
Concept explainers
The eTech Company is a fairly recent entry in the electronic device area. The company competes with Apple. Samsung, and other well-known companies in the manufacturing and sales of personal handheld devices. Although eTech recognizes that it is a niche player and will likely remain so in the foreseeable future, it is trying to increase its current small market share in this huge competitive market. Jim Simons, VP of Production, and Catherine Dolans, VP of Marketing, have been discussing the possible addition of a new product to the company’s current (rather limited) product line. The tentative name for this new product is ePlayerX. Jim and Catherine agree that the ePlayerX, which will feature a sleeker design and more memory, is necessary to compete successfully with the “big boys,” but they are also worried that the ePlayerX could cannibalize sales of their existing products—and that it could even detract from their bottom line. They must eventually decide how much to spend to develop and manufacture the ePlayerX and how aggressively to market it. Depending on these decisions, they must
The expected timeline for the ePlayerX is that development will take no more than a year to complete and that the product will be introduced in the market a year from now. Jim and Catherine are aware that there are lots of decisions to make and lots of uncertainties involved, but they need to start somewhere. To this end. Jim and Catherine have decided to base their decisions on a planning horizon of four years, including the development year. They realize that the personal handheld device market is very fluid, with updates to existing products occurring almost continuously. However, they believe they can include such considerations into their cost, revenue, and demand estimates, and that a four-year planning horizon makes sense. In addition, they have identified the following problem parameters. (In this first pass, all distinctions are “binary”: low-end or high-end, small-effect or large-effect, and so on.)
- In the absence of cannibalization, the sales of existing eTech products are expected to produce year I net revenues of $10 million, and the forecast of the annual increase in net revenues is 2%.
- The ePIayerX will be developed as either a low-end or a high-end product, with corresponding fixed development costs ($1.5 million or $2.5 million), variable
manufacturing costs ($ 100 or $200). and selling prices ($150 or $300). The fixed development cost is incurred now, at the beginning of year I, and the variable cost and selling price are assumed to remain constant throughout the planning horizon. - The new product will be marketed either mildly aggressively or very aggressively, with corresponding costs. The costs of a mildly aggressive marketing campaign are $1.5 million in year 1 and $0.5 million annually in years 2 to 4. For a very aggressive campaign, these costs increase to $3.5 million and $1.5 million, respectively. (These marketing costs are not part of the variable cost mentioned in the previous bullet; they are separate.)
- Depending on whether the ePlayerX is a low-end or high-end produce the level of the ePlayerX’s cannibalization rate of existing eTech products will be either low (10%) or high (20%). Each cannibalization rate affects only sales of existing products in years 2 to 4, not year I sales. For example, if the cannibalization rate is 10%, then sales of existing products in each of years 2 to 4 will be 10% below their projected values without cannibalization.
- A “base case” forecast of demand for the ePlayerX is that in its first year on the market, year 2, demand will be for 100,000 units, and then demand will increase by 5% annually in years 3 and 4. This base forecast is based on a low-end version of the ePlayerX and mildly aggressive marketing. It will be adjusted for a high-end will product, aggressive marketing, and competitor behavior. The adjustments with no competing product appear in Table 2.3. The adjustments with a competing product appear in Table 2.4. Each adjustment is to demand for the ePlayerX in each of years 2 to 4. For example, if the adjustment is −10%, then demand in each of years 2 to 4 will be 10% lower than it would have been in the base case.
- Demand and units sold are the same—that is, eTech will produce exactly what its customers demand so that no inventory or backorders will occur.
Table 2.3 Demand Adjustments When No Competing Product Is Introduced
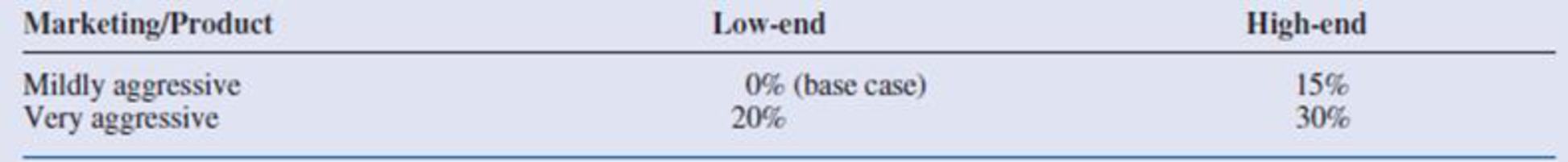
Table 2.4 Demand Adjustments When a Competing Product Is Introduced
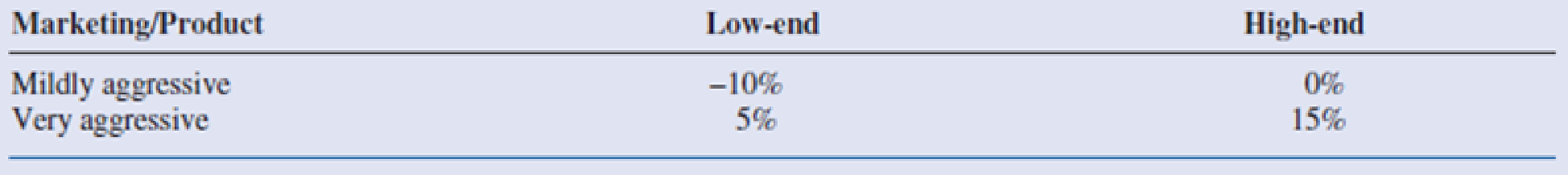
Because Jim and Catherine are approaching the day when they will be sharing their plans with other company executives, they have asked you to prepare an Excel spreadsheet model that will answer the many what-if questions they expect to be asked. Specifically, they have asked you to do the following:
- You should enter all of the given data in an “inputs” section with clear labeling and appropriate number formatting. If you believe that any explanations are required, you can enter them in text boxes or cell comments. In this section and in the rest of the model, all monetary values (other than the variable cost and the selling price) should be expressed in millions of dollars, and all demands for the ePlayerX should be expressed in thousands of units.
