
Concept explainers
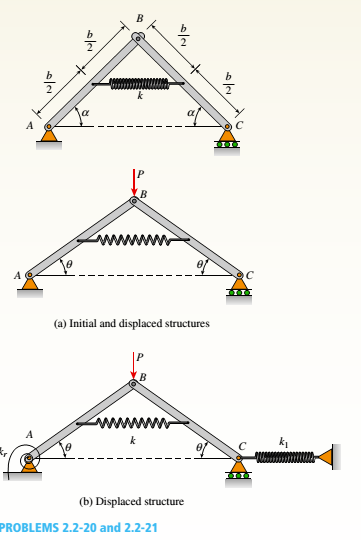
A framework ABC consists of two rigid bars AB and BC. Each having a length b (see the first part of the figure part a). The bars have pin connections at A, B, and C and are joined by a spring of stiffness k. The spring is attached at the midpoints of the bars. The framework has a pin support at A and a roller support al C, and the bars are at an angle a to the horizontal.
When a vertical load P is applied at joint B (see the second part of the figure part a.) the roller support C moves to the right, the spring is stretched, and the angle of the bars decreases from a to the angle ??.
(a) Determine the angle 0 and the increase S in the distance between points A and C. Also find reactions at A and C. (Use the following data: b = 200 mm. ft = 3.2 kN/m. a = 45°. and
P = 50 N.)
(b) Repeat part (a) if a translational spring kt= kll is added at C and a rotational spring kr= kb-l2 is added at A (see figure pan b).
(a)
The angle
Answer to Problem 2.2.20P
The angle
The distance between points A and C,
The reaction at support C
The reaction at support A
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The length of the rigid bars b = 200 mm
The stiffness of the spring k = 3.2 kN/m
The angle of bars from the horizontal =
The valueof load P = 50 N
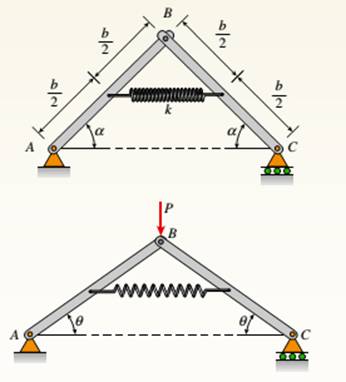
Figure: Initial and displaced positions of the framework.
Calculation:
Let us consider the structure in its displaced position. Let us use the free body diagrams of left-hand bars and right-hand bars.
From the free body diagram of left-hand bar,
Reaction at support A,
From the free body diagram of right-hand bar,
From overall FBD of the beams,
We have two expressions for Rc, equating both of the expressions and then substitute expressions for L2, kr, k1, h and
Now,
Let us substitute the numerical values of variables and calculate the values of angle
Solving the above equation gives,
Now, let us compute the reactions at point C and A.
The reaction at point C
And the reaction at point A is
Conclusion: Thus, the angle
The distance between points A and C,
The reaction at support C
The reaction at support A
(b)
The angle
Answer to Problem 2.2.20P
The angle
The distance between points A and C,
The reaction at support C
The reaction at support A
The moment reaction at point A is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The length of the rigid bars b = 200 mm
The stiffness of the spring k = 3.2 kN/m
The angle of bars from the horizontal =
The value of load P = 50 N
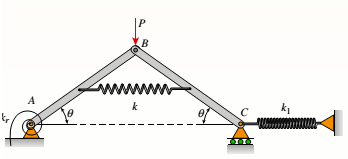
Figure: Initial and displaced positions of the framework.
Calculation:
Let us consider the structure in its displaced position. Let us use the free body diagrams of left-hand bars and right-hand bars.
From the free body diagram of left-hand bar,
Reaction at support A,
From the free body diagram of right-hand bar,
From overall FBD of the beams,
We have two expressions for Rc, equating both of the expressions and then substitute expressions for L2, kr, k1, h and
Now,
Let us substitute the numerical values of variables and calculate the values of angle
Solving the above equation gives,
Now, let us compute the reactions at point C and A.
The reaction at point C,
And the reaction at point A is
Now, moment reaction at point A is,
Conclusion: Thus, the angle
The distance between points A and C,
The reaction at support C
The reaction at support A
The moment reaction at point A is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Bundle: Mechanics Of Materials, Loose-leaf Version, 9th + Mindtap Engineering, 1 Term (6 Months) Printed Access Card
- +1. 0,63 fin r= 0.051 P The stepped rod in sketch is subjected to a tensile force that varies between 4000 and 7000 lb. The rod has a machined surface finish everywhere except the shoulder area, where a grinding operation has been performed to improve the fatigue resistance of the rod. Using a 99% probability of survival, determine the safety factor for infinite life if the rod is made of AISI 1080 steel, quenched and tempered at 800°c Use the Goodman line. Does the part fail at the fillet? Explainarrow_forwardSolve this problem and show all of the workarrow_forwardSolve this problem and show all of the workarrow_forward
- Qu. 17 Compute linear density values for [100] for silver (Ag). Express your answer in nm''. . Round off the answer to three significant figures. Qu. 18 Compute linear density value for [111] direction for silver (Ag). Express your answer in nm'. Round off the answer to three significant figures. Qu. 19 Compute planar density value for (100) plane for chromium (Cr). Express your answer in nm?. Round off the answer to two significant figures. Qu. 20 Compute planar density value for (110) plane for chromium (Cr). Express your answer in nm ≥ to four significant figures. show all work please in material engineeringarrow_forward3-142arrow_forwardI need solutionsarrow_forward
- 3-137arrow_forwardLarge wind turbines with a power capacity of 8 MW and blade span diameters of over 160 m areavailable for electric power generation. Consider a wind turbine with a blade span diameter of 120m installed at a site subjected to steady winds at 8.25 m/s. Taking the overall efficiency of thewind turbine to be 33 percent and the air density to be 1.25 kg/m3, determine the electric powergenerated by this wind turbine. Also, assuming steady winds of 8.25 m/s during a 24-h period,determine the amount of electric energy and the revenue generated per day for a unit price of$0.08/kWh for electricity.arrow_forwardThe basic barometer can be used to measure the height of a building. If the barometric readingsat the top and at the bottom of a building are 672 and 696 mmHg, respectively, determine theheight of the building. Take the densities of air and mercury to be 1.18 kg/m3 and 13,600 kg/m3,respectivelyarrow_forward
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
