(a)
Interpretation:
6-phosphoglucono-⏹-lactone should be identified.
Concept introduction:
6-phosphoglucono-⏹-lactone is formed during the pentose phosphate pathway. In the first step of pentose phosphate pathway, dehydrogenation of glucose-6-phosphate at C-1 takes produce 6-phosphoglucono-⏹-lactone.
Answer to Problem 21P
The compound C in the reaction is 6-phosphoglucono-⏹-lactone.
Explanation of Solution
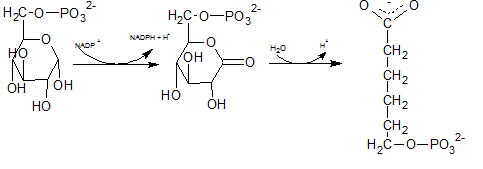
6-phosphoglucono-⏹-lactone is an intramolecular ester formed by the reaction of C-1 carboxyl group and C-5 hydroxyl group. It is formed by dehydrogenation of C-1 carbon of Glucose-6-phosphate. Hydroxyl group at C-1 of glucose-6-phosphate is converted to carbonyl group. Therefore, the structure of 6-phosphoglucono-⏹-lactone is (C).
(b)
Interpretation:
The reactions producing NADPH should be determined.
Concept introduction:
Two molecules of NADPH are produced duringthe oxidative phase of pentose phosphate pathway.
Answer to Problem 21P
The reactions B and F produce NADPH.
Explanation of Solution
First NADPH is produced when the C-1 in glucose-6-phosphate is dehydrogenated into 6-phosphoglucono-⏹-lactone by glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. This 6-phosphoglucono-⏹-lactone is hydrolyzed by a lactonase resulting 6-phosphogluconate. This 6C sugar acid is then decarboxylated by 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase into ribulose-5-phosphate. In this step also NADP+ acts as the electron acceptor and produce NADPH.
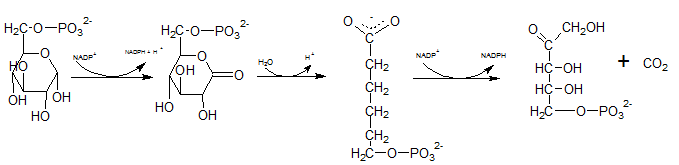
Therefore,reactions B and F produces NADPH.
(c)
Interpretation:
Ribulose-5-phosphate should be identified.
Concept introduction:
Ribulose-5-phosphate is the productof pentose phosphate pathway.
Answer to Problem 21P
The compound G in the reaction is Ribulose-5-phosphate.
Explanation of Solution
As the first step of oxidative phase of pentose phosphate pathway, C-1 of glucose-6-phosphate is dehydrogenated into 6-phosphoglucono-⏹-lactone by glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Then this 6-phosphoglucono-⏹-lactone is hydrolyzed by a lactonase resulting 6-phosphogluconate. This 6 C sugar acid is then decarboxylated by 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase into ribulose-5-phosphate.
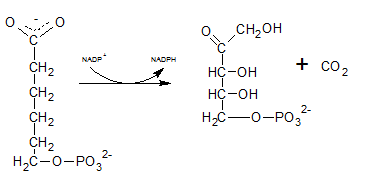
Therefore, Gis Ribulose-5-phosphate.
(d)
Interpretation:
The CO2generating reaction should be determined.
Concept introduction:
The decarboxylation reactions generate CO2 as a by-product.
Answer to Problem 21P
The reactions F produce CO2.
Explanation of Solution
The six C sugar acid, 6-phosphogluconate formed during pentose phosphate pathway is oxidatively decarboxylated by 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase into ribulose-5-phosphate. The final product is a five-carbon sugar, and release CO2.
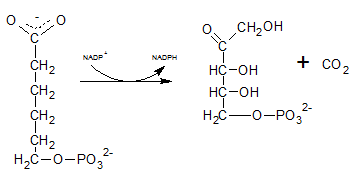
So. the reaction F produce CO2.
(e)
Interpretation:
6-phosphogluconate should be identified.
