
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The product formed by the reaction of Lewis acid
Concept introduction: Lewis acid accepts an electron pair. It acts as an electrophile as it is electron deficient. Lewis base donates an electron pair. It acts as a nucleophile as it is electron loving.
Answer to Problem 2.67P
The product formed by the reaction of
Explanation of Solution
In the given reaction, Lewis base
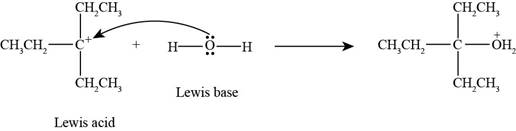
Figure 1
The product formed by the reaction of
(b)
Interpretation: The product formed by the reaction of Lewis acid
Concept introduction: Lewis acid accepts an electron pair. It acts as an electrophile as it is electron deficient. Lewis base donates an electron pair. It acts as a nucleophile as it is electron loving.
Answer to Problem 2.67P
The product formed by the reaction of
Explanation of Solution
In the given reaction, Lewis base
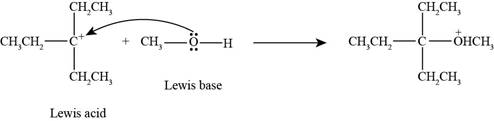
Figure 2
The product formed by the reaction of
(c)
Interpretation: The product formed by the reaction of Lewis acid
Concept introduction: Lewis acid accepts an electron pair. It acts as an electrophile as it is electron deficient. Lewis base donates an electron pair. It acts as a nucleophile as it is electron loving.
Answer to Problem 2.67P
The product formed by the reaction of
Explanation of Solution
In the given reaction, Lewis base
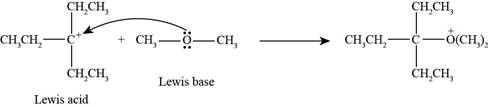
Figure 3
The product formed by the reaction of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Package: Loose Leaf for Organic Chemistry with Biological Topics with Connect Access Card
- A concentration cell consists of two Sn/Sn2+ half-cells. The cell has a potential of 0.10 V at 25 °C. What is the ratio of [Sn2+] (i.e., [Sn2+left-half] / [Sn2+right-half])?arrow_forwardElectrochemical cell potentials can be used to determine equilibrium constants that would be otherwise difficult to determine because concentrations are small. What is Κ for the following balanced reaction if E˚ = +0.0218 V? 3 Zn(s) + 2 Cr3+(aq) → 3 Zn2+(aq) + Cr(s) E˚ = +0.0218 Varrow_forwardConsider the following half-reactions: Hg2+(aq) + 2e– → Hg(l) E°red = +0.854 V Cu2+(aq) + 2e– → Cu(s)E°red = +0.337 V Ni2+(aq) + 2e– → Ni(s) E°red = -0.250 V Fe2+(aq) + 2e– → Fe(s) E°red = -0.440 V Zn2+(aq) + 2e– → Zn(s) E°red = -0.763 V What is the best oxidizing agent shown above (i.e., the substance that is most likely to be reduced)?arrow_forward
- Calculate the equilibrium constant, K, for MnO2(s) + 4 H+(aq) + Zn(s) → Mn2+(aq) + 2 H2O(l) + Zn2+(aq)arrow_forwardIn the drawing area below, draw the condensed structures of formic acid and ethyl formate. You can draw the two molecules in any arrangement you like, so long as they don't touch. Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. A C narrow_forwardWrite the complete common (not IUPAC) name of each molecule below. Note: if a molecule is one of a pair of enantiomers, be sure you start its name with D- or L- so we know which enantiomer it is. molecule Ο C=O common name (not the IUPAC name) H ☐ H3N CH₂OH 0- C=O H NH3 CH₂SH H3N ☐ ☐ X Garrow_forward
- (Part A) Provide structures of the FGI products and missing reagents (dashed box) 1 eq Na* H* H -H B1 B4 R1 H2 (gas) Lindlar's catalyst A1 Br2 MeOH H2 (gas) Lindlar's catalyst MeO. OMe C6H1402 B2 B3 A1 Product carbons' origins Draw a box around product C's that came from A1. Draw a dashed box around product C's that came from B1.arrow_forwardClassify each of the amino acids below. Note for advanced students: none of these amino acids are found in normal proteins. X CH2 H3N-CH-COOH3N-CH-COO- H3N-CH-COO CH2 CH3-C-CH3 CH2 NH3 N NH (Choose one) ▼ (Choose one) S CH2 OH (Choose one) ▼ + H3N-CH-COO¯ CH2 H3N CH COO H3N-CH-COO CH2 오오 CH CH3 CH2 + O C CH3 O= O_ (Choose one) (Choose one) ▼ (Choose one) Garrow_forwardAnother standard reference electrode is the standard calomel electrode: Hg2Cl2(s) (calomel) + 2e2 Hg() +2 Cl(aq) This electrode is usually constructed with saturated KCI to keep the Cl- concentration constant (similar to what we discussed with the Ag-AgCl electrode). Under these conditions the potential of this half-cell is 0.241 V. A measurement was taken by dipping a Cu wire and a saturated calomel electrode into a CuSO4 solution: saturated calomel electrode potentiometer copper wire CuSO4 a) Write the half reaction for the Cu electrode. b) Write the Nernst equation for the Cu electrode, which will include [Cu2+] c) If the voltage on the potentiometer reads 0.068 V, solve for [Cu²+].arrow_forward
- 2. (Part B). Identify a sequence of FGI that prepares the Synthesis Target 2,4-dimethoxy- pentane. All carbons in the Synthesis Target must start as carbons in either ethyne, propyne or methanol. Hint: use your analysis of Product carbons' origins (Part A) to identify possible structure(s) of a precursor that can be converted to the Synthesis Target using one FGI. All carbons in the Synthesis Target must start as carbons in one of the three compounds below. H = -H H = -Me ethyne propyne Synthesis Target 2,4-dimethoxypentane MeOH methanol OMe OMe MeO. OMe C₂H₁₂O₂ Product carbons' origins Draw a box around product C's that came from A1. Draw a dashed box around product C's that came from B1.arrow_forwardDraw the skeletal ("line") structure of the smallest organic molecule that produces potassium 3-hydroxypropanoate when reacted with KOH. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Sarrow_forwardDraw the skeleatal strucarrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





