
For each IUPAC name, draw the corresponding structural formula and line-angle formula.
- (a) Ethanol
- (b) Butanal
- (c) Butanoic acid
- (d) Ethanoic acid
- (e) Heptanoic acid
- (f) Propanoic acid
- (g) Octanal
- (h) Cyclopentene
- (i) Cyclopentanol
- (j) Cyclopentanone
- (k) Cyclohexanol
- (l) Propanone
(a)
Interpretation:
For the given IUPAC name, the corresponding structural formula and line–angle formula has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Condensed structural formula:
Structural formula in which grouping of atoms are done and in which the central atoms along with the other atoms are connected to them are treated as group is known as Condensed structural formula.
Line–angle formula:
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula. This is a shorthand representation of an organic molecule with lines which represents its molecular bonding. In line–angle formula, hydrogen atoms are not shown.
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Ethanol
Structural formula and line–angle formula:
From the name it is known that the compound has two carbon atoms. The name ends with suffix –ol which indicates that there will be an alcoholic
The structural formula and line–angle formula for ethanol is drawn below.

(b)
Interpretation:
For the given IUPAC name, the corresponding structural formula and line–angle formula has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Condensed structural formula:
Structural formula in which grouping of atoms are done and in which the central atoms along with the other atoms are connected to them are treated as group is known as Condensed structural formula.
Line–angle formula:
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula. This is a shorthand representation of an organic molecule with lines which represents its molecular bonding. In line–angle formula, hydrogen atoms are not shown.
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Butanal
Structural formula and line–angle formula:
From the name it is known that the compound has four carbon atoms. The name ends with suffix –al which indicates that there will be an aldehyde
The structural formula and line–angle formula for Butanal is drawn below.
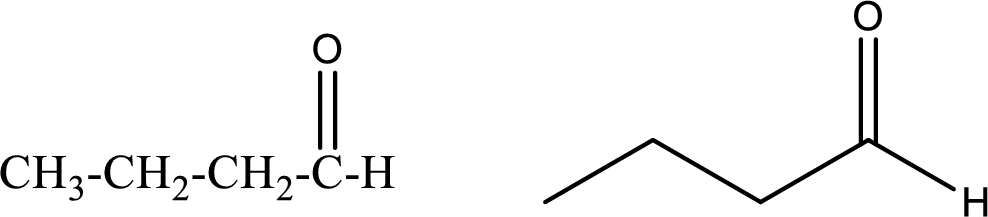
(c)
Interpretation:
For the given IUPAC name, the corresponding structural formula and line–angle formula has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Condensed structural formula:
Structural formula in which grouping of atoms are done and in which the central atoms along with the other atoms are connected to them are treated as group is known as Condensed structural formula.
Line–angle formula:
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula. This is a shorthand representation of an organic molecule with lines which represents its molecular bonding. In line–angle formula, hydrogen atoms are not shown.
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
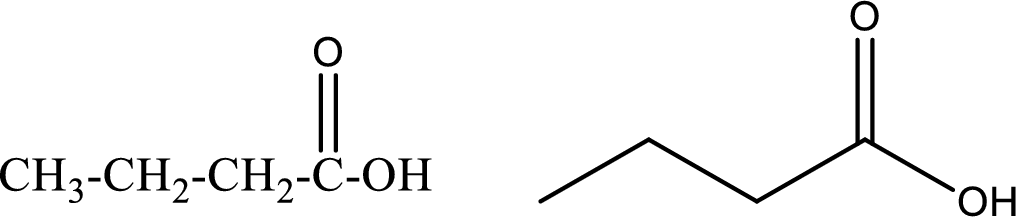
Butanoic acid
Structural formula and line–angle formula:
From the name it is known that the compound has four carbon atoms. The name ends with suffix –oic acid which indicates that there will be an acid
The structural formula and line–angle formula for butanoic acid is drawn below.
(d)
Interpretation:
For the given IUPAC name, the corresponding structural formula and line–angle formula has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Condensed structural formula:
Structural formula in which grouping of atoms are done and in which the central atoms along with the other atoms are connected to them are treated as group is known as Condensed structural formula.
Line–angle formula:
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula. This is a shorthand representation of an organic molecule with lines which represents its molecular bonding. In line–angle formula, hydrogen atoms are not shown.
