
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The mechanism for the formation of compound A has to be proposed.
Concept Introduction:
Diels-Alder reaction:
It is the reaction of conjugated dienes with double or triple bonded compounds which are known as “dienophiles”. The reaction is a
Example:
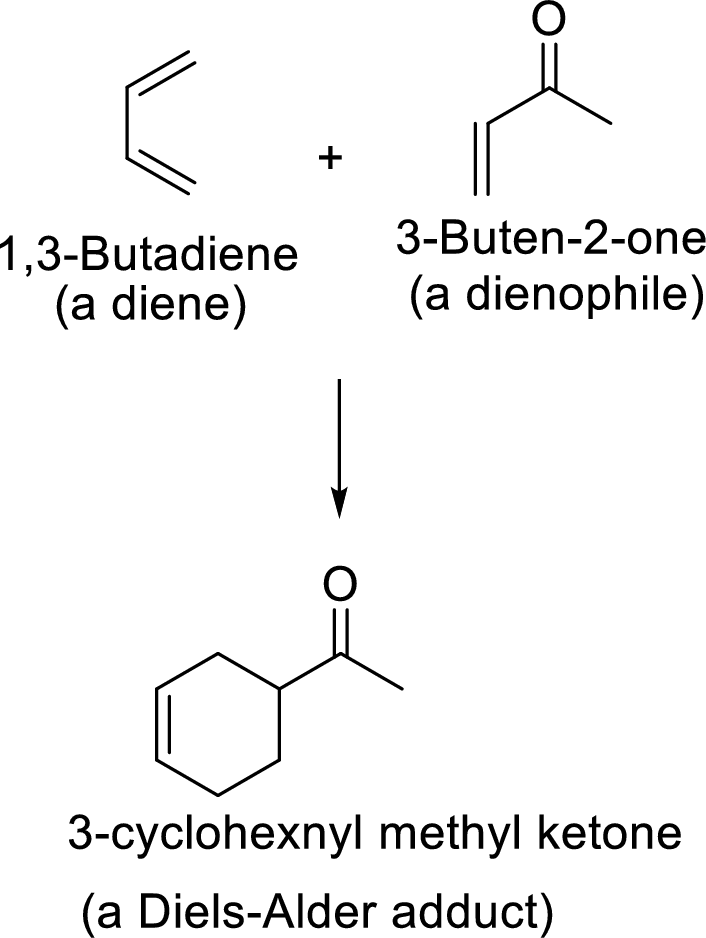
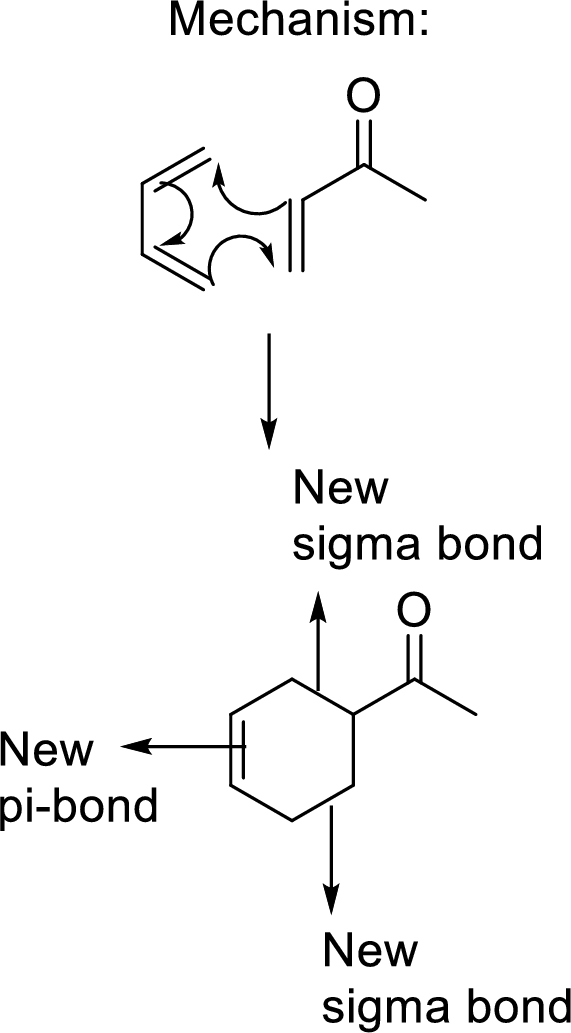
This mechanism shown that three
Formation of Benzyne:
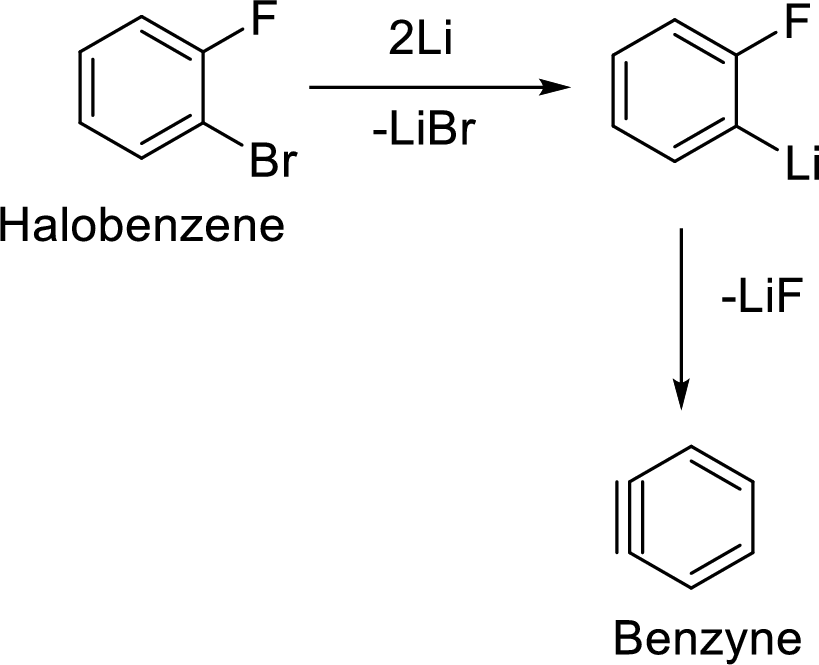
The elimination of two halogens from the halobenzene forms the most reactive neutral intermediate with triple bond which is known as Benzyne intermediate.
Diels-Alder reaction with Benzyne intermediate:
