
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap Course List)
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781305970939
Author: Braja M. Das, Khaled Sobhan
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 2, Problem 2.6P
Repeat Problem 2.4 with the following data.
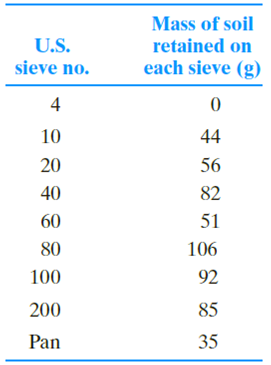
2.4 The following are the results of a sieve analysis.
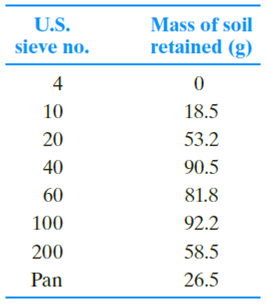
a. Determine the percent finer than each sieve and plot a grain-size distribution curve.
b. Determine D10, D30, and D60 for each soil.
c. Calculate the uniformity coefficient Cu.
d. Calculate the coefficient of gradation Cc.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
2
1d/T₁₂ = 1/2
n
First impulse
E
("œw / ])÷(1) '7
J-1
-1-
-2+
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
Bars AD and CE (E=105 GPa, a = 20.9×10-6 °C) support a rigid bar
ABC carrying a linearly increasing distributed load as shown. The
temperature of Bar CE was then raised by 40°C while the temperature of Bar
AD remained unchanged. If Bar AD has a cross-sectional area of 200 mm²
while CE has 150 mm², determine the following: the normal force in bar AD, the
normal force in bar CE, and the vertical displacement at Point A.
D
0.4 m
-0.8 m
A
-0.4 m-
B
-0.8 m-
E
0.8 m
C
18 kN/m
Draw the updated network. Calculate the new project completion date. Check if there are changes to the completion date and/or to the critical path. Mention the causes for such changes, if any.
New network based on the new information received after 15 days (Correct calculations, professionally done).
Mention if critical path changes or extended.
Write causes for change in critical path or extension in the critical path.
Chapter 2 Solutions
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap Course List)
Ch. 2 - For a gravel with D60 = 0.48 mm, D30 = 0.25 mm,...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.2PCh. 2 - Prob. 2.3PCh. 2 - The following are the results of a sieve analysis....Ch. 2 - Repeat Problem 2.4 with the following data. 2.4...Ch. 2 - Repeat Problem 2.4 with the following data. 2.4...Ch. 2 - Repeat Problem 2.4 with the following data. 2.4...Ch. 2 - The following are the results of a sieve and...Ch. 2 - Repeat Problem 2.8 using the following data. 2.8...Ch. 2 - Repeat Problem 2.8 using the following data. 2.8...
Ch. 2 - The grain-size characteristics of a soil are given...Ch. 2 - Repeat Problem 2.11 with the following data. 2.11...Ch. 2 - Repeat Problem 2.11 with the following data. 2.11...Ch. 2 - A hydrometer test has the following result: Gs =...Ch. 2 - Repeat Problem 2.14 with the following values: Gs...Ch. 2 - Three groups of students from the Geotechnical...Ch. 2 - Refer to Problem 2.C.1. Results of the sieve...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The single degree of freedom system shown in Figure 3 is at its undeformed position. The SDOF system consists of a rigid beam that is massless. The rigid beam has a pinned (i.e., zero moment) connection to the wall (left end) and it supports a mass m on its right end. The rigid beam is supported by two springs. Both springs have the same stiffness k. The first spring is located at distance L/4 from the left support, where L is the length of the rigid beam. The second spring is located at distance L from the left support.arrow_forwardFor the system shown in Figure 2, u(t) and y(t) denote the absolute displacements of Building A and Building B, respectively. The two buildings are connected using a linear viscous damper with damping coefficient c. Due to construction activity, the floor mass of Building B was estimated that vibrates with harmonic displacement that is described by the following function: y(t) = yocos(2πft). Figure 2: Single-degree-of-freedom system in Problem 2. Please compute the following related to Building A: (a) Derive the equation of motion of the mass m. (20 points) (b) Find the expression of the amplitude of the steady-state displacement of the mass m. (10 pointsarrow_forwardAssume a Space Launch System (Figure 1(a)) that is approximated as a cantilever undamped single degree of freedom (SDOF) system with a mass at its free end (Figure 1(b)). The cantilever is assumed to be massless. Assume a wind load that is approximated with a concentrated harmonic forcing function p(t) = posin(ωt) acting on the mass. The known properties of the SDOF and the applied forcing function are given below. • Mass of SDOF: m =120 kip/g • Acceleration of gravity: g = 386 in/sec2 • Bending sectional stiffness of SDOF: EI = 1015 lbf×in2 • Height of SDOF: h = 2000 inches • Amplitude of forcing function: po = 6 kip • Forcing frequency: f = 8 Hzarrow_forward
