
Concept explainers
a.
To compute: The rate of
Introduction:
Rate of return: When the annual income earned through an investment is expressed as a proportion in the form of percentage of the original investment, it is called as rate of return.
a.
Answer to Problem 6PS
The table comparing the
| Particulars | Amount (in $) when stock price is $80 | Amount (in $ ) when stock price is $100 | Amount (in $) when stock price is $110 | Amount (in $) when stock price is $120 |
| Rate of return in percentages | -20% | 0 | 10% | 20% |
Explanation of Solution
Stock price S0=$100
Call option with exercise price X=$100
Call option’s selling price C=$10
Call option’s expiration=1 year
Available amount for investment=$10000
Let us follow the following steps to calculation the rate of return.
Step 1: Calculation of investment amount:
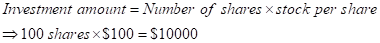
So, therefore in each case of price variation at an expiry period of 1 year i.e., at, $80, $100, $110, $120 the investment amount will $10000.
Step 2: Calculation of
| Particulars | Amount (in $) when stock price is $80 | Amount (in $ ) when stock price is $100 | Amount (in $) when stock price is $110 | Amount (in $) when stock price is $120 |
| Profit/ Loss per share when the current price is $100. (Stock price after 1 year − Current price) | 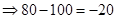 | 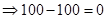 | 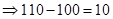 | 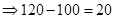 |
| Profit/Loss per total shares | 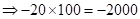 | 0 | 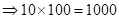 | 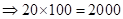 |
Step 3: Calculation of rate of return in different prices at maturity
Calculation of rate of return:
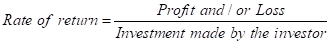
The same formula is used in calculations shown in the table.
| Particulars | Amount (in $) when stock price is $80 | Amount (in $ ) when stock price is $100 | Amount (in $) when stock price is $110 | Amount (in $) when stock price is $120 |
| Rate of return | 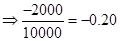 | 0 | 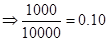 | 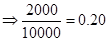 |
| Rate of return in percentages (Rate of return *100) | 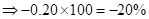 | 0 | 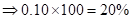 | 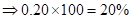 |
The maximum profit earned is 20 % and maximum loss to be borne is -20% when all of the investment amount is invested in stocks by the investor.
b.
To compute: The rate of return when the investment amount is invested in the stock options.
Introduction:
Rate of return: When the annual income earned through an investment is expressed as a proportion in the form of percentage of the original investment, it is called as rate of return.
b.
Answer to Problem 6PS
The table comparing the rate of return in percentages at different stock prices at maturity is as follows:
| Particulars | Amount (in $) when stock price is $80 | Amount (in $ ) when stock price is $100 | Amount (in $) when stock price is $110 | Amount (in $) when stock price is $120 |
| Rate of return in percentages | -300% | -100% | 0 | 100% |
Explanation of Solution
Stock price S0=$100
Call option with exercise price X=$100
Call option’s selling price C=$10
Call option’s expiration=1 year
Available amount for investment=$10000\
Let us follow the following steps to calculate the rate of return in this alternative.
Step 1: Calculation of investment amount:
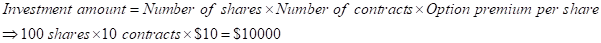 So, therefore in each case of price variation at an expiry period of 1 year i.e., at, $80, $100, $110, $120 the investment amount will $10000.
So, therefore in each case of price variation at an expiry period of 1 year i.e., at, $80, $100, $110, $120 the investment amount will $10000.
Step 2: Calculation of profit/loss in different maturity prices
Note1: Calculation of profit/loss for long call= Stock price at maturity − Strike Price- Option premium paid by the investor
| Particulars | Amount (in $) when stock price is $80 | Amount (in $ ) when stock price is $100 | Amount (in $) when stock price is $110 | Amount (in $) when stock price is $120 |
| Payoff per share when the strike price is $100. (Payoff=Stock price after 1 year − Strike price) | 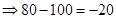 | 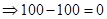 | 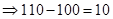 | 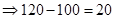 |
| Option premium per share paid by the investor | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Profit/Loss per share (Note 1) |  | 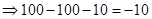 | 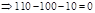 | 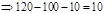 |
| Profit/Loss for 10 contracts | 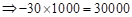 | 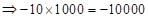 | 0 | 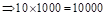 |
Calculation of value of total contracts:
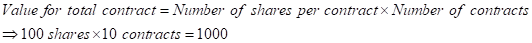
The same is used in all price variation cases in the above table.
Step 3: Calculation of rate of return:
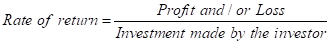
The same formula is used in calculations shown in the table.
| Particulars | Amount (in $) when stock price is $80 | Amount (in $ ) when stock price is $100 | Amount (in $) when stock price is $110 | Amount (in $) when stock price is $120 |
| Rate of return | 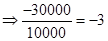 | 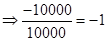 | 0 | 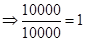 |
| Rate of return in percentages (Rate of return *100) | 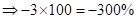 | 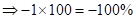 | 0 | 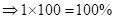 |
In this alternative, a maximum return of 100% and maximum loss to be borne is 300%. The reason is simple. It is a type of insurance contract where investor pays a premium and exercise the option only when required.
c.