The reaction of Benzyne with furan serves as an example for this reaction:
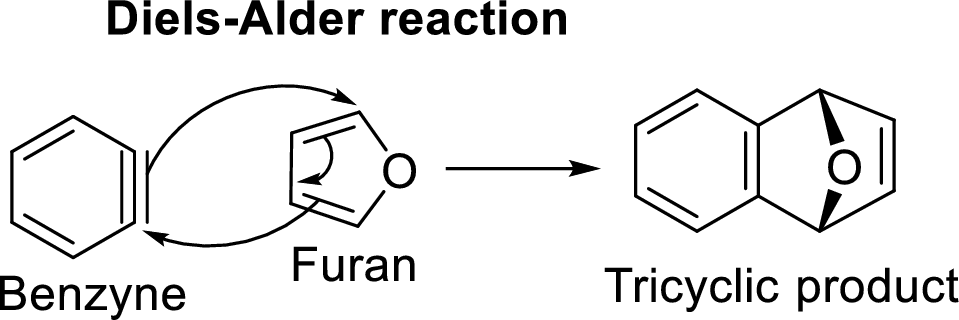
Benzyne is an extremely reactive species because of the presence of triple bond in it. It undergoes Diels-Alder reaction in which it acts as dienophile and reacts with furan which acts a diene. The resulted product will be a tricyclic product which is known as Diels-Alder adduct.
(b)
Interpretation: Using the given sources, the conversion of compound (A) into Tolciclate has to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Acidic hydrolysis of ether:
Ether on hydrolysis gets converted into two moles of alcohols of same type in the case of symmetrical ether and of different types in the case of unsymmetrical ether. .
