
(a)
Interpretation:
The detailed mechanism and the major product of the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The carbonyl carbon atom in compounds such as
Answer to Problem 20.1P
The mechanism of the given reaction can be drawn as
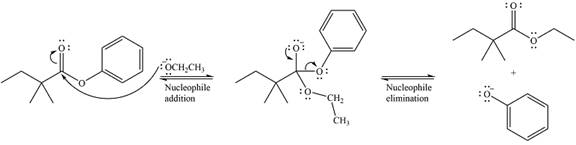
The major product of the reaction is
Explanation of Solution
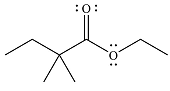
The given reaction is
The carbonyl carbon in the ester substrate is partially positively charged, i.e., electron-poor. The reagent
In the next step, the leaving group, the phenoxy ion, from the original ester is eliminated. This step forms the major product, another ester.
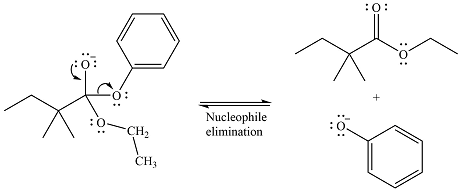
Since the substrate and the product are both esters, of comparable stability, the two steps are reversible.
Thus, the complete detailed mechanism for the reaction can be drawn as
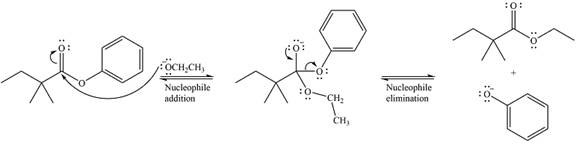
And the major product of the reaction is

The mechanism of the reaction and the major product were drawn based on nucleophilic addition-elimination step.
(b)
Interpretation:
The detailed mechanism of the reaction and its major product are to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The carbonyl carbon atom in compounds such as aldehydes, ketones, and esters is relatively electron-poor. It can add a nucleophile, forming a tetrahedral transition state. This is followed by the elimination of the leaving group, itself a nucleophile, to form the product. When an ester is treated with an alkoxide, it replaces the original alkoxide group in from the ester substrate. Since the reaction results in formation of another ester, it is known as transesterification.
Answer to Problem 20.1P
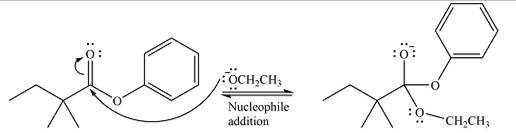
The complete mechanism for the reaction can be drawn as
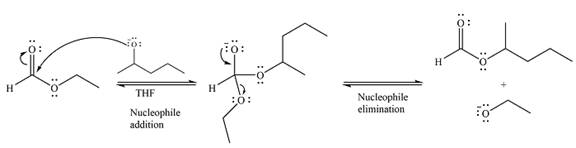
And the major product of the reaction as
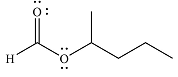
Explanation of Solution
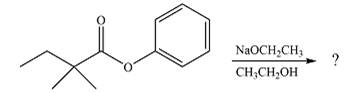
The given reaction is
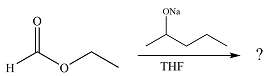
The substrate is an ester, with an electron-poor carbonyl carbon. The reagent is ionic and essentially acts as the negativey charged nucleophile
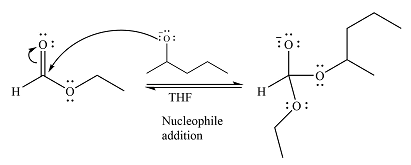
Next, the leaving group (ethoxide) from the original ester is eliminated to formt eh major product.
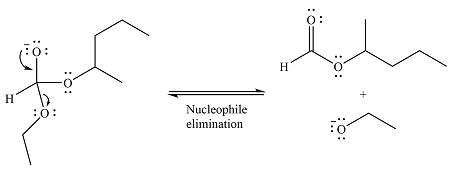
The major product is another ester, of comparable stability. Therefore, both steps will be reversible steps.
Thus, the complete mechanism for the reaction can be drawn as
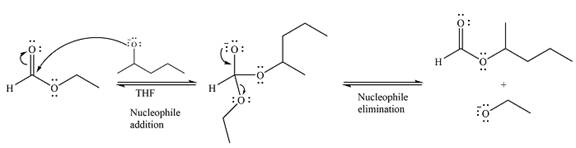
And the major product of the reaction as

The complete mechanism and the major product of the reaction were drawn based on nucleophilic addition-elimination steps.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
ORG CHEM W/ EBOOK & SW5 + STUDY GUIDE
- In reactions whose kinetic equation is v = k[A]m, the rate coefficient k is always positive. Is this correct?arrow_forwardIf the concentration of A decreases exponentially with time, what is the rate equation? (A). -d[A] (B). dt d[A] = k[A] e-kt dtarrow_forwardGiven the first-order reaction: aA → products. State its kinetic equation.arrow_forward
- The following chemical structure represents a molecule of what molecular formula?arrow_forwardWhich region(s) of the following phospholipid is/are hydrophobic? RO I hydro-water phobic-dislikes = Hydrophobic dislikes water ○ I only Il only I and III only II and IV only O II, III, and IV only III || IVarrow_forwardPredict the product of the following reactions: O 0= excess Х Кон ОН H+ H+ Iarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





