
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The stronger acid has to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Relative Acid strength: As going down the group, the size of the atoms increases. The larger the size, the negative charge can be easily polarizable over the larger volume of the atom. Hence, the proton attached to the larger sized atom, the acid becomes the stronger.
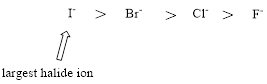
(b)
Interpretation:
The stronger acid has to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Relative Acid strength: As going down the group, the size of the atoms increases. The larger the size, the negative charge can be easily polarizable over the larger volume of the atom. Hence, the proton attached to the larger sized atom, the acid becomes the stronger.
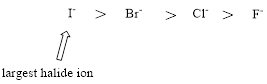
(c)
Interpretation:
The stronger acid has to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Relative Acid strength: As going down the group, the size of the atoms increases. The larger the size, the negative charge can be easily polarizable over the larger volume of the atom. Hence, the proton attached to the larger sized atom, the acid becomes the stronger.
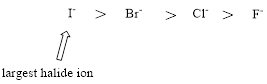
(d)
Interpretation:
The stronger acid has to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Relative Acid strength: As going down the group, the size of the atoms increases. The larger the size, the negative charge can be easily polarizable over the larger volume of the atom. Hence, the proton attached to the larger sized atom, the acid becomes the stronger.
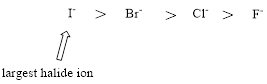
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 2 Solutions
EP ESSENTIAL ORG.CHEM.-MOD.MASTERING
- Use diagram to answer the following: 1.Is the overall rxn endo- or exothermic. Explain briefly your answer____________________2. How many steps in this mechanism?_____________3. Which is the rate determining step? Explain briefly your answer____________________4. Identify (circle and label) the reactants,the products and intermediate (Is a Cation, Anion, or a Radical?) Please explain and provide full understanding.arrow_forwardDraw the entire mechanism and add Curved Arrows to show clearly how electrons areredistributed in the process. Please explain and provide steps clearly.arrow_forward15) Create Lewis structure Br Brarrow_forward
- LIOT S How would you make 200. mL of a 0.5 M solution of CuSO4 5H2O from solid copper (II) sulfate? View Rubricarrow_forwardSteps and explantions pleasearrow_forwardMatch the denticity to the ligand. Water monodentate ✓ C₂O2 bidentate H₂NCH₂NHCH2NH2 bidentate x EDTA hexadentate Question 12 Partially correct Mark 2 out of 2 Flag question Provide the required information for the coordination compound shown below: Na NC-Ag-CN] Number of ligands: 20 Coordination number: 2✔ Geometry: linear Oxidation state of transition metal ion: +3 x in 12 correct out of 2 question Provide the required information for the coordination compound shown below. Na NC-Ag-CN] Number of ligands: 20 Coordination number: 2 Geometry: linear 0 Oxidation state of transition metal ion: +3Xarrow_forward
- Can you explain step by step behind what the synthetic strategy would be?arrow_forwardPlease explain step by step in detail the reasoning behind this problem/approach/and answer. thank you!arrow_forward2. Predict the product(s) that forms and explain why it forms. Assume that any necessary catalytic acid is present. .OH HO H₂N OHarrow_forward

 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning





