
(a)
Interpretation:
A synthesis of the given compound by using acetyl chloride is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Sodium benzoate is the salt of conjugate base or sodium salt of benzoic acid. When acyl halide reacts with sodium benzoate, it gives the ester. Sodium benzoate acts as the nucleophile. Nucleophile is the negatively charged ion attacks the carbonyl carbon and expels the good leaving group.
Answer to Problem 20.65P
The way of synthesis of the given compound by using acetyl chloride is as follows:
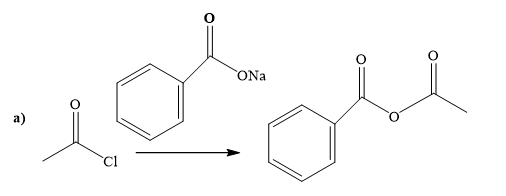
Explanation of Solution
The way of synthesis of the given compound by using acetyl chloride is as follows:

Sodium benzoate is a sodium salt of benzoic acid. When acyl halide reacts with sodium benzoate, it gives the ester. Sodium benzoate, as s nucleophile, is used to undergo nucleophilic addition- elimination reaction with acid chloride. Benzoate’s negatively charged ion attacks the carbonyl carbon of acetyl chloride and expels the good leaving group chlorine.
From the structure of the given reactant and product, structure of the reagent is determined.
(b)
Interpretation:
A synthesis of the given compound by using the acetyl chloride is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Sodium phenoxide is produced by sodium hydroxide and Phenol. Ester can be prepared by treating acetyl chloride with phenoxide. Sodium phenoxide is a moderately strong base.
Answer to Problem 20.65P
The way of synthesis of the given compound by using acetyl chloride is as follows:
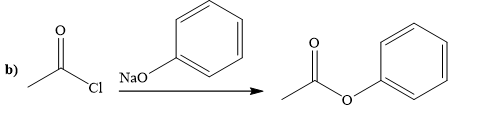
Explanation of Solution
The way of synthesis of the given compound by using acetyl chloride is as follows:

Ester can be prepared by treating acetyl chloride with sodium phenoxide. Sodium phenoxide, as a nucleophile, is used to undergo nucleophilic addition- elimination reaction with acid chloride. Phenoxide, the negatively charged ion attacks the carbonyl carbon of acetyl chloride and expels the good leaving group chlorine and forms ester.
From the structure of given reactant and product, structure of reagent is determined.
(c)
Interpretation:
A synthesis of the given compound by using acetyl chloride is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
It converts the acid chloride or anhydrides to primary alcohol. It’s also used for reduction of carbonyl compound to corresponding alcohol, and after removing the hydrogen from alcohol, it gives alkoxide. Alkoxide ion attacks the carbonyl carbon of the acid chloride and expels the good leaving group and forms the ester as product.
Answer to Problem 20.65P
The way of synthesis of the given compound by using acetyl chloride is as follows:
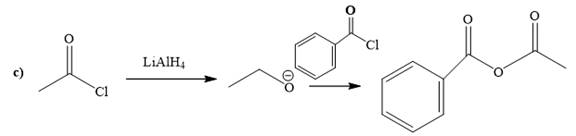
Explanation of Solution
The way of synthesis of the given compound by using acetyl chloride is as follows:

Acetyl halide is converted to alkoxide by treating it with
From the structure of the given reactant and product, structure of reagent is determined.
(d)
Interpretation:
A synthesis of the given compound by using acetyl chloride is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
It is also used for reduction of amides to corresponding
Answer to Problem 20.65P
The way of synthesis of given compound by using acetyl chloride is as follows:
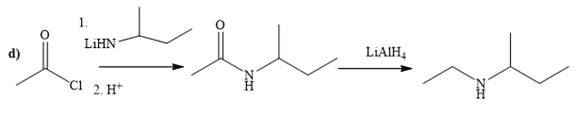
Explanation of Solution
The way of synthesis of given compound by using acetyl chloride is as follows:

In the first step, acid chloride converts to amide in the presence of organolithium amine reagent. Amide is reduced with
From the structure of given reactant and product, structure of reagent is determined.
(e)
Interpretation:
A synthesis of given compound by using the acetyl chloride is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
It converts the acid chloride or anhydrides to primary alcohol. It’s also used for reduction of carbonyl a compound to corresponding alcohol. And after remove the hydrogen from alcohol to get alkoxide. Alkoxide ion attacks the carbonyl carbon of the acid chloride and expels the good leaving group and form the ester as product. Alcohol is reacting with strong acid at required temperature to get the ester.
Answer to Problem 20.65P
The way of synthesis of given compound by using acetyl chloride is as follows:
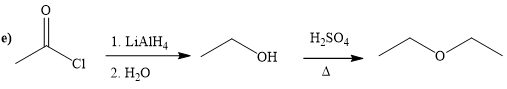
Explanation of Solution
The way of synthesis of given compound by using acetyl chloride is as follows:

