
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure of
Concept introduction:
Answer to Problem 21.1P
The structure of
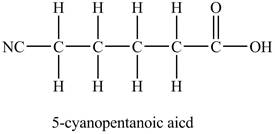
Explanation of Solution
In
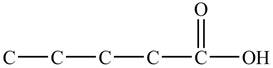
Figure 1
At the fifth carbon, there is a cyano group
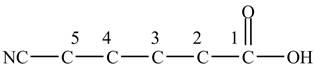
Figure 2
The above skeleton is completed by adding hydrogens as per the tetravalency of carbon as shown below.
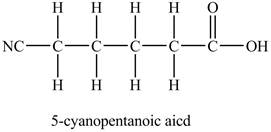
Figure 3
The structure of
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure of isopropyl valerate is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acid is a class of organic compound that contains a
Answer to Problem 21.1P
The structure of isopropyl valerate is shown below.
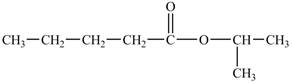
Explanation of Solution
The structure of isopropyl valerate consists of eight carbons, sixteen hydrogen atoms and two oxygen atoms. Isopropyl valerate is a common name of isopropyl pentanoate. It is a five carbon carboxylic acid. The structure of pentanoic acid is shown below.
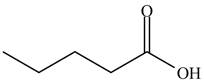
Figure 4
The hydrogen of carboxylic group is replaced by an isopropyl group to form an ester. The structure of isopropyl valerate is shown below.
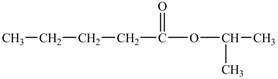
Figure 5
The structure of isopropyl valerate is shown in Figure 5.
(c)
Interpretation:
The structure of ethyl methyl malonate is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acid is a class of organic compound that contains a
Answer to Problem 21.1P
The structure of ethyl methyl malonate is shown below.
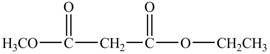
Explanation of Solution
The structure of ethyl methyl malonate consists of a eight carbons, fourteen hydrogen and four oxygen. Ethyl methyl malonate consists of propane dioic acid as parent chain.
The structure of propane dioic acid is shown below.
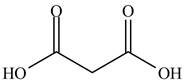
Figure 6
In the above structure, at first position hydrogen is substituted by a methyl group and at the last carboxyl group an ethyl group replaces the hydrogen of the carboxyl group. The structure of ethyl methyl malonate is shown below.
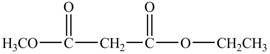
Figure 7
The structure of ethyl methyl malonate is shown in Figure 6.
(d)
Interpretation:
The structure of cyclohexyl acetate is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acid is a class of organic compound that contains a
Answer to Problem 21.1P
The structure of cyclohexyl acetate is shown below.
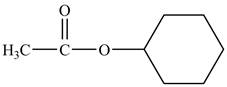
Explanation of Solution
Cyclohexyl acetate consists of a cyclohexane ring and an acetate group. The acetate group is given by the formula
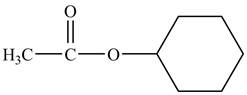
Figure 8
The structure of cyclohexyl acetate is shown in Figure 8
(e)
Interpretation:
The structure of
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acid is a class of organic compound that contains a
Answer to Problem 21.1P
The structure of
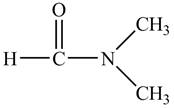
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
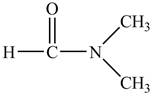
Figure 9
The structure of
(f)
Interpretation:
The structure of
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acid is a class of organic compound that contains a
Answer to Problem 21.1P
The structure of
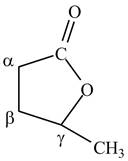
Explanation of Solution
Lactones are cyclic esters. The structure of
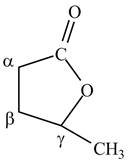
Figure 10
The structure of
(g)
Interpretation:
The structure of glutarimide is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acid is a class of organic compound that contains a
Answer to Problem 21.1P
The structure of glutarimide is shown below.
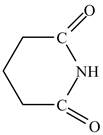
Explanation of Solution
The structure of glutarimide consists of a piperidine ring. There are two carbonyl group present adjacent to the nitrogen group. The structure of a piperidine ring is shown below.
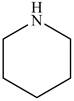
Figure 11
Therefore, the structure of glutarimide is shown below.
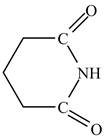
Figure 12
The structure of glutarimide is shown in Figure 12.
(h)
Interpretation:
The structure of
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acid is a class of organic compound that contains a
Answer to Problem 21.1P
The structure of
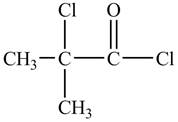
Explanation of Solution
There is carboxyl group present in
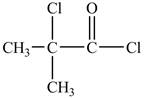
Figure 13
The structure of
(i)
Interpretation:
The structure of
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acid is a class of organic compound that contains a
Answer to Problem 21.1P
The structure of
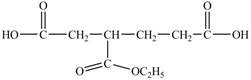
Explanation of Solution
In
Figure 14
In the above structure there is a ethoxy carbonyl group at the third position. Therefore, the structure of
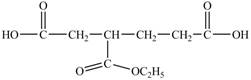
Figure 15
The structure of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Identify the compound with the longest carbon - nitrogen bond. O CH3CH2CH=NH O CH3CH2NH2 CH3CH2C=N CH3CH=NCH 3 The length of all the carbon-nitrogen bonds are the samearrow_forwardIdentify any polar covalent bonds in epichlorohydrin with S+ and 8- symbols in the appropriate locations. Choose the correct answer below. Η H's+ 6Η Η Η Η Η Ηδ Η Ο Ο HH +Η Η +Η Η Η -8+ CIarrow_forwardH H:O::::H H H HH H::O:D:D:H HH HH H:O:D:D:H .. HH H:O:D:D:H H H Select the correct Lewis dot structure for the following compound: CH3CH2OHarrow_forward
- Rank the following compounds in order of decreasing boiling point. ннннн -С-С-Н . н-с- ННННН H ΗΤΗ НННН TTTĪ н-с-с-с-с-о-н НННН НН C' Н н-с-с-с-с-н НН || Ш НННН H-C-C-C-C-N-H ННННН IVarrow_forwardRank the following compounds in order of decreasing dipole moment. |>||>||| ||>|||>| |>|||>|| |||>||>| O ||>>||| H F H F H c=c || H c=c F F IIIarrow_forwardchoose the description that best describes the geometry for the following charged species ch3-arrow_forward
- Why isn't the ketone in this compound converted to an acetal or hemiacetal by the alcohol and acid?arrow_forwardWhat is the approximate bond angle around the nitrogen atom? HNH H Harrow_forwardOH 1. NaOCH2CH3 Q 2. CH3CH2Br (1 equiv) H3O+ Select to Draw 1. NaOCH2 CH3 2. CH3Br (1 equiv) heat Select to Edit Select to Drawarrow_forward
- Complete and balance the following half-reaction in acidic solution. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. S₂O₃²⁻(aq) → S₄O₆²⁻(aq)arrow_forwardQ Select to Edit NH3 (CH3)2CHCI (1 equiv) AICI 3 Select to Draw cat. H2SO4 SO3 (1 equiv) HO SOCl2 pyridine Select to Edit >arrow_forwardComplete and balance the following half-reaction in basic solution. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. Zn(s) → Zn(OH)₄²⁻(aq)arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