General scheme for symmetrical ether:
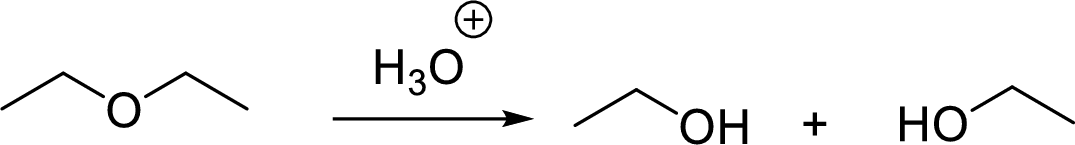
General scheme for unsymmetrical ether:
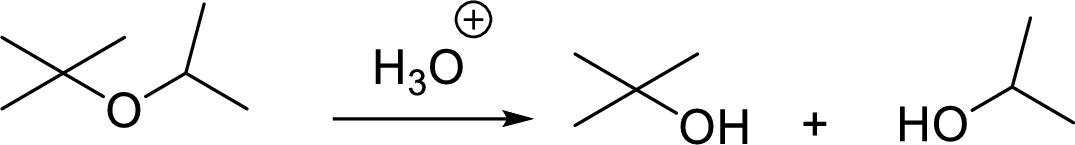
Tosylation reaction:
When an alcohol is treated with any tosyl chloride (methane sulfonyl chloride) it gets converted into tosylated product and this reaction is called as Tosylation reaction which is shown below:
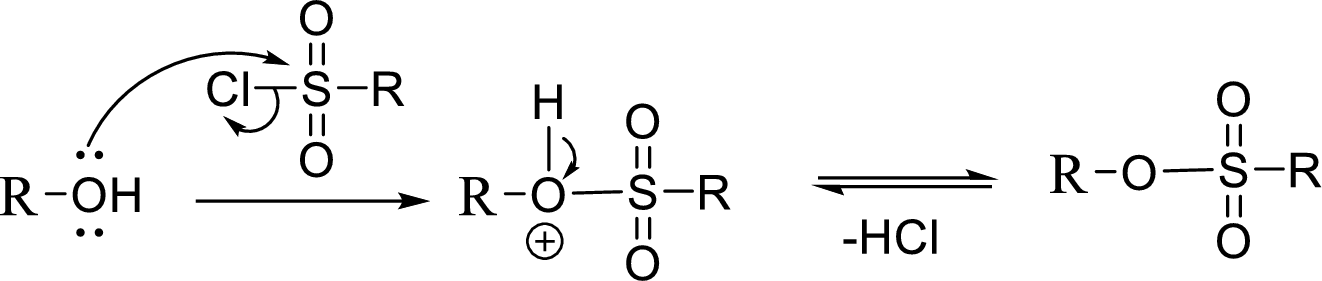
The reaction of acetyl chloride with
The acyl group of acetyl chloride is very reactive and the chloride group attached to it is a good leaving group. The nucleophile from amine attacks the carbonyl carbon of the acetylchloride to form N- methylacetamide. The chloride group leaves and gets attached to hydrogen of the amine and leaves as hydrochloric acid.
The reaction is:
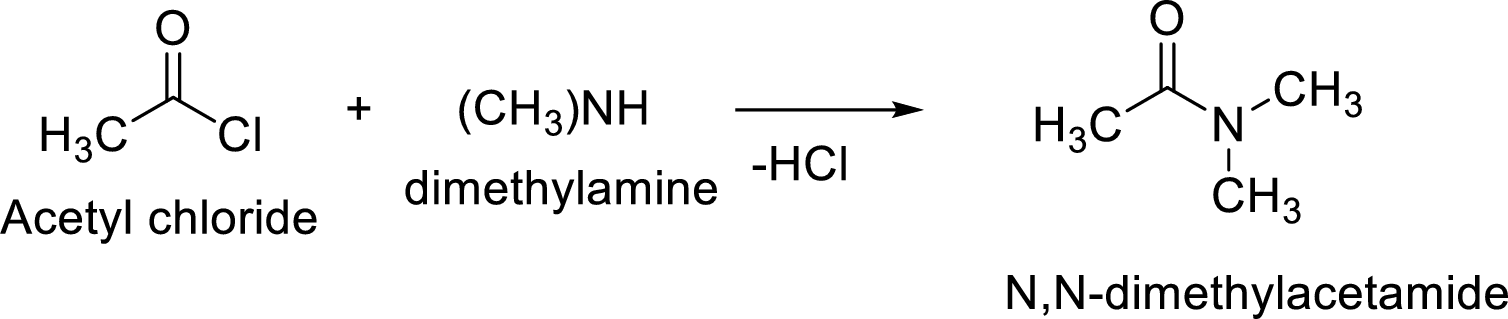
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 20 Solutions
EP ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-OWL V2 ACCESS
- Can I please get help with identifying these?arrow_forward4. Calculate the pH of a 0.10 M acetic acid (CH3COOH) solution if the Ka of acetic acid = 1.8 x 10-5arrow_forwardDraw the Zaitsev product of the dehydration of this alcohol. + I X 5 OH ざ~ TSOH Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forward
- Please help with identifying these.arrow_forwardFor the reaction: CO2(g) + H2(g) --> CO (g) + H2O (g) Kc= 0.64 at 900 degrees celcius. if initially you start with 1.00 atmoshpere of carbon dioxide and 1 atmoshpere of hydrogen gas, what are the equilibrium partial pressuses of all species.arrow_forwardCan I please get this answered? With the correct number of significant digits.arrow_forward
- Draw the Hofmann product of the dehydroiodination of this alkyl iodide. ☐ : + Explanation Check esc F1 2 3 I 88 % 5 F5 I. X © tBuOK Click and drag to sta drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Te BI BB F6 W E R Y S H Karrow_forwardCan I please get help with this graph, if you could show exactly where it needs to pass through please.arrow_forwardDraw the condensed structure of 1,3-dihydroxy-2-pentanone. Explanation Check Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. Х C © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of use +arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning



