
(a)
Interpretation:
The detailed mechanism and the major product of the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The carbonyl carbon atom in compounds such as
Answer to Problem 20.1P
The mechanism of the given reaction can be drawn as
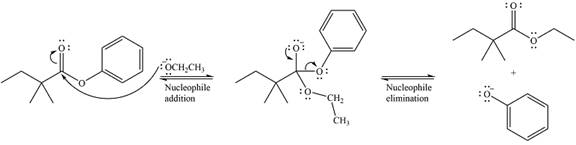
The major product of the reaction is
Explanation of Solution
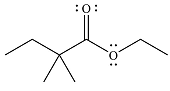
The given reaction is
The carbonyl carbon in the ester substrate is partially positively charged, i.e., electron-poor. The reagent
In the next step, the leaving group, the phenoxy ion, from the original ester is eliminated. This step forms the major product, another ester.
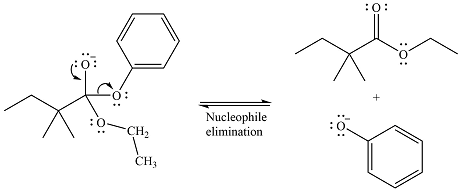
Since the substrate and the product are both esters, of comparable stability, the two steps are reversible.
Thus, the complete detailed mechanism for the reaction can be drawn as
And the major product of the reaction is

The mechanism of the reaction and the major product were drawn based on nucleophilic addition-elimination step.
(b)
Interpretation:
The detailed mechanism of the reaction and its major product are to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
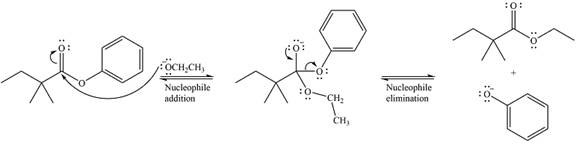
The carbonyl carbon atom in compounds such as aldehydes, ketones, and esters is relatively electron-poor. It can add a nucleophile, forming a tetrahedral transition state. This is followed by the elimination of the leaving group, itself a nucleophile, to form the product. When an ester is treated with an alkoxide, it replaces the original alkoxide group in from the ester substrate. Since the reaction results in formation of another ester, it is known as transesterification.
Answer to Problem 20.1P
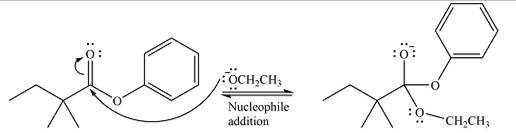
The complete mechanism for the reaction can be drawn as
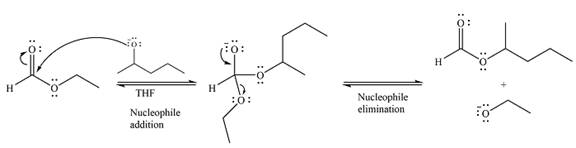
And the major product of the reaction as
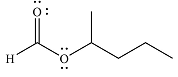
Explanation of Solution
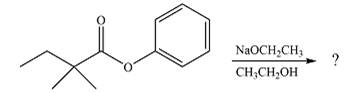
The given reaction is
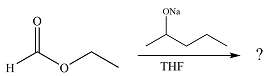
The substrate is an ester, with an electron-poor carbonyl carbon. The reagent is ionic and essentially acts as the negativey charged nucleophile
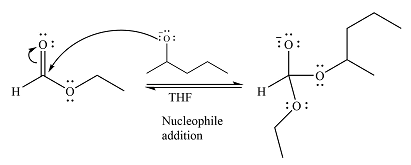
Next, the leaving group (ethoxide) from the original ester is eliminated to formt eh major product.
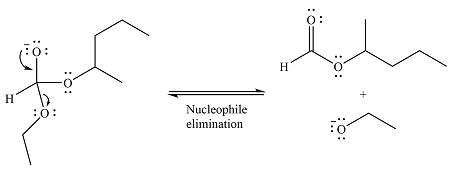
The major product is another ester, of comparable stability. Therefore, both steps will be reversible steps.
Thus, the complete mechanism for the reaction can be drawn as
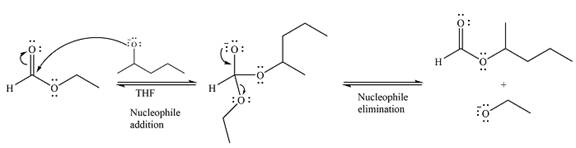
And the major product of the reaction as

The complete mechanism and the major product of the reaction were drawn based on nucleophilic addition-elimination steps.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles and Mechanisms (Second Edition)
- 19) Which metal is most commonly used in galvanization to protect steel structures from oxidation? Lead a. b. Tin C. Nickel d. Zinc 20) The following molecule is an example of a: R₁ R2- -N-R3 a. Secondary amine b. Secondary amide c. Tertiary amine d. Tertiary amidearrow_forwardpls helparrow_forwardIndicate the product of the reaction OH OH CH3-CC- Ph + H2SO4 a 20°C | CH3 Pharrow_forward
- 35) Complete the following equation by drawing the line the structure of the products that are formed. Please note that in some cases more than one product is possible. You must draw all possible products to recive full marks! a. ethanol + 2-propanol + H2SO4 → b. OH conc. H2SO4 CH2 H3C CH + K2Cr2O7 C. d. H3C A pressure CH3 + H2 CH Pt catalystarrow_forward21) The rate of reaction depends upon: a. the concentration and nature of reactants b. the temperature of the reaction C. whether or not a catalyst was used d. all of the above 22) A Maxwell-Boltzmann curve shows the distribution of molecular energies in a reaction system. When the temperature in this system is increased, the peak is a. higher and further to the right. b. higher and further to the left. c. lower and further to the right. d. lower and further to the left. 23) Which of the following correctly describes the reaction represented by the reaction below? CaCO3 (s) + energy → CaO (s) + CO2 (g) a. It is exothermic and the potential energy is greater in the reactants than the products. b. c. It is exothermic and the potential energy is greater in the products than the reactants. It is endothermic and the potential energy is greater in the products than the reactants. d. It is endothermic and the potential energy is equal for the products and reactants.arrow_forwardpls helparrow_forward
- 27) Draw the energy level diagram and write the full and shorthand electron configuration for a neutral sulfur atom.arrow_forwardIndicate whether these compounds are isomers, enantiomers, or tautomers. OCH OCH محمد ممدarrow_forward30) Substance A to E below are listed with several of their properties. The identities of the substances are identified in random order below: Iron, ethane, ethanol, sodium nitrate, graphite First classify each substance as either a polar covalent compound, non-polar covalent compound, ionic compound, metallic solid, or network solid. Write your predictions in the sixth coloumn of the chart, under "type of substance." Then, identify the identity of the substance in the last coloumn. Substance Melting Point Boiling Point Solubility in H₂O Electrical Conductivity Type of Substance Identity of Substance (°C) (°C) as: Solid, Liquids, Solution A -182 -88 Insoluble No/No/- B 1538 2862 Insoluble Yes/Yes/- C 308 380 Soluble Yes/Yes/Yes Ꭰ 3456 Insoluble No/-/- E -114 78 Soluble No/No/Noarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