- You should have a “scenario” section that contains a 0/1 variable for each of the binary options discussed here. For example, one of these should be 0 if the low-end product is chosen and it should be 1 if the high-end product is chosen.
- You should have a “parameters” section that contains the values of the various parameters listed in the case, depending on the values of the 0/1 variables in the previous bullet For example, the fixed development cost will be $1.5 million or $2.5 million depending on whether the 0/1 variable in the previous bullet is 0 or 1, and this can be calculated with a simple IF formula. You can decide how to implement the IF logic for the various parameters.
- You should have a “cash flows” section that calculates the annual cash flows for the four-year period. These cash flows include the net revenues from existing products, the marketing costs for ePlayerX, and the net revenues for sales of ePlayerX (To calculate these latter values, it will help to have a row for annual units sold of ePlayerX.) The cash flows should also include depreciation on the fixed development cost, calculated on a straight-line four-year basis (that is. 25% of the cost in each of the four years). Then, these annual revenues/costs should be summed for each year to get net cash flow before taxes, taxes should be calculated using a 32% tax rate, and taxes should be subtracted and depreciation should be added back in to get net cash flows after taxes. (The point is that depreciation is first subtracted, because it is not taxed, but then it is added back in after taxes have been calculated.)
- You should calculate the company's
NPV for the four-year horizon using a discount rate of 10%. You can assume that the fixed development cost is incurred now. so that it is not discounted, and that all other costs and revenues are incurred at the ends of the respective years. - You should accompany all of this with a line chart with three series: annual net revenues from existing products; annual marketing costs for ePlayerX; and annual net revenues from sales of ePlayerX.
Once all of this is completed. Jim and Catherine will have a powerful tool for presentation purposes. By adjusting the 0/1 scenario variables, their audience will be able to see immediately, both numerically and graphically, the financial consequences of various scenarios. ■
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 2 Solutions
Practical Management Science
- As part of your new role, as a strategy consultant and member of the steering committee, discuss what logistics and transportation strategies you will execute to achieve operational efficiencies and facilitate economic growth in SA. The committee would like to have a implementable strategic transport and logistics plan to realise the roadmap vision based on the subsection numbering given below: QUESTION ONE Marks 5 Introduction: Must include an overview and history of South Africa's Road, rail and freight transport network. 1.1 Assess what led to such logistical inefficiencies/collapse of a previously world class freight network 10 1.2 What are the current freight and logistic challenges on the road network 10 1.3 Discuss key relevant financials of infrastructure, industries and revenue resulting in this logistics crisis. 15 1.4 Discuss how the key stakeholder partnerships - current and future are critical to government and business as part of the overall intermodal transport strategy.…arrow_forwardWhat are the current freight and logistic challenges on the road network Discuss key relevant financials of infrastructure, industries and revenue resulting in this logistics crisis. 10 15arrow_forward1.5 If you examine the freight supply and value chain, what transport and infrastructure strategies and 25 plans need to be implemented to improve operation efficiencies and reduce costs. 5 1.6 15 Discuss how implementation of a strategic intermodal transport plan can further unlock and improve South Africa's GDP and international recognition.arrow_forward
- A certain business process is no longer providing the desired benefits, therefore it needs to be re-designed through a project. You have to: Choose the business process to re-design and specify the reason why it is no longer satisfactory. Ask ChatGPT (or a similar generative AI; specify name and version) to create a Project Charter for the process redesign project. Modify and refine the response provided by the AI tool ensuring it complies with the instructor’s lesson, with particular focus on the project goals, project objectives, and deliverables (remember: project objectives must be SMART!). Your work must be delivered in the following format: a)Describe the business process to re-design (example: “The process of hiring and integrating new employees into the Sales Administration department”. Do not exceed 20 words) b)Specify the reason to re-design the business process which is already in place (describe the reason why the current process is no longer satisfactory, for…arrow_forwardThe demand for subassembly S is 100 units in week 7. Each unit of S requires 1 unit of T and 2 units of U. Each unit of T requires 1 unit of V, 2 units of W, and 1 unit of X. Finally, each unit of U requires 2 units of Y and 3 units of Z. One firm manufactures all items. It takes 2 weeks to make S, 1 week to make T, 2 weeks to make U, 2 weeks to make V, 3 weeks to make W, 1 week to make X, 2 weeks to make Y, and 1 week to make Z. Click the icon to view the product structure and the time-phased product structure. Click the icon to view the on-hand inventory. Construct a net material requirements plan using on-hand inventory (enter your responses as whole numbers). Item 1 2 3 Week 4 Lead Time 5 6 7 (weeks) S Gross req On hand Net req Order receipt Order release T Gross req On hand Net req Order receipt Order release Gross rea 100 100arrow_forwardIt is January 1 of year 0, and Merck is trying to determine whether to continue development of a newdrug. The following information is relevant. You can assume that all cash flows occur at the ends of therespective years.■ Clinical trials (the trials where the drug is tested on humans) are equally likely to be completed in year1 or 2.■ There is an 80% chance that clinical trials will succeed. If these trials fail, the FDA will not allow thedrug to be marketed.■ The cost of clinical trials is assumed to follow a triangular distribution with best case $100 million,most likely case $150 million, and worst case $250 million. Clinical trial costs are incurred at the end ofthe year clinical trials are completed.■ If clinical trials succeed, the drug will be sold for five years, earning a profit of $6 per unit sold.■ If clinical trials succeed, a plant will be built during the same year trials are completed. The cost of theplant is assumed to follow a triangular distribution with best case $1…arrow_forward
- 1) Under “Costs of Quality”, costs associated with quality can be classified into four categories: appraisal, prevention, internal failures, and external failures. The costs of quality for Corley Motors Logistics is given in the table. Cost Elements Amount Checking outbound boxes for errors $31,000 Quality planning $10,625 Downtime due to conveyor/computer problems $342,125 Incoming product inspection $21,000 Customer complaint rework $33,000 Correcting erroneous orders before shipping $36,550 Quality training of associates $25,925 Correction of typographical errors--pick tickets $11,475 a) Classify the quality cost elements given in the table into the different quality cost categories (prevention, appraisal, internal failure, external failure). b) Total the quality costs in each of the different quality cost categories (prevention, appraisal, internal failure, external failure). c) Using a) and b), suggest which areas…arrow_forwardNote: In chapter 9, section 9.4 of the Stevenson text, the costs of quality are covered; chapter 9 Stevenson lecture power point slide 7 touches upon this topic; see lecture video, 3.55 mins to 4.54 mins. 2) The production process at Hansa Ceylon Coffee fills boxes with dark arabica coffee. The data for the fill weight (in ounces) of eight samples are presented below. A sample size of six was used. The firm’s operations analyst wants to construct X-bar and R-charts to monitor the filling process. Sample Sample Mean Sample Range 1 15.80 0.42 2 16.10 0.38 3 16.02 0.08 4 15.95 0.15 5 16.12 0.42 6 16.18 0.23 7 15.87 0.36 8 16.20 0.40 a) Calculate the upper and lower control limits for the X-bar chart. b) Calculate the upper and lower control limits for the R chart. c) Is the process under control? Why or why not? Note: In chapter 10, section 10.3 of the Stevenson text, control charts for variables are…arrow_forwardDo the inherent differences between private and public sector objectives—profit versus publicgood—render private sector category management practices unsuitable for public sectorpurchasing, where open tendering is the norm?You have now undergone the Category Management classes and your superiors have requestedfor your input on how to integrate some of the learnings into the public sector policy. Discuss and elaborate what are the activities and governance you would introduce in yourrecommendations without violating the principle of transparency and accountability withinyour organisation. This is based on Singapore context. Pls provide a draft with explanation, examples and useful links for learning purposes. Citations will be good too. This is a module in SUSS called category management and supplier evaluationarrow_forward
- Travelling and working internationally can lead to a life of adventure and unique career experiences. For businesses, selecting the right candidates to take on foreign assignments can propel, delay, or deny the success of the international ventures. As an international manager, identify key competencies you would look for in choosing expatriates. What might be some of their concerns in taking on overseas assignments? What are some best practices in supporting expats during and after their assignments?arrow_forwardTravelling and working internationally can lead to a life of adventure and unique career experiences. For businesses, selecting the right candidates to take on foreign assignments can propel, delay, or deny the success of the international ventures. As an international manager, identify key competencies you would look for in choosing expatriates. What might be some of their concerns in taking on overseas assignments? What are some best practices in supporting expats during and after their assignments?arrow_forwardI need answer typing clear urjent no chatgpt used pls i will give 5 Upvotes.arrow_forward
- MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033791Author:Pride, William MPublisher:South Western Educational Publishing
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,


