
Fox and McDonald's Introduction to Fluid Mechanics
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781118912652
Author: Philip J. Pritchard, John W. Mitchell
Publisher: WILEY
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 2, Problem 47P
A torque of 4 N · m is required to rotate the intermediate cylinder at 30 r/min. Calculate the viscosity of the oil. All cylinders are 450 mm long. Neglect end effects.
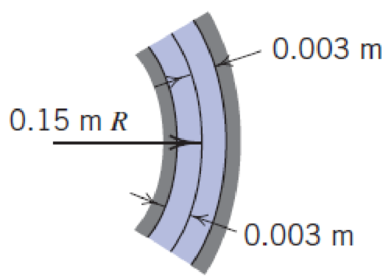
P2.47
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
3-55 A multifluid container is connected to a U-tube,
as shown in Fig. P3–55. For the given specific gravities
and fluid column heights, determine the gage pressure at
A. Also determine the height of a mercury column that
would create the same pressure at A. Answers: 0.415 kPa,
0.311 cm
I need help answering parts a and b
Required information
Water initially at 200 kPa and 300°C is contained in a piston-cylinder device fitted with stops. The water is allowed to cool
at constant pressure until it exists as a saturated vapor and the piston rests on the stops. Then the water continues to cool
until the pressure is 100 kPa.
NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part.
Water
200 kPa
300°C
On the T-V diagram, sketch, with respect to the saturation lines, the process curves passing through the initial, intermediate, and final states of the water. Label the
T, P, and V values for end states on the process curves.
Please upload your response/solution by using the controls provided below.
Chapter 2 Solutions
Fox and McDonald's Introduction to Fluid Mechanics
Ch. 2 - For the velocity fields given below, determine:...Ch. 2 - For the velocity fields given below, determine:...Ch. 2 - A viscous liquid is sheared between two parallel...Ch. 2 - For the velocity field V=Ax2yi+Bxy2j, where A = 2...Ch. 2 - A fluid flow has the following velocity...Ch. 2 - When an incompressible, nonviscous fluid flows...Ch. 2 - For the free vortex flow the velocities are t =...Ch. 2 - For the forced vortex flow the velocities are t =...Ch. 2 - A velocity field is specified as V=axyi+by2j,...Ch. 2 - A velocity field is given by V=ax3i+bxy3j, where a...
Ch. 2 - The velocity for a steady, incompressible flow in...Ch. 2 - The flow field for an atmospheric flow is given by...Ch. 2 - For the velocity field V=AxiAyj,, where A = 2s 1....Ch. 2 - A velocity field in polar coordinates is given...Ch. 2 - The flow of air near the Earths surface is...Ch. 2 - A velocity field is given by V=aytibxj, where a =...Ch. 2 - Air flows downward toward an infinitely wide...Ch. 2 - Consider the flow described by the velocity field...Ch. 2 - Consider the velocity field V = axi + by(1 + ct)...Ch. 2 - Consider the flow field given in Eulerian...Ch. 2 - A velocity field is given by V=axti+byj, where A =...Ch. 2 - Consider the garden hose of Fig. 2.5. Suppose the...Ch. 2 - Consider the velocity field of Problem 2.18. Plot...Ch. 2 - Streaklines are traced out by neutrally buoyant...Ch. 2 - Consider the flow field V=axti+bj, where a = 1/s2...Ch. 2 - A flow is described by velocity field V=ay2i+bj,...Ch. 2 - Tiny hydrogen bubbles are being used as tracers to...Ch. 2 - A flow is described by velocity field V=ai+bxj,...Ch. 2 - A flow is described by velocity field V=ayi+btj,...Ch. 2 - A flow is described by velocity field V=ati+bj,...Ch. 2 - The variation with temperature of the viscosity of...Ch. 2 - The variation with temperature of the viscosity of...Ch. 2 - Some experimental data for the viscosity of helium...Ch. 2 - The velocity distribution for laminar flow between...Ch. 2 - What is the ratio between the viscosities of air...Ch. 2 - Calculate velocity gradients and shear stress for...Ch. 2 - A very large thin plate is centered in a gap of...Ch. 2 - A female freestyle ice skater, weighing 100 lbf,...Ch. 2 - A block of mass 10 kg and measuring 250 mm on each...Ch. 2 - A 73-mm-diameter aluminum (SG = 2.64) piston of...Ch. 2 - A vertical gap 25 mm wide of infinite extent...Ch. 2 - A cylinder 8 in. in diameter and 3 ft long is...Ch. 2 - Crude oil at 20C fills the space between two...Ch. 2 - The piston in Problem 2.40 is traveling at...Ch. 2 - A block of mass M slides on a thin film of oil....Ch. 2 - A block 0.1 m square, with 5 kg mass, slides down...Ch. 2 - A torque of 4 N m is required to rotate the...Ch. 2 - A circular disk of diameter d is slowly rotated in...Ch. 2 - The fluid drive shown transmits a torque T for...Ch. 2 - A block that is a mm square slides across a flat...Ch. 2 - In a food-processing plant, honey is pumped...Ch. 2 - SAE 10W-30 oil at 100C is pumped through a tube L...Ch. 2 - The lubricant has a kinematic viscosity of 2:8105...Ch. 2 - Calculate the approximate viscosity of the oil....Ch. 2 - Calculate the approximate power lost in friction...Ch. 2 - Fluids of viscosities 1 = 0.1 Ns/m2 and 2 = 0.15...Ch. 2 - A concentric cylinder viscometer may be formed by...Ch. 2 - A concentric cylinder viscometer is driven by a...Ch. 2 - A shaft with outside diameter of 18 mm turns at 20...Ch. 2 - A shock-free coupling for a low-power mechanical...Ch. 2 - A proposal has been made to use a pair of parallel...Ch. 2 - The cone and plate viscometer shown is an...Ch. 2 - A viscometer is used to measure