
(a)
Interpretation: The catalyst in the below mentioned scheme of the carbon-nitrogen cycle that occurs in the sun, needs to be determined.
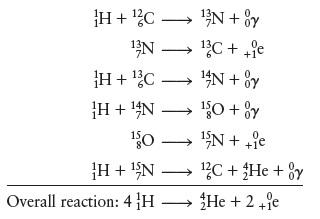
Concept Introduction: The carbon-nitrogen cycle which occurs in the sun is a fusion reaction, wherein Hydrogen gets converted into Helium.
(a)
Answer to Problem 70AE
The catalyst in the mentioned scheme of carbon-nitrogen cycle is
Explanation of Solution
Following is the carbon-nitrogen cycle that occurs in the sun:-
The overall reaction is
A catalyst is a substance that influences the speed of a
(b)
Interpretation: The nucleons that are intermediates in the below mentioned scheme of the carbon-nitrogen cycle that occurs in the sun needs to be determined.
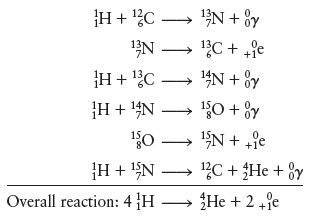
Concept Introduction: The carbon-nitrogen cycle which occurs in the sun is a fusion reaction, wherein Hydrogen gets converted into Helium.
(b)
Answer to Problem 70AE
The nucleons that are intermediates in the mentioned scheme are
Explanation of Solution
Following is the carbon-nitrogen cycle that occurs in the sun:-
The overall reaction is
The molecular entity which is evolved from the reactants and will further react in order to give the products, in a chemical reaction, are called as intermediates. In this case, the nucleon intermediates formed are
(c)
Interpretation: The energy that is released per mole of Hydrogen nuclei in the below mentioned scheme of the carbon-nitrogen cycle that occurs in the sun needs to be determined.
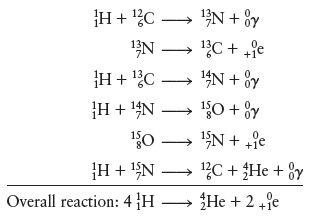
Concept Introduction: The carbon-nitrogen cycle which occurs in the sun is a fusion reaction, wherein Hydrogen gets converted into Helium.
(c)
Answer to Problem 70AE
Explanation of Solution
In order to start with, the mass defect
In the Helium atom
The number of neutrons =
The number of electrons = atomic number = 2
The overall reaction is as shown below:-
The above derived is the difference in the mass per nucleus.
Further the energy change
Wherein
Speed of light
Substituting these values in the energy change equation:-
Hence
Further the energy released per mole of
Therefore the energy released per mole of Hydrogen nuclei is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
Chemical Principles
- Can I please get help with this.arrow_forwardDetermine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. N₂H₅ClO₄arrow_forwardPlease help me with identifying these.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co