- A study of the ability of individuals to walk in a straight line reported the accompanying data on cadence (strides per second) for a sample of n = 20 randomly selected healthy men. 0.95 0.85 0.92 0.95 0.93 0.85 1.00 0.92 0.85 0.81 0.78 0.93 0.93 1.05 0.93 1.06 1.08 0.96 0.81 0.96 A normal probability plot gives substantial support to the assumption that the population distribution of cadence is approximately normal. A descriptive summary of the data from Minitab follows. Variable cadence Variable N Mean 20 cadence 0.9260 Min 0.7800 Median 0.9300 Max 1.0800 TrMean 0.9256 Q1 0.8500 StDev 0.0832 Q3 0.9600 SEMean 0.0186 (a) Calculate and interpret a 95% confidence interval for population mean cadence. (Round your answers to two decimal places.) strides per second Interpret this interval. ○ with 95% confidence, the value of the true mean cadence of all such men falls inside the confidence interval. With 95% confidence, the value of the true mean cadence of all such men falls above the…arrow_forwardWhat is the purchase quantity of 2 x 6 rafters needed for the roof and how many pieces of ridge shingles are needed for the roof? The slope of the roof is 4:12 and the exposure is 5 inches wide. arrow_forwardFor the system shown in Figure 2, u(t) and y(t) denote the absolute displacements of Building A and Building B, respectively. The two buildings are connected using a linear viscous damper with damping coefficient c. Due to construction activity, the floor mass of Building B was estimated that vibrates with harmonic displacement that is described by the following function: y(t) = yocos(2πft). Figure 2: Single-degree-of-freedom system in Problem 2. Please compute the following related to Building A: (a) Derive the equation of motion of the mass m. (20 points) (b) Find the expression of the amplitude of the steady-state displacement of the mass m. (10 pointsarrow_forward
- The direction of the force F_11 is __________LB. The magnitude of the force F_11 is __________LB.arrow_forwardIn the figure below, assume that complete mixing occurs between the two inflows before the mixture discharges from the pipe at C. Find: a. the mass flow rate in pipe C b. the velocity in pipe C Closed tank A c. the specific gravity of the mixture in pipe C Q=3 cfs SG=0.95 Diameter 6 in. Q = 1 cfs SG=0.85 B Diameter 4 in. Diameter 6 in. Q= 4 cfsarrow_forwardMANUALLY DRAW THE FLOW NET. SHOW THE SCALE USED. do not just explain how to draw it, give me a completed flow net.arrow_forward
- In a simulation experiment on a single lane road, one vehicle is travelling at 18 m/s.After 1.5seconds, the vehicle suddenly accelerates at a rate of 1.5 m/s2 for the next2 seconds and remains0 acceleration then after. Simulate the behavior of subsequent vehicle with an initial speedof16 m/s using GM car following model for the first 3 seconds if the initial distanceheadwayis 20 m. Tabulate the results. Assume headway exponent 1.2, speed exponent1.5, sensitivitycoefficient 0.8, reaction time 0.6 seconds, and update interval of0.3 seconds.arrow_forwardFORWARD FROM POINT B TO POINT A GIVEN THE FOLLOWING: POINT BN=13,163,463.03'E=3,072,129.30' DIRECTION FROM B TO A (NAZ)=276.07529° DISTANCE FROM B TO A = 10.00'arrow_forwardIt proposed to provide pile foundation for a heavy column; the pile group consisting of 4 piles. placed at 2.0 m centre to centre, forming a square pattern. The under-ground soil is clay, having cu at surface as 60 kN/m², and at depth 10 m, as 100 kN/m². Compute the allowable column load on the pile cap with factor of safety of 3.0, if the piles are circular having diameters 0.5 m each and length as 10 m.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning Construction Materials, Methods and Techniques (M...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305086272Author:William P. Spence, Eva KultermannPublisher:Cengage Learning
Construction Materials, Methods and Techniques (M...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305086272Author:William P. Spence, Eva KultermannPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305970939
Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled Sobhan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305635180
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Construction Materials, Methods and Techniques (M...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305086272
Author:William P. Spence, Eva Kultermann
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305081550
Author:Braja M. Das
Publisher:Cengage Learning
How Are Highways Designed?; Author: Practical Engineering;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9XIjqdk69O4;License: Standard Youtube License