the viscosity of a...Ch. 2 - A concentric-cylinder viscometer is shown. Viscous...Ch. 2 - Design a concentric-cylinder viscometer to measure...Ch. 2 - A cross section of a rotating bearing is shown....Ch. 2 - Small gas bubbles form in soda when a bottle or...Ch. 2 - You intend to gently place several steel needles...Ch. 2 - According to Folsom [6], the capillary rise h...Ch. 2 - Calculate and plot the maximum capillary rise of...Ch. 2 - Calculate the maximum capillary rise of water...Ch. 2 - Calculate the maximum capillary depression of...Ch. 2 - Water usually is assumed to be incompressible when...Ch. 2 - The viscous boundary layer velocity profile shown...Ch. 2 - In a food industry process, carbon tetrachloride...Ch. 2 - What is the Reynolds number of water at 20C...Ch. 2 - A supersonic aircraft travels at 2700 km/hr at an...Ch. 2 - SAE 30 oil at 100C flows through a 12-mm-diameter...Ch. 2 - A seaplane is flying at 100 mph through air at...Ch. 2 - An airliner is cruising at an altitude of 5.5 km...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Porter’s competitive forces model: The model is used to provide a general view about the firms, the competitors...
Management Information Systems: Managing The Digital Firm (16th Edition)
In the following exercises, write a program to carry out the task. The program should use variables for each of...
Introduction To Programming Using Visual Basic (11th Edition)
Write an evaluation of some programming language you know, using the criteria described in this chapter.
Concepts Of Programming Languages
17–1C A high-speed aircraft is cruising in still air. How does the temperature of air at the nose of the aircra...
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Miles-per-Gallon A cars miles-per-gallon (MPG) can be calculated with the following formula: MPG=Milesdriven/Ga...
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Data Structures (4th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
For the circuit shown, use the node-voltage method to find v1, v2, and i1.
How much power is delivered to the c...
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A piston-cylinder device contains 0.87 kg of refrigerant-134a at -10°C. The piston that is free to move has a mass of 12 kg and a diameter of 25 cm. The local atmospheric pressure is 88 kPa. Now, heat is transferred to refrigerant-134a until the temperature is 15°C. Use data from the tables. R-134a -10°C Determine the change in the volume of the cylinder of the refrigerant-134a if the specific volume and enthalpy of R-134a at the initial state of 90.4 kPa and -10°C and at the final state of 90.4 kPa and 15°C are as follows: = 0.2418 m³/kg, h₁ = 247.77 kJ/kg 3 v2 = 0.2670 m³/kg, and h₂ = 268.18 kJ/kg The change in the volume of the cylinder is marrow_forwardA piston-cylinder device contains 0.87 kg of refrigerant-134a at -10°C. The piston that is free to move has a mass of 12 kg and a diameter of 25 cm. The local atmospheric pressure is 88 kPa. Now, heat is transferred to refrigerant-134a until the temperature is 15°C. Use data from the tables. R-134a -10°C Determine the final pressure of the refrigerant-134a. The final pressure is kPa.arrow_forwardThe hydraulic cylinder BC exerts on member AB a force P directed along line BC. The force P must have a 560-N component perpendicular to member AB. A M 45° 30° C Determine the force component along line AB. The force component along line AB is N.arrow_forward
- ! Required information A telephone cable is clamped at A to the pole AB. The tension in the left-hand portion of the cable is given to be T₁ = 815 lb. A 15° 25° B T₂ Using trigonometry, determine the required tension T₂ in the right-hand portion if the resultant R of the forces exerted by the cable at A is to be vertical. The required tension is lb.arrow_forwardWhat are examples of at least three (3) applications of tolerance fitting analysis.arrow_forwardThe primary material used in the production of glass products is silica sand. True or Falsearrow_forward
- Which one of the following is the most common polymer type in fiber-reinforced polymer composites? thermosets thermoplastics elastomers none of the abovearrow_forwardA pattern for a product is larger than the actual finished part. True or Falsearrow_forwardIn the lost foam process, the pattern doesn’t need to be removed from the mold. True or Falsearrow_forward
- Tempering eliminates internal stresses in glass. True or Falsearrow_forwardThermoset polymers can be recycled with little to no degradation in properties. True or Falsearrow_forwardTwo forces are applied as shown to a hook support. The magnitude of P is 38 N. 50 N 25° DG a 터 Using trigonometry, determine the required angle a such that the resultant R of the two forces applied to the support will be horizontal. The value of a isarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Properties of Fluids: The Basics; Author: Swanson Flo;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TgD3nEO1iCA;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Fluid Mechanics-Lecture-1_Introduction & Basic Concepts; Author: OOkul - UPSC & SSC Exams;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6bZodDnmE0o;License: Standard Youtube License