In the first step, acetyl chloride is converted to
From the structure of given reactant and product, structure of reagent is determined.
(f)
Interpretation:
A synthesis of given compound by using acetyl chloride is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The reagent
Answer to Problem 20.65P
The way of synthesis of given compound by using acetyl chloride is as follows:
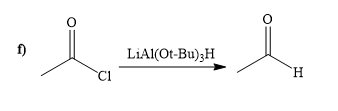
Explanation of Solution
The way of synthesis of given compound by using acetyl chloride is as follows:

When acyl chloride react with
From the structure of given reactant and product, structure of reagent is determined.
(g)
Interpretation:
A synthesis of given compound by using acetyl chloride is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Acid chloride reacts with Gilmann reagent to give the
Answer to Problem 20.65P
The way of synthesis of given compound by using acetyl chloride is as follows:
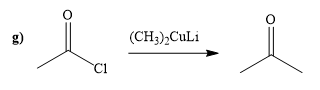
Explanation of Solution
The way of synthesis of given compound by using acetyl chloride is as follows:
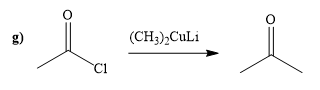
Acetyl chloride is converted to ketone in the presence lithium dimethylcuprate. Ketone does not undergo nucleophilic attack by Gilmann reagent as the reagent is a soft nucleophile.
From the structure of given reactant and product, structure of reagent is determined.
(h)
Interpretation:
A synthesis of given compound by using the acetyl chloride is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Acid chloride is converted to ester in presence of sodium alkoxide. Alkoxide ion attacks the carbonyl carbon of acid chloride and expels the good leaving group forming ester as the product.
Answer to Problem 20.65P
The way of synthesis of given compound by using acetyl chloride is as follows:
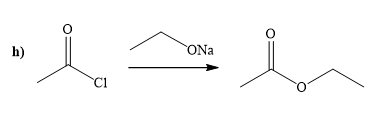
Explanation of Solution
The way of synthesis of given compound by using acetyl chloride is as follows:

Acetyl chloride is converted to ester in presence of sodium ethoxide. Ethoxide ion attacks the carbonyl carbon of acid chloride and expels the good leaving group, forming the ester as a product.
From the structure of given reactant and product, structure of reagent is determined.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles and Mechanisms (Second Edition)
- The emission data in cps displayed in Table 1 is reported to two decimal places by the chemist. However, the instrument output is shown in Table 2. Table 2. Iron emission from ICP-AES Sample Blank Standard Emission, cps 579.503252562 9308340.13122 Unknown Sample 343.232365741 Did the chemist make the correct choice in how they choose to display the data up in Table 1? Choose the best explanation from the choices below. No. Since the instrument calculates 12 digits for all values, they should all be kept and not truncated. Doing so would eliminate significant information. No. Since the instrument calculates 5 decimal places for the standard, all of the values should be limited to the same number. The other decimal places are not significant for the blank and unknown sample. Yes. The way Saman made the standards was limited by the 250-mL volumetric flask. This glassware can report values to 2 decimal places, and this establishes our number of significant figures. Yes. Instrumental data…arrow_forwardSteps and explanation pleasearrow_forwardSteps and explanation to undertand concepts.arrow_forward
- Nonearrow_forward7. Draw a curved arrow mechanism for the following reaction. HO cat. HCI OH in dioxane with 4A molecular sievesarrow_forwardTry: Convert the given 3D perspective structure to Newman projection about C2 - C3 bond (C2 carbon in the front). Also, show Newman projection of other possible staggered conformers and circle the most stable conformation. Use the template shown. F H3C Br Harrow_forward
- Nonearrow_forward16. Consider the probability distribution p(x) = ax", 0 ≤ x ≤ 1 for a positive integer n. A. Derive an expression for the constant a, to normalize p(x). B. Compute the average (x) as a function of n. C. Compute σ2 = (x²) - (x)², the variance of x, as a function of n.arrow_forward451. Use the diffusion model from lecture that showed the likelihood of mixing occurring in a lattice model with eight lattice sites: Case Left Right A B C Permeable Barrier → and show that with 2V lattice sites on each side of the permeable barrier and a total of 2V white particles and 2V black particles, that perfect de-mixing (all one color on each side of the barrier) becomes increasingly unlikely as V increases.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