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Ethanoic acid
Structural formula and line–angle formula:
From the name it is known that the compound has two carbon atoms. The name ends with suffix –oic acid which indicates that there will be an acid
The structural formula and line–angle formula for ethanoic acid is drawn below.
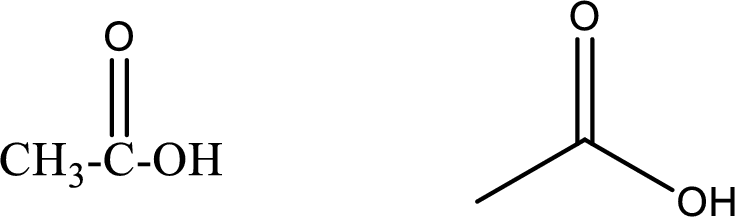
(e)
Interpretation:
For the given IUPAC name, the corresponding structural formula and line–angle formula has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Condensed structural formula:
Structural formula in which grouping of atoms are done and in which the central atoms along with the other atoms are connected to them are treated as group is known as Condensed structural formula.
Line–angle formula:
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula. This is a shorthand representation of an organic molecule with lines which represents its molecular bonding. In line–angle formula, hydrogen atoms are not shown.
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
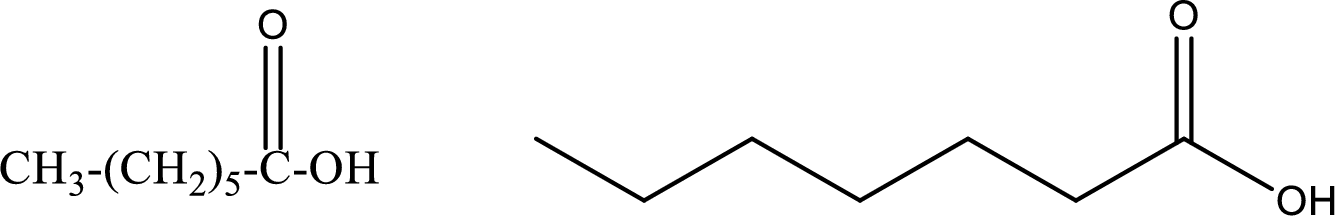
Heptanoic acid
Structural formula and line–angle formula:
From the name it is known that the compound has seven carbon atoms. The name ends with suffix –oic acid which indicates that there will be an acid
The structural formula and line–angle formula for Heptanoic acid is drawn below.
(f)
Interpretation:
For the given IUPAC name, the corresponding structural formula and line–angle formula has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Condensed structural formula:
Structural formula in which grouping of atoms are done and in which the central atoms along with the other atoms are connected to them are treated as group is known as Condensed structural formula.
Line–angle formula:
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula. This is a shorthand representation of an organic molecule with lines which represents its molecular bonding. In line–angle formula, hydrogen atoms are not shown.
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Propanoic acid
Structural formula and line–angle formula:
From the name it is known that the longest chain has three carbon atoms. The name ends with suffix –oic acid which indicates that there will be an acid
The structural formula and line–angle formula for Propanoic acid is drawn below.
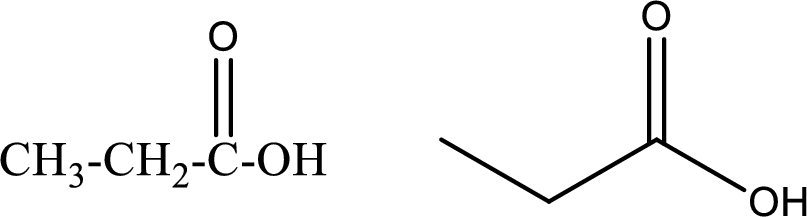
(g)
Interpretation:
For the given IUPAC name, the corresponding structural formula and line–angle formula has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Condensed structural formula:
Structural formula in which grouping of atoms are done and in which the central atoms along with the other atoms are connected to them are treated as group is known as Condensed structural formula.
Line–angle formula:
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula. This is a shorthand representation of an organic molecule with lines which represents its molecular bonding. In line–angle formula, hydrogen atoms are not shown.
