
Inquiry into Physics
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781337515863
Author: Ostdiek
Publisher: Cengage
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 2, Problem 2C
Two forces, one equal to 15 N and another equal to 40 N, act on a 50-kg crate resting on a horizontal surface as shown in Figure 2.55.
(a) What is the net horizontal force on the crate?
(b) What is its horizontal acceleration?
(c) If the crate starts from rest, what is its horizontal speed after 5 s?
(d) How far has the crate traveled along the surface in this time?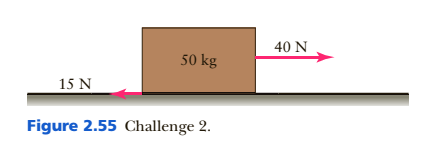
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Identical rays of light enter three transparent blocks composed of
different materials. Light slows down upon entering the blocks.
For single-slit diffraction, calculate the first three values of (the total phase difference between rays from each
edge of the slit) that produce subsidiary maxima by a) using the phasor model, b) setting dr = 0, where I is
given by,
I
=
Io (sin (10) ².
2
A capacitor with a capacitance of C = 5.95×10−5 F is charged by connecting it to a 12.5 −V battery. The capacitor is then disconnected from the battery and connected across an inductor with an inductance of L = 1.55 H .
(D)What is the charge on the capacitor 0.0235 s after the connection to the inductor is made? Interpret the sign of your answer. (e) At the time given in part (d), what is the current in the inductor? Interpret the sign of your answer. (f) Atthe time given in part (d), how much electrical energy is stored in the capacitor and how much is stored in the inductor?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Inquiry into Physics
Ch. 2 - Give three important “laws” that characterize...Ch. 2 - Describe the adhesion model of friction.Ch. 2 - Prob. 1MACh. 2 - Name a key invention that Newton contributed to...Ch. 2 - What important mathematical “tool” did Newton...Ch. 2 - Reread Section 2.7 on the law of universal...Ch. 2 - In this chapter, you've encountered a large number...Ch. 2 - (Indicates a review question. which means it...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2QCh. 2 - (Indicates a review question, which means it...
Ch. 2 - (Indicates a review question. which means it...Ch. 2 - Prob. 5QCh. 2 - (Indicates a review question. which means it...Ch. 2 - (Indicates a review question, which means it...Ch. 2 - (Indicates a review question. which means it...Ch. 2 - (Indicates a review question, which means it...Ch. 2 - (Indicates a review question. which means it...Ch. 2 - (Indicates a review question, which means it...Ch. 2 - (Indicates a review question. which means it...Ch. 2 - (Indicates a review question, which means it...Ch. 2 - Prob. 14QCh. 2 - Prob. 15QCh. 2 - Prob. 16QCh. 2 - (Indicates a review question. which means it...Ch. 2 - Prob. 18QCh. 2 - Prob. 19QCh. 2 - Prob. 20QCh. 2 - (Indicates a review question. which means it...Ch. 2 - (Indicates a review question, which means it...Ch. 2 - (Indicates a review question. which means it...Ch. 2 - (Indicates a review question, which means it...Ch. 2 - Prob. 25QCh. 2 - Prob. 26QCh. 2 - Prob. 27QCh. 2 - (Indicates a review question, which means it...Ch. 2 - Prob. 29QCh. 2 - (Indicates a review question. which means it...Ch. 2 - (Indicates a review question, which means it...Ch. 2 - (Indicates a review question, which means it...Ch. 2 - (Indicates a review question, which means it...Ch. 2 - (Indicates a review question, which means it...Ch. 2 - Express your weight in newtons. From this...Ch. 2 - A child weighs 300 N. What is the child’s mass in...Ch. 2 - Suppose au airline allows a maximum of 30 kg for...Ch. 2 - The mass of a certain elephant is 1,130 kg. (a)...Ch. 2 - The mass of a subway car and passenger is 40,000...Ch. 2 - A motorcycle and rider have a total mass equal to...Ch. 2 - As a 2-kg ball rolls down a ramp, the net force on...Ch. 2 - In an experiment performed in a space station, a...Ch. 2 - The engines in a supertanker carrying crude oil...Ch. 2 - . The Kingda Ka roller coaster in New Jersey is...Ch. 2 - . A person stands on a scale inside an elevator at...Ch. 2 - . A jet aircraft with a mass of 4,500 kg has an...Ch. 2 - . At the end of Section 1.4, we mentioned that the...Ch. 2 - . A sprinter with a mass of 80 kg accelerates...Ch. 2 - . As a baseball is being caught, its speed goes...Ch. 2 - . On aircraft carriers, catapults are used to...Ch. 2 - . At the end of an amusement park ride, it is...Ch. 2 - . An airplane is built to withstand a maximum...Ch. 2 - . Under certain conditions, the human body can...Ch. 2 - . A race car rounds a curve at 60 m/s. The radius...Ch. 2 - . A hang glider and its pilot have a total mass...Ch. 2 - . A 0.1-kg ball is attached to a string and...Ch. 2 - On a highway curve with radius 50 m, the maximum...Ch. 2 - . A centripetal force of 200 N acts on a 1,000-kg...Ch. 2 - . As a spacecraft approaches a planet, the rocket...Ch. 2 - . A space probe is launched from Earth headed for...Ch. 2 - . A hand exerciser utilizes a coiled spring. A...Ch. 2 - . A mass of 0.75 kg is attached to a relaxed...Ch. 2 - The force on a baseball as with a bat can be more...Ch. 2 - Two forces, one equal to 15 N and another equal to...Ch. 2 - Why does banking a curve on a highway allow a...Ch. 2 - As a horse and wagon are accelerating From rest,...Ch. 2 - Prob. 5CCh. 2 - Perhaps you’ve noticed that the rockets used to...Ch. 2 - Prob. 7CCh. 2 - Prob. 8CCh. 2 - Prob. 9CCh. 2 - Prob. 10C
