
Concept explainers
To determine:
The parts of the given figure of a virus.
Introduction:
A virus can be defined as a biological agent which reproduces inside the living cells of the hosts. When there is an infection by a virus, the host cell produces thousands of similar copies of the original virus at an unexpected rate.
Explanation of Solution
Given figure of virus structure has the following parts:
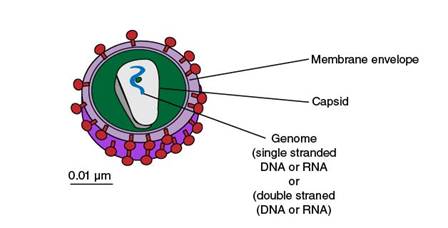
Viruses are made up of genetic material which is surrounded by a protein coat. The virus core is made up of
The envelopes are usually derived from the parts of the host cell membranes such as phospholipids and proteins. These contain some viral glycoproteins. They may assist the viruses to evade the host immune system. Glycoproteins present on the surface of the envelope helps to recognize and fix to the receptor spots on the host membrane.
Hence, the given figure of virus structure has the following parts: membrane envelope, capsid, and genome.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
BELK SCIENCE F/LIFE-MASTRG. BIOL.AC+EBK
- You expect to find which of the following in the Microtubule Organizing Center (MTOC)...(mark all that apply) A. Gamma tubulin B. XMAP215 C. Centrioles D. Kinesin-13arrow_forwardThe actin-nucleating protein formin has flexible “arms” containing binding sites that help recruit subunits in order to enhance microfilament polymerization. What protein binds these sites? A.Thymosin B.Profilin C.Cofilin D.Actin E.Tropomodulinarrow_forwardWhile investigating an unidentified motor protein, you discover that it has two heads that bind to actin. Based on this information, you could confidently determine that it is NOT... (mark all that apply) A. A myosin I motor B. A dynein motor C. A myosin VI motor D. A kinesin motorarrow_forward
- You isolate the plasma membrane of cells and find that . . . A. it contains regions with different lipid compositions B. it has different lipid types on the outer and cytosolic leaflets of the membrane C. neither are possible D. A and B both occurarrow_forwardYou are studying the mobility of a transmembrane protein that contains extracellular domains, one transmembrane domain, and a large cytosolic domain. Under normal conditions, this protein is confined to a particular region of the membrane due to the cortical actin cytoskeletal network. Which of the following changes is most likely to increase mobility of this protein beyond the normal restricted region of the membrane? A. Increased temperature B. Protease cleavage of the extracellular domain of the protein C. Binding to a free-floating extracellular ligand, such as a hormone D. Protease cleavage of the cytosolic domain of the protein E. Aggregation of the protein with other transmembrane proteinsarrow_forwardTopic: Benthic invertebrates as an indicator species for climate change, mapping changes in ecosystems (Historical Analysis & GIS) What objects or events has the team chosen to analyze? How does your team wish to delineate the domain or scale in which these objects or events operate? How does that limited domain facilitate a more feasible research project? What is your understanding of their relationships to other objects and events? Are you excluding other things from consideration which may influence the phenomena you seek to understand? Examples of such exclusions might include certain air-born pollutants; a general class of water bodies near Ottawa, or measurements recorded at other months of the year; interview participants from other organizations that are involved in the development of your central topic or issue. In what ways do your research questions follow as the most appropriate and/or most practical questions (given the circumstances) to pursue to better understand…arrow_forward
- The Esp gene encodes a protein that alters the structure of the insulin receptor on osteoblasts and interferes with the binding of insulin to the receptor. A researcher created a group of osteoblasts with an Esp mutation that prevented the production of a functional Esp product (mutant). The researcher then exposed the mutant strain and a normal strain that expresses Esp to glucose and compared the levels of insulin in the blood near the osteoblasts (Figure 2). Which of the following claims is most consistent with the data shown in Figure 2 ? A Esp expression is necessary to prevent the overproduction of insulin. B Esp protein does not regulate blood-sarrow_forwardPredict the per capita rate of change (r) for a population of ruil trees in the presence of the novel symbiont when the soil moisture is 29%. The formula I am given is y= -0.00012x^2 + 0.0088x -0.1372. Do I use this formula and plug in 29 for each x variable?arrow_forwardPlease answer the following chart so I can understand how to do it.arrow_forward
- Digoxin: Intravenous Bolus - Two Compartment Model Drug Digoxin Route: IV Bolus Dose: 0.750 mg Plasma Concentration Time Profile Beta Alpha Time (hrs) Conc (ng/ml) LN (ng/ml) LN (ng/ml) LN 0.00 #NUM! #NUM! #NUM! 0.10 12.290 2.509 #NUM! #NUMI 0.60 6.975 1.942 #NUM! #NUMI 1.00 4.649 1.537 #NUM! #NUMI 2.00 2.201 0.789 #NUM! #NUM! 3.00 1.536 0.429 #NUM! #NUM! 4.00 1.342 0.294 #NUM! #NUM! 5.00 1.273 0.241 #NUM! #NUMI 6.00 1.238 0.213 #NUM! #NUM! 7.00 1.212 0.192 #NUM! #NUM! 8.00 1.188 0.172 #NUMI #NUM! 9.00 1.165 0.153 #NUM! #NUMI 10.00 1.143 0.134 #NUMI #NUM! 11.00 1.122 0.115 #NUM! 12.00 1.101 0.096 #NUMI 13.00 1.080 0.077 #NUMI 16.00 1.020 0.020 #NUMI 24.00 0.876 -0.132 #NUMI Pharmacokinetic Parameters Parameter Value Alpha B Beta Units ng/ml hr-1 ng/ml hr-1 CO ng/ml H.C AUC ng x hr/ml Vc Vbeta Vss C L/hr TK (alpha) hr TX (beta) days 5+ F3 F4 F5 0+ F6 F7 % 6 95 14 #3 29 & t F8 F9 FW EWarrow_forwardLinuron, a derivative of urea, is used as an herbicide. Linuron serum levels were measured in 4Kg rabbits following a bolus IV injection of 10mg/kg. Time (minutes) Serum Linuron Levels (ug/ml) following IV dose 10 15.48 20 8.60 30 5.90 45 3.78 60 2.42 90 1.49 120 0.93 180 0.60 240 0.41 300 0.29 360 0.22 Analyze this data and perform the necessary calculations to determine the following pharmacokinetic parameters from the IV data: (5 points per parameter, 24 parameters/variables ■ 120 points possible). You do NOT need to submit graphs or data tables. Give the terminal regression line equation and R or R² value: Give the x axis (name and units, if any) of the terminal line: Give the y axis (name and units, if any) of the terminal line: Give the residual regression line equation and R or R² value: Give the x axis (name and units, if any) of the residual line: Give the y axis (name and units, if any) of the residual line:arrow_forward3. In the tomato, red fruit (O+) is dominant over orange fruit (0), and yellow flowers (W+) are dominant over white flowers (w). A cross was made between true-breeding plants with red fruit and yellow flowers, and plants with orange fruit and white flowers. The F₁ plants were then crossed to plants with orange fruit and white flowers, which produced the following results: a. b. 333 red fruit, yellow flowers 64 red fruit, white flowers 58 orange fruit, yellow flowers 350 orange fruit, white flowers Conduct a chi-square analysis to demonstrate that these two genes DO NOT assort independently. Make sure to interpret the P value obtained from your chi-square test. Calculate and provide the map distance (in map units) between the two genes.arrow_forward
 Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning





