
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The conjugate base of given acid is to be stated.
Concept introduction: An acid is a substance that is capable to donate a
Answer to Problem 2.36P
The conjugate base of given acid is
Explanation of Solution
The given acid is
An acid is a substance that is capable to donate a
Thus, the
Hence, the conjugate base of given acid is
The conjugate base of given acid is
(b)
Interpretation: The conjugate base of given acid is to be stated.
Concept introduction: An acid is a substance that is capable to donate a
Answer to Problem 2.36P
The conjugate base of given acid is
Explanation of Solution
The given acid is
An acid is a substance that is capable to donate a
Thus, the
Hence, the conjugate base of given acid is
The conjugate base of given acid is
(c)
Interpretation: The conjugate base of given acid is to be stated.
Concept introduction: An acid is a substance that is capable to donate a
Answer to Problem 2.36P
The conjugate base of given acid is
Explanation of Solution
The given acid is
An acid is a substance that is capable to donate a
Thus, the
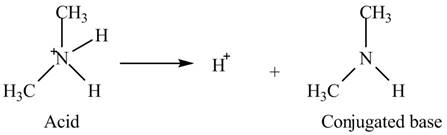
Figure 1
Hence, the conjugate base of given acid is
The conjugate base of given acid is
(d)
Interpretation: The conjugate base of given acid is to be stated.
Concept introduction: An acid is a substance that is capable to donate an
Answer to Problem 2.36P
The conjugate base of given acid is
Explanation of Solution
The given acid is
An acid is a substance that is capable to donate a
Thus, the
Hence, the conjugate base of given acid is
The conjugate base of given acid is
(e)
Interpretation: The conjugate base of given acid is to be stated.
Concept introduction: An acid is a substance that is capable to donate a
Answer to Problem 2.36P
The conjugate base of given acid ispropionate ion.
Explanation of Solution
The given acid is propionic acid.
An acid is a substance that is capable to donate a
Thus, the
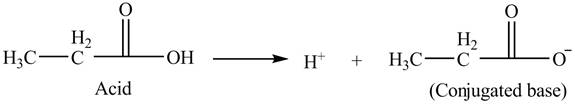
Figure 2
Hence, the conjugate base of given acid is propionate.
The conjugate base of given acid is shown in figure 2.
(f)
Interpretation: The conjugate base of given acid is to be stated.
Concept introduction: An acid is a substance that is capable to donate a
Answer to Problem 2.36P
The conjugate base of given acid is
Explanation of Solution
The given acid is
The given acid is ethynylcyclohexane.
An acid is a substance that is capable to donate a
Thus, the
Hence, the conjugate base of given acid is
The conjugate base of given acid is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- For benzene, the ∆H° of vaporization is 30.72 kJ/mol and the ∆S° of vaporization is 86.97 J/mol・K. At 1.00 atm and 228.0 K, what is the ∆G° of vaporization for benzene, in kJ/mol?arrow_forwardThe reaction Q(g) + R(g) → Z(l) is shown to be exothermic. Which of the following is true concerning the reaction. it is spontaneous only at High T, it is spontaneous at low T it is nonspontaneous at all T it is spontanrous at all T. it is non spontaneous only at low T.arrow_forwardThe reaction Q(g) + R(g) → Z(l) is shown to be exothermic. Which of the following is true concerning the reactionarrow_forward
- Which of the following has the largest standard molar entropy, S° (298.15 K) He H2 NaCl KBr Hgarrow_forwardWhich of the following is true for a particular reaction if ∆G° is -40.0 kJ/mol at 290 K and –20.0 kJ/mol at 390 K?arrow_forwardWhat is the major product of the following reaction? O O OH OH 1. BH 2. H₂O₂, NaOH OH OHarrow_forward
- How many products are possible from the following reaction? Do not take into account stereoisomers. 01 04 03 O O O O 02 CH H₂SO4 heatarrow_forwardplease helparrow_forwardChoose the major product of the reaction with correct regio- and stereochemistry. Br2 H₂O O "Br Br & O 'Br OH Br 吡 O OH OH Br "OH Brarrow_forward
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning





