
Concept explainers
- a. List the following alcohols in order from strongest acid to weakest acid:
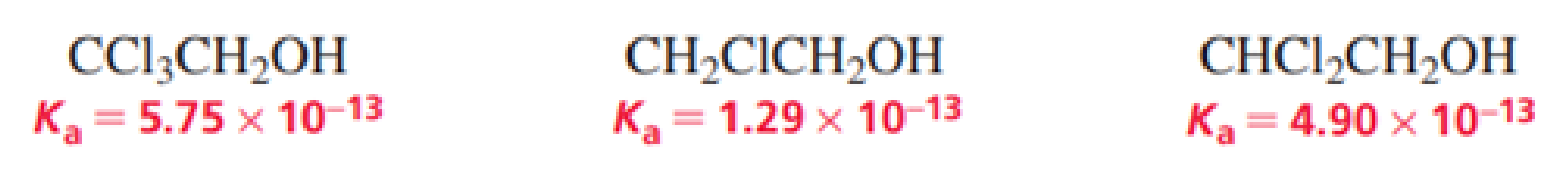
- b. Explain the relative acidities.
(a)
Interpretation:
The given alcohols have to be ranked from strongest to weakest acid.
Concept introduction:
If a base receives one proton, then the formed species is a conjugate acid whereas an acid lose one proton, then the formed species is a conjugated base.
If an acid lose one proton, then the formed species is a conjugated base. Weak base forms stronger conjugated acid.
Acidity of species depends on the electronegativity of atom attached to the acidic proton. Order of electronegativity of hybridization is
Acid dissociation constant
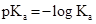
The strength of acid increases as the value of
Answer to Problem 38P
The given alcohols are ranked from strongest to weakest acid as follows,
Explanation of Solution
In hydrocarbons, if hydrogen atoms are replaced by electronegative atoms, it causes inductive electron withdrawal. It stabilizes its conjugate base thus increases the strength of the acid. The conjugated base of a weak acid is very strong. As the electronegativity of substituent increases, the greater will be the inductive electron withdrawal of the substituent making it a strong acid.
Therefore, the acidity order is:
The compound with three chlorine atoms near to the
The alcohol with high
(b)
Interpretation:
The relative acidities of the given alcohol compounds have to be explained briefly.
Concept introduction:
If a base receives one proton, then the formed species is a conjugate acid whereas an acid lose one proton, then the formed species is a conjugated base.
If an acid lose one proton, then the formed species is a conjugated base. Weak base forms stronger conjugated acid.
Acidity of species depends on the electronegativity of atom attached to the acidic proton. Order of electronegativity of hybridization is
Explanation of Solution
In hydrocarbons, if hydrogen atoms are replaced by electronegative atoms, it causes inductive electron withdrawal. It stabilizes its conjugate base thus increases the strength of the acid. The electron density near
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
EBK ESSENTIAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- Q: Draw the molecular orbital energy level diagram for the following molecules. 1- The SF4 molecule is seesaw molecular geometry and has C2v point group. 2- The Mn(CO)s molecule with C4v point group is square pyramidal.arrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't use hand ratingarrow_forwardwhen a 0.150 g sample of the compound was burned, it produced 0.138 g CO2 & 0.0566 g H2O. All the nitrogen in a different 0.200 g sample of the compound was converted to NH3, which was found to weigh 0.0238 g. Finally, the chlorine in a 0.125 g sample of the compound was converted to Cl- and by reacting it with AgNO3, all of the chlorine was recovered as the solid AgCl. The AgCl, when dried was found to weigh 0.251 g. What is the empirical formulaarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