To compute: The rate of return when $1000 is invested in options and $9000 is invested in
Introduction:
Money market fund: There are many types of securities in which the investment can be made. When the investor has the intention of investing in short term debt securities he/she can always opt for the money market fund. The money market fund is supposed to be an open-minded type of mutual fund. These are managed to maintain the net asset value’s stability at the highest point and at the same time pay the sufficient dividend to the investors in the form of dividends.
c.
Answer to Problem 6PS
The combined weighted average rate of return at different stock prices at maturity is as follows:
| Particulars | Amount (in $) when stock price is $80 | Amount (in $ ) when stock price is $100 | Amount (in $) when stock price is $110 | Amount (in $) when stock price is $120 |
| Weighted average rate of return from options contract | -30 | -10 | 0 | 10 |
| Weighted average rate of return from money market fund | 3.60 | 3.6 | 3.6 | 3.6 |
| Total | -26.40 | -6.40 | 3.60 | 13.60 |
Explanation of Solution
Stock price S0=$100
Call option with exercise price X=$100
Call option’s selling price C=$10
Call option’s expiration=1 year
Available amount for investment=$10000
Let us follow the following steps to calculate the rate of return in this alternative
Step 1: Calculation of investment amount when $1000 is invested in options contract
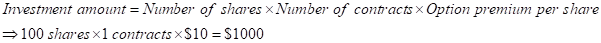 The same amount is applicable in all prices at maturity.
The same amount is applicable in all prices at maturity.
Step2: Calculation of Profit/Loss at different prices at maturity:
| Particulars | Amount (in $) when stock price is $80 | Amount (in $ ) when stock price is $100 | Amount (in $) when stock price is $110 | Amount (in $) when stock price is $120 |
| Payoff per share when the strike price is $100. (Payoff=Stock price after 1 year − Strike price) | 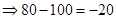 | 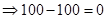 | 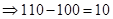 | 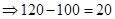 |
| Option premium per share paid by the investor | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Profit/Loss per share (Note 1) |  | 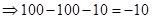 | 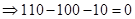 | 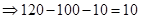 |
| Profit/Loss for 1 contracts | 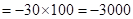 | 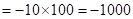 | 0 | 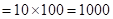 |
Calculation of value of total contracts:
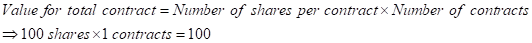
The same is used in all price variation cases in the above table.
Step 3: Calculation of rate of return:
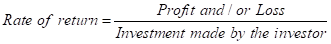
The same formula is used in calculations shown in the table.
| Particulars | Amount (in $) when stock price is $80 | Amount (in $ ) when stock price is $100 | Amount (in $) when stock price is $110 | Amount (in $) when stock price is $120 |
| Rate of return | 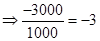 | 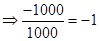 | 0 | 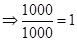 |
| Rate of return (profit/loss amount) in percentages (Rate of return *100) | 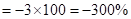 | 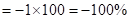 | 0 | 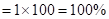 |
Step 4: Calculation of Weighted average rate of return- Note 2
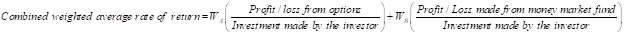
Calculation of weighted average rate of return for option contract:
| Particulars | Amount (in $) when stock price is $80 | Amount (in $ ) when stock price is $100 | Amount (in $) when stock price is $110 | Amount (in $) when stock price is $120 |
Weight of option contract investment 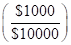 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 |
Weighted average rate of return 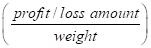 | 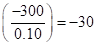 | 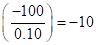 | 0 | 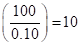 |
Calculation of Profit/Loss of investment in money market fund at different price at maturity:
| Particulars | Amount (in $) when stock price is $80 | Amount (in $ ) when stock price is $100 | Amount (in $) when stock price is $110 | Amount (in $) when stock price is $120 |
Return from money market fund 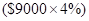 | 360 | 360 | 360 | 360 |
Rate of return 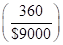 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 |
| Rate of return in percentages (Rate of return *100) | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
Weight of option contract investment 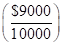 | 0.90 | 0.90 | 0.90 | 0.90 |
Weighted average rate of return 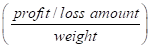 | 3.60 | 3.6 | 3.6 | 3.6 |
Step5: Calculation of combined weighted average rate of return:
| Particulars | Amount (in $) when stock price is $80 | Amount (in $ ) when stock price is $100 | Amount (in $) when stock price is $110 | Amount (in $) when stock price is $120 |
| Weighted average rate of return from options contract | -30 | -10 | 0 | 10 |
| Weighted average rate of return from money market fund | 3.60 | 3.6 | 3.6 | 3.6 |
| Total | -26.40 | -6.40 | 3.60 | 13.60 |
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
EBK INVESTMENTS
- Meticulous Drill & Reamer (MD&R) specializes in drilling and boring precise holes in hard metals (e.g., steel alloys, tungsten carbide, and titanium). The company recently contracted to drill holes with 3-centimeter diameters in large carbon-steel alloy disks, and it will have to purchase a special drill to complete this job. MD&R has eliminated all but two of the drills it has been considering: Davis Drills' T2005 and Worth Industrial Tools' AZ100. These producers have each agreed to allow MD&R to use a T2005 and an AZ100 for one week to determine which drill it will purchase. During the one-week trial, MD&R uses each of these drills to drill 31 holes with a target diameter of 3 centimeters in one large carbon-steel alloy disk, then measures the diameter of each hole and records the results. MD&R's results are provided in the table that follows and are available in the DATAfile named MeticulousDrills, Hole Diameter T2005 AZ100 3.06 2.91 3.04 3.31 3.13 2.82 3.01 3.01 2.95 2.94 3.02…arrow_forwardI mistakenly submitted blurr image please comment i will write values. please dont Solve with incorrect values otherwise unhelpful.arrow_forwardhello tutor:If submitted image is blurr then please comment i will write values. i will give unhelpful please.arrow_forward
- Lara Fredericks is interested in two mutually exclusive investments. Both investments cover the same time horizon of 5 years. The cost of the first investment is $9900, and Lara expects equal and consecutive year-end payments of $3400. The second investment promises equal and consecutive payments of $4100 with an initial outlay of $12500 required. The current required return on the first investment is 8.4 %, and the second carries a required return of 10.4 %.a. What is the net present value of the first investment?b. What is the net present value of the second investment?c. Being mutually exclusive, which investment should Lara choose? d. Which investment is relatively more risky? Explain.arrow_forwardWhat are some of the characteristics of a firm with a long operating cycle?arrow_forwardAbout this Assignment For this Corporate Finance 301 assignment, you will submit a research paper that analyzes the types of organizational business structures. You will apply knowledge of business structure concepts as acquired in the course. The research paper should follow APA formatting style. Project Prompts The written research paper should be at least 1,000 to 1,200 words in length and should include four sections based on the business structures studied throughout the course. Define each business structure, compare the corporate finance strategies of the four business structures, discuss the advantages and disadvantages of each business structure, and how each varies in taxation. Research Paper Sections ⚫ Sole Proprietorship ⚫ Partnership • Corporation ⚫ Limited Liability Company (LLC)arrow_forward
- PLEASE ANSWER THE COLUMN FULLY AND CORRECTLY PLEASE DO THE RIGHT CALCULATION DOUBLE CHECK AS WELL TO GIVE ME THE RIGHT ANSWER REQUIRED: Given the following information, what are the NZD/SGD currency against currency bid-ask quotations? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to 4 decimal places. Bank Quotations American Terms European Terms Bid Ask Bid Ask New Zealand dollar 0.733 0.7340 1.3870 1.3884 Singapore dollar 0.6186 0.6191 1.6423 1.6436 answer Bid Ask New Zealand dollar ? ? Singapore dollar ? ?arrow_forwardAbout this Assignment For the Corporate Finance 301 assignment, you will submit a research paper that analyzes and discusses organizational financial risks. You will apply knowledge acquired in the course and use the concepts of multiple financial risks as the basis of research and analysis. The research paper should follow APA formatting style. Audience: upper-level business students. Project Prompt Write a 1,000-1,200-word analysis discussing financial risk concepts and assess the impact of the different financial risks on an organization. For this assignment, you will structure your assignment using four research paper sections associated with corporate risk management, as studied in the course. Base your research paper on the financial statements analyzed in Corporate Finance 301 assignment 2 and apply the knowledge acquired in the analysis. Define each financial risk, discuss the risk associated components, and evaluate the financial risks and how they affect the corporation's…arrow_forwardBobby Nelson, made deposits of $880 at the end of each year for 6 years. Interest is 6% compounded annually. What is the value of Bobby’s annuity at the end of 6 years?arrow_forward
- 1. Find the future value if $1,250 is invested in Simple interest account paying 6.5%: a. for 5 years b. for 20 years 2. Find the future amount $ 35,000 is invested for 30 years at 4.25% compounded: a. annually b. Quarterly c. monthly d. weekly 3. How much should be put into an account today that pays 7.75% compounded monthly if you need $10,000 in 5 years. 4. Find the effective rate for: a. 5.75% compounded quarterly b. 6.25% compounded daily. 5. $50 is invested at the end of each month into an account paying 7.5% compounded monthly. How much will be in the account after 5 years?…arrow_forwardSolve step by step no aiarrow_forwardDont use ai solve itarrow_forward
 Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

 Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson,
Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson, Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





