
Three groups of students from the

(a)
(b)
Figure 2.35 (a) Soil-aggregate stockpile; (b) sieve analysis (Courtesy of Khaled Sobhan, Florida Atlantic University, Boca Raton, Florida)
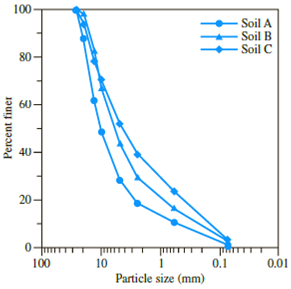
a. Determine the coefficient of uniformity and the coefficient of gradation for Soils A, B, and C.
b. Which one is coarser: Soil A or Soil C? Justify your answer.
c. Although the soils are obtained from the same stockpile, why are the curves so different? (Hint: Comment on particle segregation and representative field sampling.)
d. Determine the percentages of gravel, sand and fines according to Unified Soil Classification System.
(a)
Calculate the coefficient of uniformity
Answer to Problem 2.1CTP
The uniformity coefficient of soil A is
The coefficient of gradation of soil A is
The uniformity coefficient of soil B is
The coefficient of gradation of soil B is
The uniformity coefficient of soil C is
The coefficient of gradation of soil C is
Explanation of Solution
Sketch the grain size distribution curve for soils A, B, and C as shown in Figure 1.
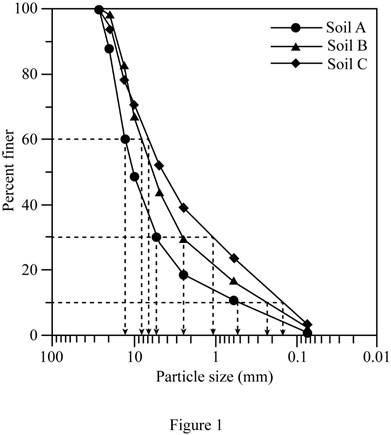
Refer to Figure 1.
For soil A:
The diameter of the particle corresponding to
The diameter of the particle corresponding to
The diameter of the particle corresponding to
For soil B:
The diameter of the particle corresponding to
The diameter of the particle corresponding to
The diameter of the particle corresponding to
For soil C:
The diameter of the particle corresponding to
The diameter of the particle corresponding to
The diameter of the particle corresponding to
Calculate the uniformity coefficient
For soil A:
Substitute
Hence, the uniformity coefficient for soil A is
For soil B:
Substitute
Hence, the uniformity coefficient for soil B is
For soil C:
Substitute
Hence, the uniformity coefficient for soil C is
Calculate the coefficient of gradation
For soil A:
Substitute
Hence, the coefficient of gradation for soil A is
For soil B:
Substitute
Hence, the coefficient of gradation for soil B is
For soil C:
Substitute
Therefore, the coefficient of gradation for soil C is
(b)
State which of the soil is coarser from soil A and C.
Answer to Problem 2.1CTP
Soil A is coarser than soil C.
Explanation of Solution
Refer to part (a).
The uniformity coefficient of soil A is
The uniformity coefficient of soil C is
The percent of soil finer than
The percent of soil finer than
Hence, a higher percentage of soil C is finer than soil A.
Hence, soil A is coarser than soil C.
(c)
Explain the reason for curve different of soil A, B and C if it is obtained from same stockpile.
Explanation of Solution
The particle-size distribution curve shows the range of particle sizes present in a soil and the type of distribution of various-size particles.
Refer to Figure 1.
Particle separation of coarser and finer particles may take place in aggregate stockpiles. This makes representative sampling difficult.
Therefore, the particle-size distribution curve is different for soils A, B, and C.
(d)
Calculate the percentages of gravel, sand, and fines according to the Unified Soil Classification System.
Answer to Problem 2.1CTP
The percentage of gravel for soil A is
The percentage of sand for soil A is
The percentage of fines for soil A is
The percentage of gravel for soil B is
The percentage of sand for soil B is
The percentage of fines for soil B is
The percentage of gravel for soil C is
The percentage of sand for soil C is
The percentage of fines for soil C is
Explanation of Solution
Refer to Figure 1.
For soil A.
The percent passing through
The percent passing through
Calculate the percentage of gravel as shown below.
Hence, the percentage of gravel is
Calculate the percentage of sand as shown below.
Hence, the percentage of sand is
Calculate the percentage of fines as shown below.
Hence, the percentage of fines is
Refer to Figure 1.
For soil B.
The percent passing through
The percent passing through
Calculate the percentage of gravel as shown below.
Hence, the percentage of gravel is
Calculate the percentage of sand as shown below.
Hence, the percentage of sand is
Calculate the percentage of fines as shown below.
Hence, the percentage of fines is
Refer to Figure 1.
For soil C.
The percent passing through
The percent passing through
Calculate the percentage of gravel as shown below.
Hence, the percentage of gravel is
Calculate the percentage of sand as shown below.
Hence, the percentage of sand is
Calculate the percentage of fines as shown below.
Hence, the percentage of fines is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap Course List)
- 8. A prestressed concrete beam is subjected to the following stress distributions: Pi is the initial prestressing force, Pe is the effective prestressing force, M, is the bending moment due to self- weight, Ma and M, are the dead load and live load bending moment, respectively. The concrete has the following properties: fr = 6000 psi and fri = 4200 psi +250 -85 -2500 +550 Pe+ Mo+Ma+Mi P alone P₁+ Mo -2450 -3500 Stress at midspan +210 +250 P, alone Pe alone -2500 -3500 Stress at ends Using Table 22.1, evaluate whether the stresses at the center of the span and the end of the span comply with the permissible stress limits. The beam is classified as U-class. Provide justifications for each condition listed in the table. Note: Calculated stresses are to be taken from the above diagram, and permissible stresses are to be calculated using Table 22.1. Compressive stresses immediately after transfer Tensile stresses immediately after transfer Compressive stresses under sustained and total…arrow_forward10. A short column is subjected to an eccentric loading. The axial load P = 1000 kips and the eccentricity e = 12 in. The material strengths are fy = 60 ksi and f = 6000 psi. The Young's modulus of steel is 29000 ksi. (a) Fill in the blanks in the interaction diagram shown below. (2pts each, 10pt total) Po Pn (1) failure range H 3" 30" Ast 6 No. 10 bars = P 22" I e H 3" (4) e = e small Load path for given e Radial lines show constant (2) eb (3) e large failure range Mn (5) e= Mo (b) Compute the balanced failure point, i.e., P and Mb.arrow_forwardNo chatgpt plsarrow_forward
- 11. The prestressed T beam shown below is pretensioned using low relaxation stress-relieved Grade 270 strands. The steel area Aps = 2.5 in². The tensile strength is fpu = 270 ksi, and the concrete compressive strength is fr = 6000 psi. (a) Calculate the nominal moment strength Mn with hr = 6 in. 22" 15" T hf (b) Since this beam is a T-beam, the nominal moment strength M₁ increases with a thicker hf. However, M, stops increasing if he reaches a value. Determine the minimum thickness hy that can achieve the maximum nominal moment strength Mr. Also, calculate the corresponding maximum nominal moment strength Mn with the computed hf.arrow_forward10. A short column is subjected to an eccentric loading. The axial load P = 1000 kips and the eccentricity e = 12 in. The material strengths are fy = 60 ksi and f = 6000 psi. The Young's modulus of steel is 29000 ksi. (a) Fill in the blanks in the interaction diagram shown below. 30" Ast 6 No. 10 bars = Pn (1) Po (4) e = e small Load path for given e failure range Radial lines show constant (2) eb (3) e large failure range Mn (5) e= Mo (b) Compute the balanced failure point, i.e., P and Mb. H 3" P 22" I e H 3"arrow_forward10. A short column is subjected to an eccentric loading. The axial load P = 1000 kips and the eccentricity e = 12 in. The material strengths are fy = 60 ksi and f = 6000 psi. The Young's modulus of steel is 29000 ksi. (a) Fill in the blanks in the interaction diagram shown below. 30" Ast 6 No. 10 bars = Pn (1) Po (4) e = e small Load path for given e failure range Radial lines show constant (2) eb (3) e large failure range Mn (5) e= Mo (b) Compute the balanced failure point, i.e., P and Mb. H 3" P 22" I e H 3"arrow_forward
- 7. Match the given strand profiles with the corresponding loading conditions for a prestressed concrete (PSC) beam. Strand profile (b) (d) (c) (a) Ꮎ Load on a beamarrow_forward4. For serviceability considerations, the effective moment of inertia (Ie) is calculated using the following formula: le 1 - 1cr ((2/3) Mcr) Ma 2 - وا ≥ Note that the upper bound was previously set as Iut in the earlier ACI equation. (a) Arrange the following moment of inertia values in ascending order (from smallest to largest): le, Ier, Ig and lut (b) Mer is the cracking moment. Choose the cross-section that should be used to compute Mcr. NA. h 5. Identify and circle the figure that represents the scenario in which the torsional effect is permitted to be reduced according to the ACI code provisions. (3 pts) mt mi B (b)arrow_forwardI will rate, thanksarrow_forward
- . 9. A reinforced concrete beam is subjected to V/ = 40 kips and Tu/ = 12 ft kips at the critical section. Given conditions: ⚫ Longitudinal reinforcements use No. 8 grade 60 steel with an effective depth d = 20 in. For shear capacity, V = 18 kips and V₂ = 22 kips • For transverse reinforcements, use No. 3 bars with grade 60. • The effective torsional area of A. = 150 in². • Crack angle = 45° ⚫ The minimum stirrup spacing is Smin = 4" and the maximum stirrup spacing is Smax = Find the required stirrup spacing at the critical section. 8".arrow_forward3. The beam shown on the right uses three No. 8 bars made of Grade 60 steel as longitudinal reinforcement. The allowable maximum center-to-center spacing of the longitudinal rebars has been determined to be 10 inches. Now assume that Grade 80 steel will be used instead. Determine whether the beam satisfies the rebar spacing requirements according to the ACI Code. Additional assumptions: • Estimate fs = fy • 20" Clear cover: ? 12" Clear side cover: 1.5" The clear cover depth cc and the clear side cover remain unchanged, regardless of the change in material.arrow_forward6. For the slender columns shown below: a) Determine the effective buckling length factor (k) for each column. b) Circle the column with the largest buckling capacity, assuming all columns have the same length (f) and the same flexural rigidity (E+I) k = (a) (b) (c) (d)arrow_forward
 Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Construction Materials, Methods and Techniques (M...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305086272Author:William P. Spence, Eva KultermannPublisher:Cengage Learning
Construction Materials, Methods and Techniques (M...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305086272Author:William P. Spence, Eva KultermannPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning




