
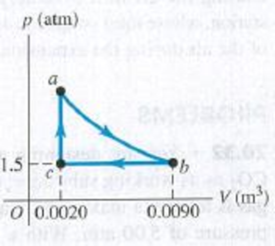
The pV-diagram in Fig. E20.5 shows a cycle of
Figure E20.5
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

Chapter 20 Solutions
University Physics with Modern Physics Plus Mastering Physics with eText -- Access Card Package (14th Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Microbiology: An Introduction
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardneed help part earrow_forwardCritical damping is the case where the mass never actually crosses over equilibrium position, but reaches equilibrium as fast as possible. Experiment with changing c to find the critical damping constant. Use the same initial conditions as in the last problem. Zoom in a bit to make sure you don't allow any oscillations to take place - even small ones.arrow_forward
- NASA's KC-135 Reduced Gravity Research aircraft, affectionately known as the "Vomit Comet," is used in training astronauts and testing equipment for microgravity environments. During a typical mission, the aircraft makes approximately 30 to 40 parabolic arcs. During each arc, the aircraft and objects inside it are in free-fall, and passengers float freely in apparent "weightlessness." The figure below shows the altitude of the aircraft during a typical mission. It climbs from 24,000 ft to 30,850 ft, where it begins a parabolic arc with a velocity of 155 m/s at 45.0° nose-high and exits with velocity 155 m/s at 45.0° nose-low. 31 000 45° nose high 45° nose low 24 000 Zero g 65 Maneuver time (s) (a) What is the aircraft's speed (in m/s) at the top of the parabolic arc? 110.0 m/s (b) What is the aircraft's altitude (in ft) at the top of the parabolic arc? 2.04e+04 What is the initial height at the start of the parabolic arc? What is the initial velocity at this point? What is the final…arrow_forward12. What could we conclude if a system has a phase trajectory that sweeps out larger and larger area as time goes by?arrow_forwardneed help part darrow_forward
- A cab driver heads south with a steady speed of v₁ = 20.0 m/s for t₁ = 3.00 min, then makes a right turn and travels at v₂ = 25.0 m/s for t₂ = 2.80 min, and then drives northwest at v3 = 30.0 m/s for t3 = 1.00 min. For this 6.80-min trip, calculate the following. Assume +x is in the eastward direction. (a) total vector displacement (Enter the magnitude in m and the direction in degrees south of west.) magnitude direction For each straight-line movement, model the car as a particle under constant velocity, and draw a diagram of the displacements, labeling the distances and angles. Let the starting point be the origin of your coordinate system. Use the relationship speed = distance/time to find the distances traveled during each segment. Write the displacement vector, and calculate its magnitude and direction. Don't forget to convert min to s! m Model the car as a particle under constant velocity, and draw a diagram of the displacements, labeling the distances and angles. Let the…arrow_forwardî A proton is projected in the positive x direction into a region of uniform electric field E = (-5.50 x 105) i N/C at t = 0. The proton travels 7.20 cm as it comes to rest. (a) Determine the acceleration of the proton. magnitude 5.27e13 direction -X m/s² (b) Determine the initial speed of the proton. 8.71e-6 magnitude The electric field is constant, so the force is constant, which means the acceleration will be constant. m/s direction +X (c) Determine the time interval over which the proton comes to rest. 1.65e-7 Review you equations for constant accelerated motion. sarrow_forwardThree charged particles are at the corners of an equilateral triangle as shown in the figure below. (Let q = 2.00 μC, and L = 0.750 m.) y 7.00 με 60.0° L 9 -4.00 μC x (a) Calculate the electric field at the position of charge q due to the 7.00-μC and -4.00-μC charges. 112 Once you calculate the magnitude of the field contribution from each charge you need to add these as vectors. KN/CI + 64 × Think carefully about the direction of the field due to the 7.00-μC charge. KN/Cĵ (b) Use your answer to part (a) to determine the force on charge q. 240.0 If you know the electric field at a particular point, how do you find the force that acts on a charge at that point? mN Î + 194.0 × If you know the electric field at a particular point, how do you find the force that acts on a charge at that point? mNarrow_forward
- In the Donkey Kong Country video games you often get around by shooting yourself out of barrel cannons. Donkey Kong wants to launch out of one barrel and land in a different one that is a distance in x of 9.28 m away. To do so he launches himself at a velocity of 22.6 m/s at an angle of 30.0°. At what height does the 2nd barrel need to be for Donkey Kong to land in it? (measure from the height of barrel 1, aka y0=0)arrow_forwardFor which value of θ is the range of a projectile fired from ground level a maximum? 90° above the horizontal 45° above the horizontal 55° above the horizontal 30° above the horizontal 60° above the horizontalarrow_forwardA map from The Legend of Zelda: The Breath of the Wild shows that Zora's Domain is 7.55 km in a direction 25.0° north of east from Gerudo Town. The same map shows that the Korok Forest is 3.13 km in a direction 55.0° west of north from Zora's Domain. The figure below shows the location of these three places. Modeling Hyrule as flat, use this information to find the displacement from Gerudo Town to Korok Forest. What is the magnitude of the displacement? Find the angle of the displacement. Measure the angle in degrees north of east of Gerudo Town.arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





