
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
Molecular geometry and electron geometry about each non-hydrogen atom in the given molecule is to be predicted using VSEPR theory.
Concept introduction:
Electron geometry and molecular geometry of molecules are determined by using Valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory. According to VSEPR theory, electron geometry describes the orientation of the electron groups about a particular atom and molecular geometry describes the arrangement of atoms about a particular atom.
The number of electron pairs describes the electron and molecular geometry. If all the electron pairs are bonds, then the molecular geometry is the same as the electron geometry. Electron geometry is different from molecular geometry if some electron groups are present as lone pairs. The bond angle depends on the electron geometry around the atom.
Electron geometry and molecular geometry from the number of electron pairs and bond angle according to VSEPR theory are as follows:
| Number of Electron Groups |
Number of Bonds |
Number of Lone Pairs |
Bond Angle (o) |
Electron Geometry | Molecular Geometry |
| 2 | 2 | 0 | 180 | Linear | Linear |
| 3 | 3 | 0 | 120 | Trigonal planar | Trigonal planer |
| 3 | 2 | 1 | 120 | Trigonal planar | Bent |
| 4 | 4 | 0 | 109.5 | Tetrahedral | Tetrahedral |
| 4 | 4 | 0 | 180 | Linear | Linear |
| 4 | 2 | 2 | 109.5 | Tetrahedral | Bent |
Answer to Problem 2.2P
According to VSEPR theory, the electron and molecular geometry about each of the non-hydrogen atom in the structure is as follows:
Oxygen = Electron geometry is tetrahedral while molecular geometry is bent.
C1 carbon atom = Electron geometry is tetrahedral while molecular geometry is also tetrahedral.
C2 and C3 carbon atoms = Electron geometry is linear while molecular geometry is also linear.
Explanation of Solution
The given structure for
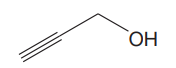
The structure showing all the atoms and lone pairs is:
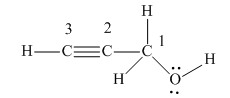
There are four non-hydrogen atoms in the above structure. They are numbered from 1 to 4.
There are four groups of electrons around the oxygen atom: two lone pairs of electrons and two single bonds. According to VSEPR theory, its electron geometry is tetrahedral, and its molecular geometry is bent.
There are four groups of electrons around the C1 carbon: four single bonds and no lone pairs of electrons. According to VSEPR theory, its electron geometry is tetrahedral, and its molecular geometry is also tetrahedral.
There are two groups of electrons around the C2 carbon: one triple bond, and one single bond, and no lone pairs of electrons. According to VSEPR theory, its electron geometry is linear, and its molecular geometry is also linear.
There are two groups of electrons around the C3 carbon: one triple bond, one single bond, and no lone pairs of electrons. According to VSEPR theory, its electron geometry is linear, and its molecular geometry is also linear.
The electron geometry and molecular geometry about each non-hydrogen atom in the given molecule is predicted on the basis of VSEPR chart.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles And Mechanisms
- How many chiral centers are there in the following molecule? HO 0 1 ○ 2 ♡ 4 'N'arrow_forwardThe following chemical structure represents a molecule of what molecular formula?arrow_forwardWhich region(s) of the following phospholipid is/are hydrophobic? RO I hydro-water phobic-dislikes = Hydrophobic dislikes water ○ I only Il only I and III only II and IV only O II, III, and IV only III || IVarrow_forward
- Given the following data, determine the order of the reaction with respect to H2. H2(g) + 21Cl(g) → I2(g) + 2HCl(g) Experiment [H2] (torr) [ICI] (torr) Rate (M/s) 1 250 325 0.266 2 250 81 0.0665 3 50 325 0.266arrow_forwardWhich one of the following molecules is chiral? H- NH₂ H3C དང་།་ OH H HO H₂N HO- -H CHO -OH H HO- OH H- -H CH₂OH OHarrow_forwardThe structure of an unsaturated phospholipid is shown below. Which region of the molecule is most hydrophilic ? H₂N-CH₂ H₂C IV CH3 CH3 hydro-water philic-likes = Hydrophilic likes water ○ IV All regions are equally hydrophilic. IIIarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





