
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap Course List)
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781305970939
Author: Braja M. Das, Khaled Sobhan
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 2, Problem 2.11P
The grain-size characteristics of a soil are given in the following table.
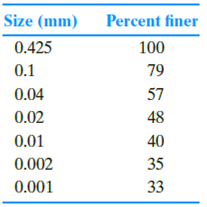
a. Draw the grain-size distribution curve.
b. Determine the percentages of gravel, sand, silt, and clay according to the MIT system.
c. Repeat Part b using the USDA system.
d. Repeat Part b using the AASHTO system.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
HOMEWORK (1) For the plan and section of the wall shown below, calculate the
following: -
1. the length of footing excavation
2, the length of bricks work under D.P.C for each step
by using:
a) Centre line method
b) Long wall-short wall method
عرف الحق
Im
D.P.C
1.00 m
Section
0.24 m
0.36 m
0.48 m
15 m
r
N
8 m
5 m
Plan
F
following:
1. the length of footing excavation
2. the length of bricks work under D.P.C for each step
by using:
a) Centre line method
b) Long wall-short wall method
D.P.C
1.00 m
0.24 m
0.36 m
y0.48 m
15 m
Section.
N
A
k
W
8 m
5 m
زف الحو
不
Z
Plan
ate the
L
Page 3
3.5) Using the Method of Components, determine the magnitude, the direction,
and the sense of the resultant for the coplanar concurrent force system shown below.
Y
76 lbs
10 kips
4
3
0
Y
12 kips
5
12
> x
60 lbs
Chapter 2 Solutions
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap Course List)
Ch. 2 - For a gravel with D60 = 0.48 mm, D30 = 0.25 mm,...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.2PCh. 2 - Prob. 2.3PCh. 2 - The following are the results of a sieve analysis....Ch. 2 - Repeat Problem 2.4 with the following data. 2.4...Ch. 2 - Repeat Problem 2.4 with the following data. 2.4...Ch. 2 - Repeat Problem 2.4 with the following data. 2.4...Ch. 2 - The following are the results of a sieve and...Ch. 2 - Repeat Problem 2.8 using the following data. 2.8...Ch. 2 - Repeat Problem 2.8 using the following data. 2.8...
Ch. 2 - The grain-size characteristics of a soil are given...Ch. 2 - Repeat Problem 2.11 with the following data. 2.11...Ch. 2 - Repeat Problem 2.11 with the following data. 2.11...Ch. 2 - A hydrometer test has the following result: Gs =...Ch. 2 - Repeat Problem 2.14 with the following values: Gs...Ch. 2 - Three groups of students from the Geotechnical...Ch. 2 - Refer to Problem 2.C.1. Results of the sieve...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- REINFORCED CONCRETE DESIGNFLEXURAL ANALYSIS OF BEAMS (CRACKED SECTION)Solution must be completeUse ballpen/inkpenAnswer in two decimal placesBox your final answerarrow_forwardA vertical parabolic curve has a back tangent of -5% and a forward tangent of +3% intersecting at station 1 + 240 at an elevation of 100m. If the stationing of PC is at 1 + 120, Evaluate the elevation at the third quarter point.arrow_forwardREINFORCED CONCRETE DESIGNFLEXURAL ANALYSIS OF BEAMS (CRACKED SECTION)Solution must be completeUse ballpen/inkpenAnswer in two decimal placesBox your final answerarrow_forward
- What is the volume of the earth's mantle in cubic kilometers? (tute problem 4d) Note: enter the number without units. For large (or small) numbers, use E notation, e.g. three million is equivalent to 3*10^6 which is 3E6 in E notation.arrow_forwardH.W: From an in-out survey conducted for a parking area consisting of 40 bays, the initial count was found to be 20 vehicles. Table gives the result of the survey. The number of vehicles coming in and out of the parking lot for a time interval of 5 minutes is as shown in the table below. Find the accumulation, total parking load, average occupancy and efficiency of the parking lot. Table: In-out survey data Time (minutes) In Out 5 3 2 10 6 2 15 3 1 20 6 7 25 6 4 30 8 6arrow_forwardcan you show me step for step? Autocad has me irritated.arrow_forward
- mummins) Is there any risk from a contaminant if 150 out of 3800 people exposed to the groundwater contaminant develop cancer and 125 out of 5000 people not exposed to the contamination also develop cancer? Why or why not? Use at least two methods to support your answer.arrow_forwardA spare buoy is a buoyant rod weighted to float and protrude vertically, as shown in thefigure below. Suppose that the buoy is made of maple wood ( specific gravity s = 0.6), has arectangular cross section ( 2.54cm by 2.54cm ), a length of 3.7 m , and is floating in seawater( specific gravity s =1.025 ). What weight of steel should be added to the bottom end of thebuoy so that h=0.45 cm? ( The specific gravity of steel s = 7.85 )arrow_forward8-42. Determine the displacement at point D. Use the principle of virtual work. El is constant. 60 kN 2m- 2 m B 30 kN/m 3 marrow_forward
- Two monitoring wells are spaced 500 m apart along the direction of groundwater flow in a confined aquifer 30.0 m thick. The difference in water level in the wells is 2.5 m. The hydraulic conductivity is 40 m/d. a) Sketch the aquifer and wells and label distances and direction of groundwater flow. b) If the real velocity of the groundwater is 0.6 m/d, what is the porosity? c) If it takes 10 years for a petroleum hydrocarbon plume to appear in the second well, what was the retardation factor?arrow_forward9. 0000) Water in a lake contains 10.5 ppb of vinyl chloride, which has a potency factor of 2.3 (mg/kg-d) 1 a. What is the incremental cancer risk for children (average weight of 15 kg) who may ingest 0.05 L of water per day while playing in the water every summer (for approximately 60 days) for 10 years? b. Is this risk acceptable? Why or why not?arrow_forward8-37. Determine the displacement of point C. Use the method of virtual work. El is constant. -12 ft- 3 k/ft -12 ft- Barrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Construction Materials, Methods and Techniques (M...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305086272Author:William P. Spence, Eva KultermannPublisher:Cengage Learning
Construction Materials, Methods and Techniques (M...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305086272Author:William P. Spence, Eva KultermannPublisher:Cengage Learning Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305970939
Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled Sobhan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305635180
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Construction Materials, Methods and Techniques (M...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305086272
Author:William P. Spence, Eva Kultermann
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305081550
Author:Braja M. Das
Publisher:Cengage Learning
How Are Highways Designed?; Author: Practical Engineering;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9XIjqdk69O4;License: Standard Youtube License