all reagents and all intermediate structures. [4 only] CH3 A. CH CH2 C Br CH3 CH3 CH3CH2 C NH2 CH3 B OH any source of carbon N MIHarrow_forward
- Consider the reaction below to answer the following questions. 0 0 25 PS ES 1919sds-III msx H H + 5% NaOCH 3, CH3OHA O CH₂OH Jeiniog 2E1 gniwool of mor]. Ignibuloni 9vil 19 A B 11 >buoqm gniwollol so dass 101 tomboy boo-11Coble or to r ton auch i viw ninlaxs, noitsausbroo 152 lobla ogsbau ton 250b br A. Which carbonyl compound functions as the electrophile in this reaction? B. Draw the structure of the enolate ion that is generated during the course of this reaction. C. This reaction is an example of: a. a mixed Claisen condensation. b. C. d. a Dieckman condensation. a Michael reaction. a mixed aldol reaction. HD HDarrow_forwardConsider the reaction below to answer the following questions: 847 Acetoacetic ester can be prepared by the Claisen self-condensation reaction of ethyl acetate. H₁C 0 H 0 IL 유 || OCH2CH3 1. NaOEt, EtOH C 2. H₂O H3C CH₂ Cold not tobizmo. S OCH2CH3 A. Write the complete stepwise mechanism for this reaction. Show all electron flow with arrows and draw all intermediate structures. B. Ethyl acetate can be prepared from ethanol as the only organic starting material. Show all reagents and structures for all intermediates in this preparation. C. Give the structures of the ester precursors for the following Claisen condensation product and formulate the reaction. ou OELarrow_forwardA. What is the correct structure for a-D-glucopyranose? CH₂OH a HO HO- OH b HO HO- OH HOH₂C OH OH OH CH₂OH HO C. HO HO- OH OH CH₂OH OH OH B. Draw structures for the products you would expect to obtain from reaction of B-D-galactopyranose with each of the following reagents. Be sure to include all relevant stereochemistry. [FOUR only] A. CH, Ag₂O B. warm dilute HNO3 C. (CH3CO)20, pryridine D. NaBH in H₂O E. CH₂OH, HCI F. Br₂, H₂O HO CH₂OH HO- OH OH B-D-galactopyranosearrow_forward
- Give the major organic product(s) for each of the following reactions or reaction sequences. CH₂CN 5% NaOEt, EIOH سجد سی . بلی H 1. NaOCH, CH,OH CH3 OCH3 2 H₂O*arrow_forwardDraw the structures for each of the intermediates in the boxes provided for the synthesis below. 004 HNO F HO CHCO) D Dydre R.SO. 1.1 NO fe HO H.SO. 2. CC1 NOH HO MCL HNO, H.50.arrow_forward. Each of the following compounds can be prepared by a mixed aldol condensation reaction. Give the Cructures of the aldehyde and/or ketone precursors for each aldol product and formulate the reaction. 0 CH=CHCCH 3. Ph 1arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