Concept introduction:
6-phosphogluconate is a 6C sugar acid which forms during pentose phosphate pathway.
Answer to Problem 21P
The compound E in the reaction is 6-phosphogluconate.
Explanation of Solution
In the first step of the oxidative phase of pentose phosphate pathway, C-1 of glucose-6-phosphate is dehydrogenated into 6-phosphoglucono-⏹-lactone by glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase which is hydrolyzed by a lactonase resulting 6-phosphogluconate.
The end product of above reaction is 6-phosphogluconate. Thus the compound E in the reaction is 6-phosphogluconate.
(f)
Interpretation:
The reaction that is catalyzed by phosphopentose isomerase should be determined.
Concept introduction:
Phosphopentose isomerase is an enzyme which involves in isomerization reaction.
Answer to Problem 21P
The reactions H uses Phosphopentose isomerase enzyme.
Explanation of Solution
Ribulose-5-phosphate is isomerized to ribose-5-phosphate by phosphopentose isomerase. The enzyme, phosphopentose isomerase catalyze the conversion of a ketose sugar (Ribulose-5-phosphate ) to an aldose sugar (ribose-5-phosphate).
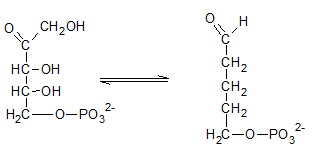
Therefore, the reaction H needs the enzyme phosphopentose isomerase.
(g)
Interpretation:
Ribose-5-phosphate should be identified.
Concept introduction:
Ribose-5-phosphate is the end product of the oxidative phase of pentose phosphate pathway.
Answer to Problem 21P
The compound I in the reaction is Ribose-5-phosphate.
Explanation of Solution
The ribulose-5-phosphate is obtained in pentose phosphate pathway when the ribose-5-phosphate is isomerized by phosphopentose isomerase.
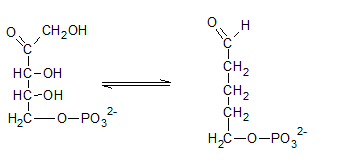
Therefore, the compound I in the reaction is Ribose-5-phosphate.
(h)
Interpretation:
Reaction catalyzed by lactonase should be determined.
Concept introduction:
Lactonases catalyzes the hydrolysis of ester bonds.
Answer to Problem 21P
The reactions D uses the enzymeLactonases.
Explanation of Solution
The degydrogenated product of glucose-6-phospahte is 6-phosphoglucono-⏹-lactone. This is a 6 membered ring structure and have an ester bond between C-1 carbonyl carbon and C-5 hydroxyl Oxygen. This bond is hydrolyzed by lactonase and to produce 6-phosphogluconate. The reaction is indicated by letter D.
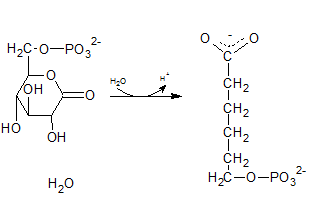
(i)
Interpretation:
Glucose-6-phosphate should be identified.
Concept introduction:
The pentose phosphate pathway is initiated by the oxidation of glucose-6-phosphate.
Answer to Problem 21P
The compound A in the reaction is glucose-6-phosphate.
Explanation of Solution
Glucose-6-phosphate is a 6-carbon sugar and have a ring structure where the hydroxyl group at C-6 is phosphorylated.
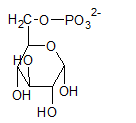
The compound A in the reaction is glucose-6-phosphate.
(j)
Interpretation:
The reaction catalyzed by 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase should be determined.
Concept introduction:
Dehydrogenases are the enzymes which catalyzes the removal of hydrogen molecules with the help of coenzymes NAD and FAD.
Answer to Problem 21P
The reactions F uses the enzymedehydrogenases.
Explanation of Solution
6-phosphogluconate is oxidatively decarboxylated by 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase into ribulose-5-phosphate which is indicated by reaction F.
