
Concept explainers
(a)
(a)
Answer to Problem 63A
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Mass of the suspended ball is
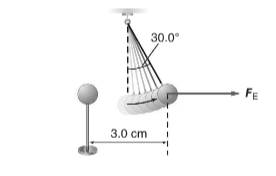
Figure 1
Formula used:
Where,
Calculation:
Substituting the numerical values in equation
Conclusion:
(b)
(b)
Answer to Problem 63A
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Mass of the suspended ball is
The suspended ball is hanging, with thread forming an angle
Formula used:
Calculation:
Rearrange the equation.
Where,
Substituting the numerical values in equation
Conclusion:
(c)
The charge on the balls.
(c)
Answer to Problem 63A
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Distance between the two balls
Both the balls have same charge.
Formula used:
Coulomb’s law: If
Where
Calculation:
From part (b),
Let
Substituting for
Substituting the numerical values in equation
Conclusion:
The charge on the balls is
Chapter 20 Solutions
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student Edition
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (4th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
- Determine the shear and moment diagram for the beam shown in Fig.1. A 2 N/m 10 N 8 N 6 m B 4m Fig.1 40 Nm Steps: 1) Determine the reactions at the fixed support (RA and MA) (illustrated in Fig 1.1) 2) Draw the free body diagram on the first imaginary cut (fig. 1.2), and determine V and M. 3) Draw the free body diagram on the second imaginary cut (fig. 1.3), and determine V and M. 4) Draw the shear and moment diagramarrow_forwardConsidering the cross-sectional area shown in Fig.2: 1. Determine the coordinate y of the centroid G (0, ỹ). 2. Determine the moment of inertia (I). 3. Determine the moment of inertia (Ir) (with r passing through G and r//x (// parallel). 4 cm 28 cm G3+ G 4 cm y 12 cm 4 cm 24 cm xarrow_forwardI need help understanding 7.arrow_forward
- The stress-strain diagram for a steel alloy is given in fig. 3. Determine the modulus of elasticity (E). σ (ksi) 40 30 20 10 0 0 0.0005 0.001 0.0015 0.002 0.0025 0.0030.0035 Earrow_forwardA Van de Graff generator, if the metal sphere on the Van de Graff has a charge of 0.14 Coulombs and the person has a mass of 62 kg, how much excess charge would the person need in order to levitate at a distance 25 cm from the center of the charged metal sphere? Assume you can treat both the person and the metal sphere as point charges a distance 25 cm from each other using Coulomb's Law to calculate the electrical force. Give your answer as the number of Coulombsarrow_forwardPlease help me answer the following question. I am having trouble understanding the directions of the things the question is asking for. Please include a detailed explanation and possibly drawings of the directions of Bsource, Binduced, and Iinduced.arrow_forward
- 43. A mass må undergoes circular motion of radius R on a hori- zontal frictionless table, con- nected by a massless string through a hole in the table to a second mass m² (Fig. 5.33). If m₂ is stationary, find expres- sions for (a) the string tension and (b) the period of the circu- lar motion. m2 R m₁ FIGURE 5.33 Problem 43arrow_forwardCH 70. A block is projected up an incline at angle 0. It returns to its initial position with half its initial speed. Show that the coefficient of ki- netic friction is μk = tano.arrow_forwardPassage Problems A spiral is an ice-skating position in which the skater glides on one foot with the other foot held above hip level. It's a required element in women's singles figure-skating competition and is related to the arabesque performed in ballet. Figure 5.40 shows Canadian skater Kaetlyn Osmond executing a spiral during her medal-winning perfor- mance at the 2018 Winter Olympics in Gangneung, South Korea. 77. From the photo, you can conclude that the skater is a. executing a turn to her left. b. executing a turn to her right. c. moving in a straight line out of the page. 78. The net force on the skater a. points to her left. b. points to her right. c. is zero. 79. If the skater were to execute the same maneuver but at higher speed, the tilt evident in the photo would be a. less. b. greater. c. unchanged. FIGURE 5.40 Passage Problems 77-80 80. The tilt angle 0 that the skater's body makes with the vertical is given ap- proximately by 0 = tan¯¹(0.5). From this you can conclude…arrow_forward
- Frictionless surfarrow_forward71. A 2.1-kg mass is connected to a spring with spring constant 72 k = 150 N/m and unstretched length 18 cm. The two are mounted on a frictionless air table, with the free end of the spring attached to a frictionless pivot. The mass is set into circular mo- tion at 1.4 m/s. Find the radius of its path. cor moving at 77 km/h negotiat CH —what's the minimum icient of frictioarrow_forward12. Two forces act on a 3.1-kg mass that undergoes acceleration = 0.91 0.27 m/s². If one force is -1.2î – 2.5ĵ N, what's the other?arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





