
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl benzoate and
Concept introduction:
An ester can be converted to a primary alcohol by reacting with
Answer to Problem 20.46P
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl benzoate and
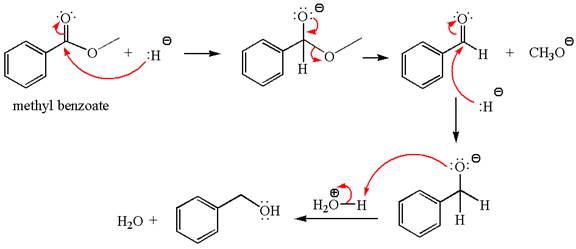
Explanation of Solution
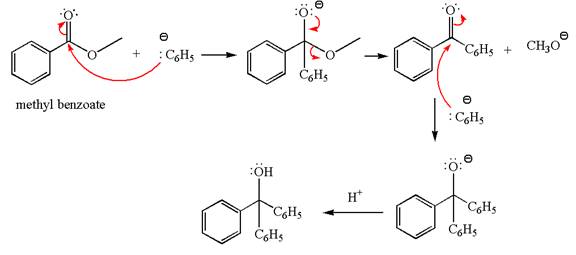
The equation for the reaction of methyl benzoate with
Methyl benzoate is an ester, which, on reaction with
The product with detailed mechanism for the given reaction is drawn based on the reactivity of
(b)
Interpretation:
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl benzoate and
Concept introduction:
An ester can be converted to a tertiary alcohol by reacting it with
Answer to Problem 20.46P
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl benzoate and
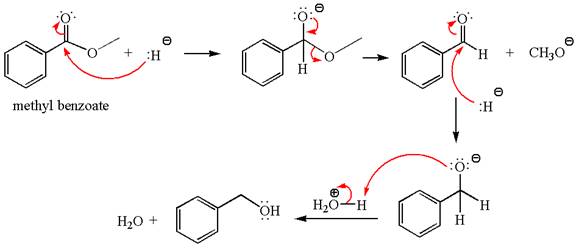
Explanation of Solution
The equation for the reaction of methyl benzoate with
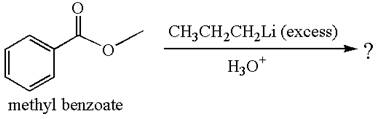
Methyl benzoate is an ester, which, on reaction with
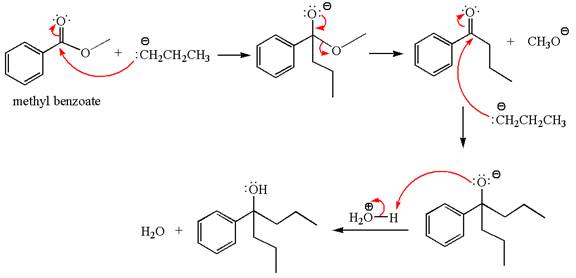
The product with detailed mechanism for the given reaction is drawn based on the reactivity of
(c)
Interpretation:
Whether methyl benzoate can react with
Concept introduction:
The reagent
Answer to Problem 20.46P
Mmethyl benzoate cannot react with
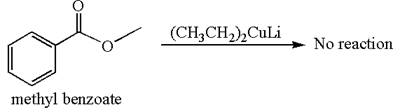
Explanation of Solution
The equation for the reaction of methyl benzoate with
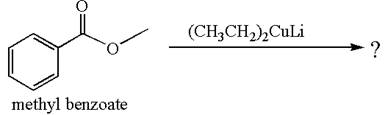
Methyl benzoate is an ester and
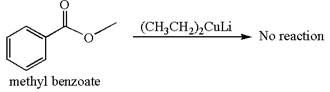
It is determined that no reaction occurs based on the reactivity of
(d)
Interpretation:
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl benzoate and
Concept introduction:
An ester can be converted to a tertiary alcohol by reacting it with
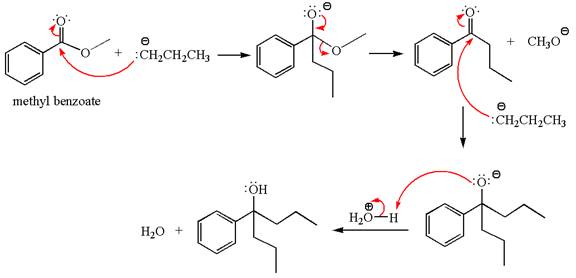
Answer to Problem 20.46P
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl benzoate and
Explanation of Solution
The equation for the reaction of methyl benzoate with
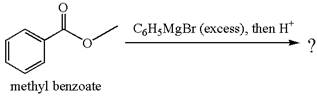
Methyl benzoate is an ester, which, on reaction with

The product with detailed mechanism for the given reaction is drawn based on the reactivity of
(e)
Interpretation:
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl benzoate and
Concept introduction:
An ester can be reduced to aldehyde without reducing it further to alcohol using a specific reagent such as
Answer to Problem 20.46P
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl benzoate and
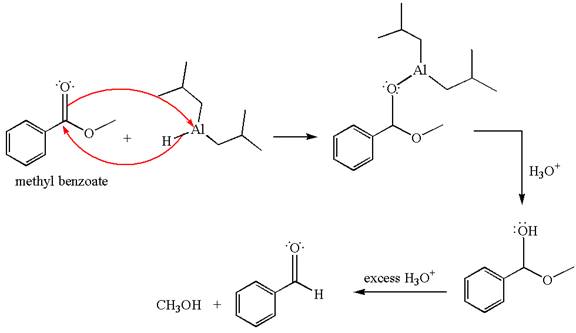
Explanation of Solution
The equation for the reaction of methyl benzoate with
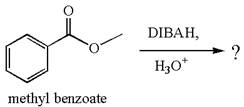
Methyl benzoate is an ester, which, on reaction with
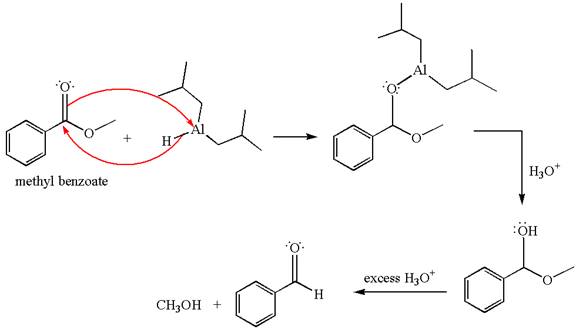
The product with detailed mechanism for the given reaction is drawn based on the reactivity of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles and Mechanisms (Second Edition)
- help 20arrow_forwardProvide the drawing of the unknown structure that corresponds with this data.arrow_forward20.44 The Diels-Alder reaction is not limited to making six-membered rings with only car- bon atoms. Predict the products of the following reactions that produce rings with atoms other than carbon in them. OCCH OCCH H (b) CH C(CH₂)s COOCH མ་ནས་བ (c) N=C H -0.X- (e) H C=N COOCHS + CH2=CHCH₂ →→arrow_forward
- 3) Draw a detailed mechanism and predict the product of the reaction shown? 1) EtMgBr 2) H3O+arrow_forwardHow to draw the mechanism for this reaction?arrow_forward> H₂C=C-CH2-CH3 B. H₂O Pt C. + H2 + H₂O H D. 16. Give the IUPAC name for each of the following: B. Cl Cl c. Cl Cl 17. Draw the line-angle formula for each of the following compounds: 1. phenol 2. 1,3-dichlorobenzene 3. 4-ethyltoluene < Previous Submit Assignment Next ▸arrow_forward