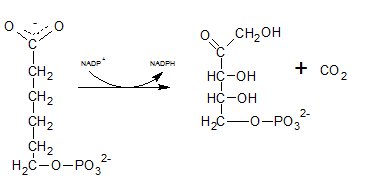
(k)
Interpretation:
Reaction that is catalyzed by glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase should be determined.
Concept introduction:
In the first reaction of pentose phosphate pathway glucose-6-phosphate is dehydrogenated to produce phosphoglucono-⏹-lactone.
Answer to Problem 21P
The reactions B uses the enzymeglucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenases.
Explanation of Solution
In the first step of pentose phosphate pathway, Glucose-6-phosphate is dehydrogenated at C-1 by glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase enzyme into 6-phosphoglucono-⏹-lactone.
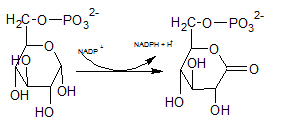
So, the reactions B uses the enzymeglucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenases.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
Biochemistry
- please answer all questions 1 identify the amino acids below by name and three letter abbrevarrow_forwardPyruvate is accepted into the TCA cycle by a “feeder” reaction using the pyruvatedehydrogenase complex, resulting in acetyl-CoA and CO2. Provide a full mechanismfor this reaction utilizing the TPP cofactor. Include the roles of all cofactors.arrow_forwardB- Vitamins are converted readily into important metabolic cofactors. Deficiency inany one of them has serious side effects. a. The disease beriberi results from a vitamin B 1 (Thiamine) deficiency and ischaracterized by cardiac and neurological symptoms. One key diagnostic forthis disease is an increased level of pyruvate and α-ketoglutarate in thebloodstream. How does this vitamin deficiency lead to increased serumlevels of these factors? b. What would you expect the effect on the TCA intermediates for a patientsuffering from vitamin B 5 deficiency? c. What would you expect the effect on the TCA intermediates for a patientsuffering from vitamin B 2 /B 3 deficiency?arrow_forward
- Draw the Krebs Cycle and show the entry points for the amino acids Alanine,Glutamic Acid, Asparagine, and Valine into the Krebs Cycle - (Draw the Mechanism). How many rounds of Krebs will be required to waste all Carbons of Glutamic Acidas CO2?arrow_forwardSodium fluoroacetate (FCH 2CO2Na) is a very toxic molecule that is used as rodentpoison. It is converted enzymatically to fluoroacetyl-CoA and is utilized by citratesynthase to generate (2R,3S)-fluorocitrate. The release of this product is a potentinhibitor of the next enzyme in the TCA cycle. Show the mechanism for theproduction of fluorocitrate and explain how this molecule acts as a competitiveinhibitor. Predict the effect on the concentrations of TCA intermediates.arrow_forwardIndicate for the reactions below which type of enzyme and cofactor(s) (if any) wouldbe required to catalyze each reaction shown. 1) Fru-6-P + Ery-4-P <--> GAP + Sed-7-P2) Fru-6-P + Pi <--> Fru-1,6-BP + H2O3) GTP + ADP <--> GDP + ATP4) Sed-7-P + GAP <--> Rib-5-P + Xyl-5-P5) Oxaloacetate + GTP ---> PEP + GDP + CO 26) DHAP + Ery-4-P <--> Sed-1,7-BP + H 2O7) Pyruvate + ATP + HCO3- ---> Oxaloacetate + ADP + Piarrow_forward
- TPP is also utilized in transketolase reactions in the PPP. Give a mechanism for theTPP-dependent reaction between Xylulose-5-phosphate and Ribose-5-Phosphate toyield Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate and Sedoheptulose-7-Phosphate.arrow_forwardWhat is the difference between a ‘synthetase’ and a ‘synthase’?arrow_forwardIn three separate experiments, pyruvate labeled with 13C at C-1, C-2, or C-3 is introduced to cells undergoing active metabolism. Trace the fate of each carbon through the TCA cycle and show when each of these carbons produces 13CO2.a. Glucose is similarly labeled at C-2 with 13C. During which reaction will this labeled carbon be released as 13CO2?arrow_forward
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning





