
ANALYSIS+DESIGN OF LINEAR CIRCUITS(LL)
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781119235385
Author: Thomas
Publisher: WILEY
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 2, Problem 2.52P
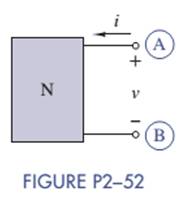
In Figure P2-52, the
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Question 3 AC Motor Drives [15]Calculate the instantaneous currents delivered by the inverter if the direct axiscurrent required at a particular instant is 8.66A and the quadrature current is5A. Derive all equations for the three currents.
A certain signal f(t) has the following PSD (assume 12 load):
Sp (w) = new + 8(w) - 1.5) + (w + 1.5)]
(a) What is the mean power in the bandwidth w≤2 rad/see?
(b) What is the mean power in the bandwidth -1.9 to 0.99 rad/sec?
Paress(w) dw
2ㅈ
-
(75 Marks)
JA signal (t) is bond
7)(t)(t) and f(t), are band-limited to 1.2 kHz each. These signals are to be
limited to 9.6 kHz, and three other signals
transmitted by means of time-division multiplexing.
Set up scheme for accomplishing this multiplexing requirement, with each signal sampled
at its Nyquist rate.
What must be the speed of the commutator (the output but ram-k bit/sec)?
the minimum band width?
(25 Marks)
Chapter 2 Solutions
ANALYSIS+DESIGN OF LINEAR CIRCUITS(LL)
Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.1PCh. 2 - The voltage across a particular resistor is 8.60 V...Ch. 2 - You can choose to connect either a 4.7-k resistor...Ch. 2 - A model railroader wants to be able to...Ch. 2 - A 100-k resistor dissipates 50mW. Find the current...Ch. 2 - The conductance of a particular semiconductor...Ch. 2 - In Figure P2—7 the resistor dissipates 25 mW. Find...Ch. 2 - In Figure P2—8 find Rx and the power supplied by...Ch. 2 - A resistor found in the lab has three orange...Ch. 2 - The iv characteristic of a nonlinear resistor is...
Ch. 2 - A 100-k resistor has a power rating of 0.25 W....Ch. 2 - A certain type of film resistor is available with...Ch. 2 - Figure P2—13 shows the circuit symbol for a class...Ch. 2 - A thermistor is a temperature-sensing element...Ch. 2 - In Figure P2-15i2=6A and i3=2A. Find i1 and i4.Ch. 2 - In Figure P2-16 determine which elements are in...Ch. 2 - For the circuit in Figure P2—17: Identify the...Ch. 2 - In Figure P2-17 i2=30mA and i4=20mA. Find i1 and...Ch. 2 - For the circuit in Figure P2—19: Identify the...Ch. 2 - In Figure P2-19 v2=20V,v3=20V, and v4=6V. Find...Ch. 2 - In many circuits the ground is often the metal...Ch. 2 - The circuit in figure P2-22 is organized around...Ch. 2 - Are any of the elements in Figure P2-23 in series...Ch. 2 - Are any of the elements in Figure P2-24 in series...Ch. 2 - Use the passive sign convention to assign voltage...Ch. 2 - If a wire is connected between nodes B and C in...Ch. 2 - The KCL equations for a three-node circuit are as...Ch. 2 - For the circuit in Figure P2—28, write a complete...Ch. 2 - For the circuit in Figure P2—29, write a complete...Ch. 2 - Find vx and ix in Figure P2-30. Compare the...Ch. 2 - A modeler wants to light his model building using...Ch. 2 - Find vx and ix in Figure P2-32.Ch. 2 - In Figure P2-33: Assign a voltage and current...Ch. 2 - Find vO in the circuit of Figure P2-34.Ch. 2 - Find the power provided by the source in Figure...Ch. 2 - Figure P2-36 shows a subcircuit connected to the...Ch. 2 - In Figure P2-37 ix=0.33mA. Find the value of R.Ch. 2 - Figure P2—38 shows a resistor with one terminal...Ch. 2 - Find the equivalent resistant REQ in Figure P2-39.Ch. 2 - Find the equivalent R EQ in Figure P2-40.Ch. 2 - Find the equivalent resistance REQ in Figure...Ch. 2 - Equivalent resistance is defined at a particular...Ch. 2 - Find REQ in Figure P2—43 when the switch is open....Ch. 2 - Find REQ between nodes A and B for each of the...Ch. 2 - Show how the circuit in Figure P2—45 could be...Ch. 2 - In Figure P2-46 find the equivalent resistance...Ch. 2 - In Figure P2-47 find the equivalent resistance...Ch. 2 - Select a value of RL in Figure P2-48 so that...Ch. 2 - Using no more than four 1-k resistors, show how...Ch. 2 - Do a source transformation at terminals A and B...Ch. 2 - For each of the circuits in Figure P2-51, find the...Ch. 2 - In Figure P2-52, the iv characteristic of network...Ch. 2 - Select the value of Rx in Figure P2-53 so that...Ch. 2 - Two 10-k potentiometers (a variable resistor whose...Ch. 2 - Select the value of R in Figure P2-55 so that...Ch. 2 - What is the range of REQ in Figure P2-56?Ch. 2 - Find the equivalent resistance between terminals A...Ch. 2 - Use voltage division in Figure P2-58 to find...Ch. 2 - Use voltage division in Figure P2-59 to obtain an...Ch. 2 - Use current division in Figure P2-60 to find...Ch. 2 - Use current division in Figure P2-61 to find an...Ch. 2 - Find ix,iy, and iz in Figure P2-62.Ch. 2 - Find vO in the circuit of Figure P2-63.Ch. 2 - You wish to drive a 1-k load from your car battery...Ch. 2 - Find the range of values of vo in Figure P2-65.Ch. 2 - Use current division in the circuit of Figure...Ch. 2 - Figure P2-67 shows a voltage bridge circuit, that...Ch. 2 - A Ideally, a voltmeter has infinite internal...Ch. 2 - Select values for R1,R2, and R3 in Figure P2-69 so...Ch. 2 - Select a value of Rx in Figure P2-70 so that...Ch. 2 - Select a value of Rx in Figure P2-71 so that...Ch. 2 - Use circuit reduction to find vx and ix in Figure...Ch. 2 - Use circuit reduction to find vx,ix, and px in...Ch. 2 - Use circuit reduction to find vx and ix in Figure...Ch. 2 - Use circuit reduction to find vx,ix, and px in...Ch. 2 - Use circuit reduction to find vx and ix in Figure...Ch. 2 - Use source transformation to find ix in Figure...Ch. 2 - Select a value for Rx so that ix=0A in Figure...Ch. 2 - Use source transformations in Figure P2-79 to...Ch. 2 - The current through RL in figure P2-80 is 100mA....Ch. 2 - Select Rx so that 50 V is across it in Figure...Ch. 2 - The box in the circuit in Figure P2-82 is a...Ch. 2 - A circuit is found to have the following element...Ch. 2 - Consider the circuit of Figure P2-88. Use MATLAB...Ch. 2 - Nonlinear Device Characteristics The circuit in...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.92IPCh. 2 - Center Tapped Voltage Divider Figure P2-93 shows a...Ch. 2 - Active Transducer Figure P2-95 shows an active...Ch. 2 - Programmable Voltage Divider Figure P2-97 shows a...Ch. 2 - Analog Voltmeter Design Figure P2-98(a) shows a...Ch. 2 - MATLAB Function for Parallel Equivalent Resistors...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Draw the digital modulation outputs, ASK Amplitude Shift Keying) FSK (Frequency Shift Keying) and PSK (Phase Shift Keying). For baseband and carriet frequency as shown 101 wwwwwwwwwwww 010 BASESAND basband CARRIER Carralarrow_forwardplease show full working. I've included the solutionarrow_forwardcan you please show working and steps. The answer is 8kohms.arrow_forward
- PSD A certain signal f(t) has the following PSD (assume 12 load): | Sƒ(w) = π[e¯\w\ + 8(w − 2) + +8(w + 2)] (a) What is the mean power in the bandwidth w≤ 1 rad/sec? (b) What is the mean power in the bandwidth 0.99 to 1.01 rad/sec? (c) What is the mean power in the bandwidth 1.99 to 2.01 rad/sec? (d) What is the total mean power in (t)? Pav= + 2T SfLw) dw - SALW)arrow_forwardAn AM modulation waveform signal:- p(t)=(8+4 cos 1000πt + 4 cos 2000πt) cos 10000nt (a) Sketch the amplitude spectrum of p(t). (b) Find total power, sideband power and power efficiency. (c) Find the average power containing of each sideband.arrow_forwardCan you rewrite the solution because it is unclear? AM (+) = 8(1+ 0.5 cos 1000kt +0.5 ros 2000ks) = cos 10000 πt. 8 cos wat + 4 cos wit + 4 cos Wat coswet. -Jet jooort J11000 t = 4 e jqooort jgoort +4e + e +e j 12000rt. 12000 kt + e +e jooxt igoo t te (w) = 8ES(W- 100007) + 8IS (W-10000) USBarrow_forward
- Can you rewrite the solution because it is unclear? AM (+) = 8(1+0.5 cos 1000kt +0.5 ros 2000 thts) = cos 10000 πt. 8 cos wat + 4 cos wit + 4 cos Wat coswet. J4000 t j11000rt $14+) = 45 jqooort +4e + e + e j 12000rt. 12000 kt + e +e +e Le jsoort -; goon t te +e Dcw> = 885(W- 100007) + 8 IS (W-10000) - USBarrow_forwardCan you rewrite the solution because it is unclear? Q2 AM ①(+) = 8 (1+0.5 cos 1000πt +0.5 ros 2000kt) $4+) = 45 = *cos 10000 πt. 8 cos wat + 4 cosat + 4 cos Wat coswet. j1000016 +4e -j10000πt j11000Rt j gooort -j 9000 πt + e +e j sooort te +e J11000 t + e te j 12000rt. -J12000 kt + с = 8th S(W- 100007) + 8 IS (W-10000) <&(w) = USB -5-5 -4-5-4 b) Pc 2² = 64 PSB = 42 + 4 2 Pt Pc+ PSB = y = Pe c) Puss = PLSB = = 32 4² = 8 w 32+ 8 = × 100% = 140 (1)³×2×2 31 = 20% x 2 = 3w 302 USB 4.5 5 5.6 6 ms Ac = 4 mi = 0.5 mz Ac = 4 ५ M2 = =0.5arrow_forwardA. Draw the waveform for the following binary sequence using Bipolar RZ, Bipolar NRZ, and Manchester code. Data sequence= (00110100) B. In a binary PCM system, the output signal-to-quantization ratio is to be hold to a minimum of 50 dB. If the message is a single tone with fm-5 kHz. Determine: 1) The number of required levels, and the corresponding output signal-to-quantizing noise ratio. 2) Minimum required system bandwidth.arrow_forward
- Find Io using Mesh analysisarrow_forwardFM station of 100 MHz carrier frequency modulated by a 20 kHz sinusoid with an amplitude of 10 volt, so that the peak frequency deviation is 25 kHz determine: 1) The BW of the FM signal. 2) The approximated BW if the modulating signal amplitude is increased to 50 volt. 3) The approximated BW if the modulating signal frequency is increased by 70%. 4) The amplitude of the modulating signal if the BW is 65 kHz.arrow_forwardAn FDM is used to multiplex two groups of signals using AM-SSB, the first group contains 25 speech signals, each has maximum frequency of 4 kHz, the second group contains 15 music signals, each has maximum frequency of 10 kHz. A guard bandwidth of 500 Hz is used bety each two signals and before the first one. 1. Find the BWmultiplexing 2. Find the BWtransmission if the multiplexing signal is modulated using AM-DSB-LC.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Norton's Theorem and Thevenin's Theorem - Electrical Circuit Analysis; Author: The Organic Chemistry Tutor;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-kkvqr1wSwA;License: Standard Youtube License