
Pipe 2 has been inserted snugly into Pipe I. but the holes Tor a connecting pin do not line up; there is a gap s. The user decides to apply either force P:lo Pipe I or force P-, to Pipe 2, whichever is smaller. Determine the following using the numerical properties in the box.
(a) If only P{is applied, find Pt{tips} required to close gap s; if a pin is then inserted and Ptremoved, what are reaction forces RAand RBfor this load case?
(b) If only P2is applied, find P2{kips) required to close gap a; if a pin is inserted and P2removed, what are reaction forces R^ and RBfor this load case?
(c) What is the maximum shear stress in the pipes, for the loads in parts (a) and (b)?
(d) If a temperature increase IT is to be applied to the entire structure to close gaps{instead of applying forces Ptand P2), find the AT required to close the gap. If a pin is inserted after the gaphas closed, what are reaction forces .''.', and RBfor this case? (e) Finally, if the structure (with pin inserted) then cools to the original ambient temperature, what are reaction forces Rtand P 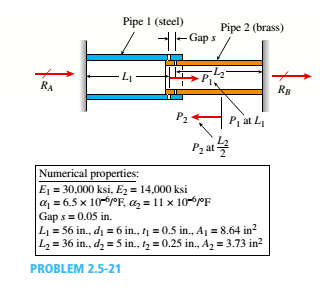
(a)
The reactions at A and B.
Answer to Problem 2.5.21P
The reaction at A is =
The reaction at B is =
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The gap between the pipes is
Write the expression for elongation in pipe 1.
Here, length of pipe 1 is
Write the expression for elongation at point B.
Here, elongation at point B is
Write the expression for net elongation at B.
Here, elongation at point 1 is
Substitute
Write the reaction at point A.
Here, reaction at A is
Calculation:
Substitute
The force required to close the gap is
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
The reaction at A is
The reaction at B is
(b)
The reaction at A is
The reaction at B is
Answer to Problem 2.5.21P
The reaction at A is
The reaction at B is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The gap between the pipes is
Write the expression for force applied at pipe 2.
Here, force applied at pipe 2 is
Calculation:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
The reaction at A is
The reaction at B is
(b)
The maximum shear stress in pipe 1 and pipe 2.
.
Answer to Problem 2.5.21P
The maximum shear stress in pipe 1 is
The maximum shear stress in pipe 2 is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The gap between the pipes is
Write the expression for maximum shear stress in pipe 1.
Here, maximum shear stress in pipe 1 is
Write the expression for maximum shear stress in pipe.
Here, maximum shear stress in pipe 2 is
Calculation:
Substitute
The maximum shear stress in pipe 1 is =
Substitute
Conclusion:
The maximum shear stress in pipe 1 is =
The maximum shear stress in pipe 2 is =
(d)
The rise in temperature required to close the gap.
The reactions.
Answer to Problem 2.5.21P
The rise in temperature required to close the gap is
The reactions are
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The gap between the pipes is
Write the expression for temperature raise.
Here, raise in temperature is
Calculation:
Substitute
Since the temperature remains constant, so the reactions are zero.
Conclusion:
The temperature raise required to close the gap is
The reactions are
(e)
The reaction at A.
The reaction at B.
Answer to Problem 2.5.21P
The reaction at A is
The reaction at B is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The gap between the pipes is
Calculation:
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
The reaction at A is =
The reaction at B is =
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Bundle: Mechanics Of Materials, Loose-leaf Version, 9th + Mindtap Engineering, 1 Term (6 Months) Printed Access Card
- Calculate for the vertical cross section moment of inertia for both Orientations 1 and 2 of a 1 x 1.5 in. horizontal hollow rectangular beam with wall thickness of t = 0.0625 in. Use the equation: I = ((bh^3)/12) - (((b-2t)(h-2t)^3)/12)arrow_forwardPlease answer 'yes' or 'no' and 'is' or 'is not' for the following:arrow_forwardConsider a large 23-cm-thick stainless steel plate (k = 15.1 W/m-K) in which heat is generated uniformly at a rate of 5 x 105 W/m³. Both sides of the plate are exposed to an environment at 30°C with a heat transfer coefficient of 60 W/m²K. The highest temperature will occur at surfaces of plate while the lowest temperature will occur at the midplane. Yes or No Yes Noarrow_forward
- My answers are incorrectarrow_forwardPicturearrow_forwardWhat is the weight of a 5-kg substance in N, kN, kg·m/s², kgf, Ibm-ft/s², and lbf? The weight of a 5-kg substance in N is 49.05 N. The weight of a 5-kg substance in kN is KN. The weight of a 5-kg substance in kg·m/s² is 49.05 kg-m/s². The weight of a 5-kg substance in kgf is 5.0 kgf. The weight of a 5-kg substance in Ibm-ft/s² is 11.02 lbm-ft/s². The weight of a 5-kg substance in lbf is 11.023 lbf.arrow_forward
- Mych CD 36280 kg. 0.36 givens Tesla truck frailer 2017 Model Vven 96154kph ronge 804,5km Cr Powertrain Across PHVAC rwheel 0.006 0.88 9M² 2 2kW 0.55M ng Zg Prated Trated Pair 20 0.95 1080 kW 1760 Nm 1,2 determine the battery energy required to meet the range when fully loaded determine the approximate time for the fully-loaded truck-trailor to accelerate from 0 to 60 mph while Ignoring vehicle load forcesarrow_forward12-217. The block B is sus- pended from a cable that is at- tached to the block at E, wraps around three pulleys, and is tied to the back of a truck. If the truck starts from rest when ID is zero, and moves forward with a constant acceleration of ap = 0.5 m/s², determine the speed of the block at D the instant x = 2 m. Neglect the size of the pulleys in the calcu- lation. When xƊ = 0, yc = 5 m, so that points C and D are at the Prob. 12-217 5 m yc =2M Xparrow_forwardsolve both and show matlab code auto controlsarrow_forward
- 12-82. The roller coaster car trav- els down the helical path at con- stant speed such that the paramet- ric equations that define its posi- tion are x = c sin kt, y = c cos kt, z = h - bt, where c, h, and b are constants. Determine the mag- nitudes of its velocity and accelera- tion. Prob. 12-82 Narrow_forwardGiven: = refueling Powertran SOURCE EMISSIONS vehide eff eff gasoline 266g co₂/kwh- HEV 0.90 0.285 FLgrid 411ilg Co₂/kWh 41111gCo₂/kWh EV 0.85 0.80 Production 11x10% og CO₂ 13.7 x 10°g CO₂ A) Calculate the breakeven pont (in km driven) for a EV against on HEV in Florida of 0.1kWh/kM Use a drive cycle conversion 5) How efficient would the powertrain of the HEV in this example have to be to break even with an EV in Florida after 150,000 Miles of service (240,000) km Is it plausible to achieve the answer from pert b Consideans the HaXINERY theoretical efficiency of the Carnot cycle is 5020 and there are additional losses of the transMISSION :- 90% efficiency ? c A what do you conclude is the leading factor in why EVs are less emissive than ICE,arrow_forwardsolve autocontrolsarrow_forward
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