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Close-up view etermine; The volume of the object given that the initial level of water in the measuring cylinder 23cm3. The density of the object. simple cell made by dipping copper and zinc plates into dilute sulfuric acid solution. A bull onnected across the plates using a wire. State what constitute current flow through the wire The bulb connected across is observed to light for some time and then goes out. State t possible asons for this observation. State two ways in which the processes named in question (b) above can be minimized t the bulb light for a longer period. ead is rated 80Ah. Determine the current that can be drawn continuouslyarrow_forwardAnswers with -1.828, -1.31 or 939.3 are not correct.arrow_forwardThree slits, each separated from its neighbor by d = 0.06 mm, are illuminated by a coherent light source of wavelength 550 nm. The slits are extremely narrow. A screen is located L = 2.5 m from the slits. The intensity on the centerline is 0.05 W. Consider a location on the screen x = 1.72 cm from the centerline. a) Draw the phasors, according to the phasor model for the addition of harmonic waves, appropriate for this location. b) From the phasor diagram, calculate the intensity of light at this location.arrow_forward
- A Jamin interferometer is a device for measuring or for comparing the indices of refraction of gases. A beam of monochromatic light is split into two parts, each of which is directed along the axis of a separate cylindrical tube before being recombined into a single beam that is viewed through a telescope. Suppose we are given the following, • Length of each tube is L = 0.4 m. • λ= 598 nm. Both tubes are initially evacuated, and constructive interference is observed in the center of the field of view. As air is slowly let into one of the tubes, the central field of view changes dark and back to bright a total of 198 times. (a) What is the index of refraction for air? (b) If the fringes can be counted to ±0.25 fringe, where one fringe is equivalent to one complete cycle of intensity variation at the center of the field of view, to what accuracy can the index of refraction of air be determined by this experiment?arrow_forward1. An arrangement of three charges is shown below where q₁ = 1.6 × 10-19 C, q2 = -1.6×10-19 C, and q3 3.2 x 10-19 C. 2 cm Y 93 92 91 X 3 cm (a) Calculate the magnitude and direction of the net force on q₁. (b) Sketch the direction of the forces on qiarrow_forward(Figure 1)In each case let w be the weight of the suspended crate full of priceless art objects. The strut is uniform and also has weight w Find the direction of the force exerted on the strut by the pivot in the arrangement (a). Express your answer in degrees. Find the tension Tb in the cable in the arrangement (b). Express your answer in terms of w. Find the magnitude of the force exerted on the strut by the pivot in the arrangement (b). Express your answer in terms of w.arrow_forward
- (Figure 1)In each case let ww be the weight of the suspended crate full of priceless art objects. The strut is uniform and also has weight w. Find the direction of the force exerted on the strut by the pivot in the arrangement (b). Express your answer in degrees.arrow_forwardA 70.0 cm, uniform, 40.0 N shelf is supported horizontally by two vertical wires attached to the sloping ceiling (Figure 1). A very small 20.0 N tool is placed on the shelf midway between the points where the wires are attached to it. Find the tension in the left-hand wire. Express your answer with the appropriate units.arrow_forwardFind the total bind Mev. binding energy for 13 Carbon, 6C (atomic mass = 13.0033554)arrow_forward
- What is the 27 energy absorbed in this endothermic Auclear reaction 2] Al + 'n → 27 Mg + ! H? (The atom mass of "Al is 26.981539u. and that of 11 Mg is 26.984341u) MeVarrow_forwardWhat is the energy released in this nuclear reaction 1 F + "', H-1 O+ He? 19 19 16 (The atomic mass of 1F is 18.998403 u, and that of 20 is 15.9949154) MeV.arrow_forwardWhat is the energy released in this B+ nuclear reaction خالد 2½ Al w/ Mg + ie? (The atomic mass of 11 Al is 23.9999394 and that > of 12 Mg is 23.985041 u) MeV.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Newton's First Law of Motion: Mass and Inertia; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1XSyyjcEHo0;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY