
Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9780618974122
Author: Andrei Straumanis
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Chapter 2, Problem 3E
(a)
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation:
The
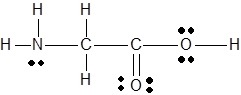
Concept Introduction :
There are three steps to determine the bond angles in a molecule.
- Lewis structure should be drawn
- The electron domain geometry should be determine using the steric number and VSEPR theory.
- Then the shape of the molecule is used to determine the angles between electron domains.
(b)
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation:
The
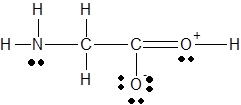
Concept Introduction :
There are three steps to determine the bond angles in a molecule.
- Lewis structure should be drawn
- The electron domain geometry should be determine using the steric number and VSEPR theory.
- Then the shape of the molecule is used to determine the angles between electron domains.
(c)
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation:
The prediction expected to be more accurate should be explained.
Concept Introduction :
There are three steps to determine the bond angles in a molecule.
- Lewis structure should be drawn
- The electron domain geometry should be determine using the steric number and VSEPR theory.
- Then the shape of the molecule is used to determine the angles between electron domains.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
What is the final product when hexanedioic acid reacts with 1º PCl5 and 2º NH3.
What is the final product when D-galactose reacts with hydroxylamine?
Indicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting methyl 5-chloro-5-oxopentanoate with 1 mole of 4-penten-1-ylmagnesium bromide.
Chapter 2 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Ch. 2 - Prob. 1CTQCh. 2 - The valence shell of an atom in a legitimate Lewis...Ch. 2 - Prob. 3CTQCh. 2 - Prob. 4CTQCh. 2 - Prob. 5CTQCh. 2 - It is impossible to draw a legitimate Lewis...Ch. 2 - Describe how to calculate the total number of...Ch. 2 - Prob. 8CTQCh. 2 - Prob. 9CTQCh. 2 - Prob. 10CTQ
Ch. 2 - Prob. 11CTQCh. 2 - Prob. 12CTQCh. 2 - A complete Lewis structure must show all nonzero...Ch. 2 - Prob. 14CTQCh. 2 - Prob. 15CTQCh. 2 - Prob. 16CTQCh. 2 - Prob. 17CTQCh. 2 - Prob. 18CTQCh. 2 - Complete the rest of the table for N, O or X by...Ch. 2 - Prob. 20CTQCh. 2 - Prob. 21CTQCh. 2 - Make a checklist that can be used to determine if...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2ECh. 2 - Prob. 3ECh. 2 - Draw the Lewis structure of a neutral molecule...Ch. 2 - Prob. 5ECh. 2 - For each element, predict (and draw a Lewis...Ch. 2 - Predict which of the following species is least...Ch. 2 - The molecules BH3 and SF6 and the ion SO42 exist...Ch. 2 - These are NOTlegitimate Lewisstructures (and...Ch. 2 - Fill in missing formal charges where needed (all...Ch. 2 - Below each structure in the previous question is a...Ch. 2 - Prob. 12ECh. 2 - Carbon monoxide (CO) is an example of an overall...Ch. 2 - Explain why this Lewis structure for CO is not as...Ch. 2 - Prob. 15ECh. 2 - Prob. 16ECh. 2 - Prob. 17ECh. 2 - Prob. 18ECh. 2 - Prob. 19E
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- The temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forwardQUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forward
- er your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward5.arrow_forward6.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133949640
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399074
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning