
Organic Chemistry
12th Edition
ISBN: 9781118875766
Author: T. W. Graham Solomons, Craig B. Fryhle, Scott A. Snyder
Publisher: WILEY
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 2, Problem 38P
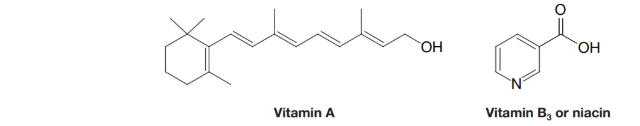
(a) Indicate the hydrophobic and hydrophilic parts of vitamin A and comment on whether you would expect it to be soluble in water. (b) Do the same for vitamin
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Using reaction free energy to predict equilibrium composition
Consider the following equilibrium:
2NOCI (g) 2NO (g) + Cl2 (g) AGº =41. kJ
Now suppose a reaction vessel is filled with 4.50 atm of nitrosyl chloride (NOCI) and 6.38 atm of chlorine (C12) at 212. °C. Answer the following questions
about this system:
?
rise
Under these conditions, will the pressure of NOCI tend to rise or fall?
x10
fall
Is it possible to reverse this tendency by adding NO?
In other words, if you said the pressure of NOCI will tend to rise, can that
be changed to a tendency to fall by adding NO? Similarly, if you said the
pressure of NOCI will tend to fall, can that be changed to a tendency to
rise by adding NO?
yes
no
If you said the tendency can be reversed in the second question, calculate
the minimum pressure of NO needed to reverse it.
Round your answer to 2 significant digits.
0.035 atm
✓
G
00.
18
Ar
Highlight each glycosidic bond in the molecule below. Then answer the questions in the table under the drawing area.
HO-
HO-
-0
OH
OH
HO
NG
HO-
HO-
OH
OH
OH
OH
NG
OH
€
+
Suppose the molecule in the drawing area below were reacted with H₂ over a platinum catalyst. Edit the molecule to show what would happen to it. That is, turn
it into the product of the reaction.
Also, write the name of the product molecule under the drawing area.
Name: ☐
H
C=0
X
H-
OH
HO-
H
HO-
-H
CH₂OH
×
Chapter 2 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Ch. 2 - Practice Problem 2.1
Propose structures for two...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2PPCh. 2 - Prob. 3PPCh. 2 - Prob. 4PPCh. 2 - Prob. 5PPCh. 2 - Practice Problem 2.6
Using a three-dimensional...Ch. 2 - Practice Problem 2.7
Trichloromethane (, also...Ch. 2 - Prob. 8PPCh. 2 - Prob. 9PPCh. 2 - Practice Problem 2.10
Write bond-line structural...
Ch. 2 - Practice Problem 2.11 Although we shall discuss...Ch. 2 - Practice Problem 2.12 Write bond-line structural...Ch. 2 - Prob. 13PPCh. 2 - Practice Problem 2.14
One way of naming ethers is...Ch. 2 - Practice Problem 2.15 Eugenol is the main...Ch. 2 - Practice Problem 2.16
One way of naming amines is...Ch. 2 - Practice Problem 2.17 Which amines in Practice...Ch. 2 - Prob. 18PPCh. 2 - Prob. 19PPCh. 2 - Practice Problem 2.20
Write bond-line formulas for...Ch. 2 - Practice Problem 2.21
Write bond-line formulas for...Ch. 2 - Practice Problem 2.22
Write bond-line formulas for...Ch. 2 - Prob. 23PPCh. 2 - Practice Problem 2.24 Write another resonance...Ch. 2 - Prob. 25PPCh. 2 - Practice Problem 2.26
Which compound would you...Ch. 2 - Practice Problem 2.27 Arrange the following...Ch. 2 - Prob. 28PPCh. 2 - Prob. 29PCh. 2 - Identify all of the functional groups in each of...Ch. 2 - 2.31 There are four alkyl bromides with the...Ch. 2 - Prob. 32PCh. 2 - Classify the following alcohols as primary,...Ch. 2 - 2.34 Classify the following amines as primary,...Ch. 2 - Prob. 35PCh. 2 - Identify all of the functional groups in Crixivan,...Ch. 2 - 2.37 Identify all of the functional groups in...Ch. 2 - 2.38 (a) Indicate the hydrophobic and hydrophilic...Ch. 2 - Hydrogen fluoride has a dipole moment of 1.83 D;...Ch. 2 - 2.40 Why does one expect the cis isomer of an...Ch. 2 - Prob. 41PCh. 2 - Prob. 42PCh. 2 - Prob. 43PCh. 2 - 2.44 Consider each of the following molecules in...Ch. 2 - True or false: For a molecule to be polar, the...Ch. 2 - 2.46 Which compound in each of the following...Ch. 2 - Prob. 47PCh. 2 - The IR spectrum of propanoic acid (Fig. 2.16)...Ch. 2 - Prob. 49PCh. 2 - Write structural formulas for four compounds with...Ch. 2 - There are four amides with the formula C3H7NO. (a)...Ch. 2 - Prob. 52PCh. 2 - Prob. 53PCh. 2 - Prob. 54PCh. 2 - Prob. 55PCh. 2 - 2.56 Compound C is asymmetric, has molecular...Ch. 2 - 2.57 Examine the diagram showing an -helical...Ch. 2 - Prob. 1LGPCh. 2 - Prob. 2LGPCh. 2 - Prob. 3LGPCh. 2 - Consider the molecular formula C4H8O2. Predict...Ch. 2 - Consider the molecular formula C4H8O2. If any of...Ch. 2 - Prob. 6LGPCh. 2 - Consider the molecular formula.
7. Pick five...Ch. 2 - Prob. 8LGP
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
3.
a. NAD+ kinase catalyzes the ATP-dependent conversion of
NAD + to
NADP+ . How many reducing equivalents ...
Biochemistry: Concepts and Connections (2nd Edition)
Distinguish between microevolution, speciation, and macroevolution.
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
15. A good scientific hypothesis is based on existing evidence and leads to testable predictions. What hypothes...
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
The following results were obtained from a broth dilution test for microbial susceptibility. Antibiotic Concent...
Microbiology: An Introduction
Assume that a DRT value for autoclaving a culture is 1.5 minutes. How long would it take to kill all the cells ...
Laboratory Experiments in Microbiology (12th Edition) (What's New in Microbiology)
In the datura plant, purple flower color is controlled by a dominant allele P. White flowers are found in plant...
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Draw the Haworth projection of the disaccharide made by joining D-glucose and D-mannose with a ẞ(1-4) glycosidic bond. If the disaccharide has more than one anomer, you can draw any of them. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Xarrow_forwardEpoxides can be opened in aqueous acid or aqueous base to produce diols (molecules with two OH groups). In this question, you'll explore the mechanism of epoxide opening in aqueous acid. 2nd attempt Be sure to show all four bonds at stereocenters using hash and wedge lines. 0 0 Draw curved arrows to show how the epoxide reacts with hydronium ion. 100 +1: 1st attempt Feedback Be sure to show all four bonds at stereocenters using hash and wedge lines. See Periodic Table See Hint H A 5 F F Hr See Periodic Table See Hintarrow_forward03 Question (1 point) For the reaction below, draw both of the major organic products. Be sure to consider stereochemistry. > 1. CH₂CH₂MgBr 2. H₂O 3rd attempt Draw all four bonds at chiral centers. Draw all stereoisomers formed. Draw the structures here. e 130 AN H See Periodic Table See Hint P C Brarrow_forward
- You may wish to address the following issues in your response if they are pertinent to the reaction(s) you propose to employ:1) Chemoselectivity (why this functional group and not another?) 2) Regioselectivity (why here and not there?) 3) Stereoselectivity (why this stereoisomer?) 4) Changes in oxidation state. Please make it in detail and draw it out too in what step what happens. Thank you for helping me!arrow_forward1) Chemoselectivity (why this functional group and not another?) 2) Regioselectivity (why here and not there?) 3) Stereoselectivity (why this stereoisomer?) 4) Changes in oxidation state. Everything in detail and draw out and write it.arrow_forwardCalculating the pH at equivalence of a titration 3/5 Izabella A chemist titrates 120.0 mL of a 0.7191M dimethylamine ((CH3)2NH) solution with 0.5501 M HBr solution at 25 °C. Calculate the pH at equivalence. The pk of dimethylamine is 3.27. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. Note for advanced students: you may assume the total volume of the solution equals the initial volume plus the volume of HBr solution added. pH = ☐ ✓ 18 Ar Boarrow_forward
- Alcohols can be synthesized using an acid-catalyzed hydration of an alkene. An alkene is combined with aqueous acid (e.. sulfuric acid in water). The reaction mechanism typically involves a carbocation intermediate. > 3rd attempt 3343 10 8 Draw arrows to show the reaction between the alkene and hydronium ion. that 2nd attempt Feedback 1st attempt تعمال Ju See Periodic Table See Hint F D Ju See Periodic Table See Hintarrow_forwardDraw the simplified curved arrow mechanism for the reaction of acetone and CHgLi to give the major product. 4th attempt Π Draw the simplified curved arrow mechanism T 3rd attempt Feedback Ju See Periodic Table See Hint H -H H -I H F See Periodic Table See Hintarrow_forwardSelect the correct reagent to accomplish the first step of this reaction. Then draw a mechanism on the Grignard reagent using curved arrow notation to show how it is converted to the final product. 4th attempt Part 1 (0.5 point) Select the correct reagent to accomplish the first step of this reaction. Choose one: OA Mg in ethanol (EtOH) OB. 2 Li in THF O C. Li in THF D. Mg in THF O E Mg in H2O Part 2 (0.5 point) Br Part 1 Bri Mg CH B CH, 1 Draw intermediate here, but no arrows. © TE See Periodic Table See Hint See Hint ין Harrow_forward
- Select the product for the following reaction. HO HO PCC OH ○ OH O HO ○ HO HO HOarrow_forward5:45 Х Select the final product for the following reaction sequence. O O 1. Mg. ether 2.D.Oarrow_forwardBased on the chart Two similarities between the molecule with alpha glycosidic linkages. Two similarities between the molecules with beta glycosidtic linkages. Two differences between the alpha and beta glycosidic linkages.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399074
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133949640
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305960060
Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. Hansen
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285869759
Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Biomolecules - Protein - Amino acids; Author: Tutorials Point (India) Ltd.;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ySNVPDHJ0ek;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY