
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The stronger acid has to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Base and its conjugate Acid: A Base is a species that can gain a proton. When a base gains a proton
Electron delocalization stabilizes base: If a base has delocalized electrons, then the negative charge that results when the base’s conjugate acid loses a proton will belong to one atom. If a base has delocalized electrons, then the negative charge that results when the base’s conjugate acid loses a proton will be shared by two or more atoms. A base with delocalized electron is more stable than a similar base with localized electrons.
Relative Acid strength: Replacing hydrogen with an electronegative substituent that pulls bonding electrons toward itself increases the strength of the acid.
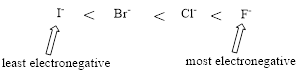
The more electronegative the substituent that replaces hydrogen, the stronger the acid becomes.
Example:
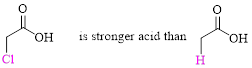
(b)
Interpretation:
The stronger acid has to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Base and its conjugate Acid: A Base is a species that can gain a proton. When a base gains a proton
Electron delocalization stabilizes base: If a base has delocalized electrons, then the negative charge that results when the base’s conjugate acid loses a proton will belong to one atom. If a base has delocalized electrons, then the negative charge that results when the base’s conjugate acid loses a proton will be shared by two or more atoms. A base with delocalized electron is more stable than a similar base with localized electrons.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 2 Solutions
EP ESSENTIAL ORG.CHEM.-MOD.MASTERING
- Complete the reaction. Not the mechanism.arrow_forwardDraw the mechanism using the arrows on conventions, including all formal charges and correct arrows. If stereochemical distinction can be made they should be included in the structure of the products.arrow_forwardDraw the epoxide formed when the following alkene is treated with mCPBA. Click the "draw structure" button to launch the drawing utility. draw structure ...arrow_forward
- Rank each of the following substituted benzene molecules in order of which will react fastest (1) to slowest (4) by electrophilic aromatic substitution. Explanation Check CF3 (Choose one) OH (Choose one) H (Choose one) (Choose one) © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacyarrow_forwardIdentifying electron-donating and electron-withdrawing effects For each of the substituted benzene molecules below, determine the inductive and resonance effects the substituent will have on the benzene ring, as well as the overall electron-density of the ring compared to unsubstituted benzene. Molecule Inductive Effects Resonance Effects Overall Electron-Density CF3 O donating O donating O electron-rich O withdrawing withdrawing O no inductive effects O no resonance effects O electron-deficient O similar to benzene OCH3 Explanation Check O donating O donating ○ withdrawing withdrawing O no inductive effects no resonance effects electron-rich electron-deficient O similar to benzene Х © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Centerarrow_forwardThe acid-base chemistry of both EDTA and EBT are important to ensuring that the reactions proceed as desired, thus the pH is controlled using a buffer. What percent of the EBT indicator will be in the desired HIn2- state at pH = 10.5. pKa1 = 6.2 and pKa2 = 11.6 of EBTarrow_forward
- CUE COLUMN NOTES (A. Determine Stereoisomers it has ⑤ Identify any meso B compounds cl Br cl -c-c-c-c-¿- 1 CI C- | 2,4-Dichloro-3-bromopentanearrow_forwardThe acid-base chemistry of both EDTA and EBT are important to ensuring that the reactions proceed as desired, thus the pH is controlled using a buffer. What percent of the EBT indicator will be in the desired HIn2- state at pH = 10.5. pKa1 = 6.2 and pKa2 = 11.6 of EBTarrow_forwardWhat does the phrase 'fit for purpose' mean in relation to analytical chemistry? Please provide examples too.arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