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
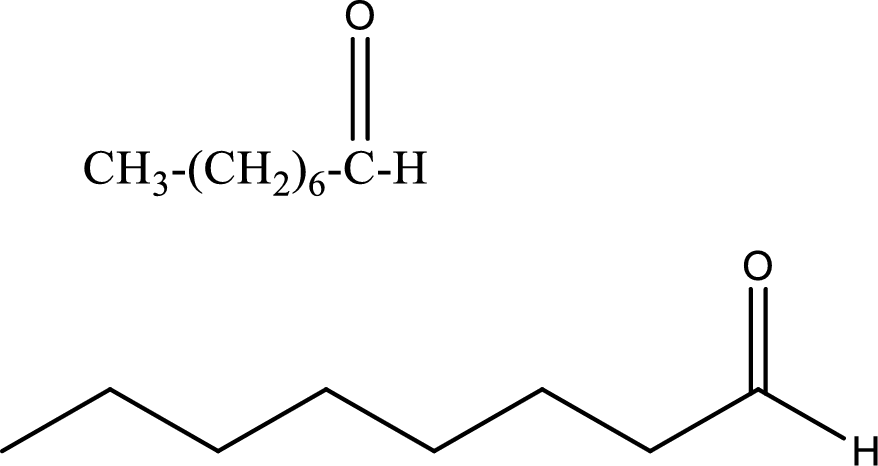
Octanal
Structural formula and line–angle formula:
From the name it is known that the longest chain has eight carbon atoms. The name ends with suffix –al which indicates that there will be an aldehyde group in the compound.
The structural formula and line–angle formula for Octanal is drawn below.
(h)
Interpretation:
For the given IUPAC name, the corresponding structural formula and line–angle formula has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Condensed structural formula:
Structural formula in which grouping of atoms are done and in which the central atoms along with the other atoms are connected to them are treated as group is known as Condensed structural formula.
Line–angle formula:
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula. This is a shorthand representation of an organic molecule with lines which represents its molecular bonding. In line–angle formula, hydrogen atoms are not shown.
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
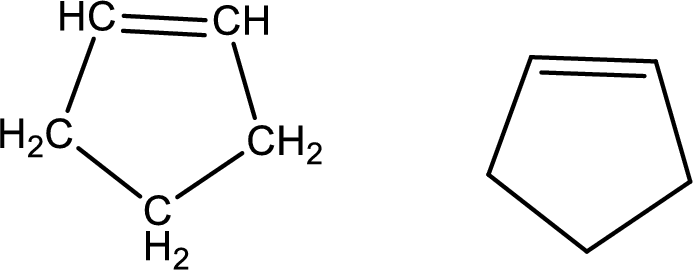
Cyclopentene
Structural formula and line–angle formula:
From the name it is known main core of the compound has a five membered cyclic ring. The name ends with suffix –ene which indicates that there will a double in the ring structure.
The structural formula and line–angle formula for Cyclopentene is drawn below.
(i)
Interpretation:
For the given IUPAC name, the corresponding structural formula and line–angle formula has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Condensed structural formula:
Structural formula in which grouping of atoms are done and in which the central atoms along with the other atoms are connected to them are treated as group is known as Condensed structural formula.
Line–angle formula:
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula. This is a shorthand representation of an organic molecule with lines which represents its molecular bonding. In line–angle formula, hydrogen atoms are not shown.
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
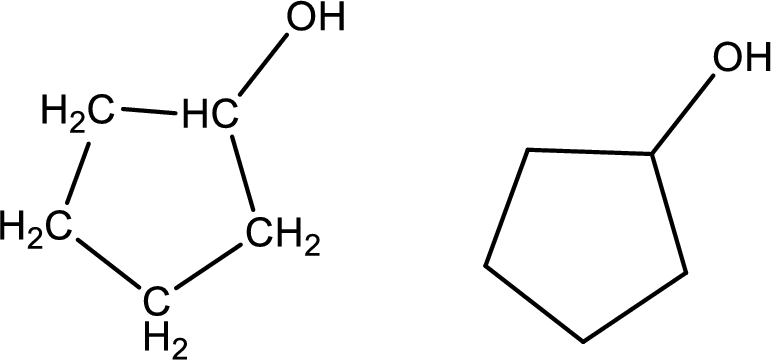
Cyclopentanol
Structural formula and line–angle formula:
From the name it is known that the main core of the compound has a five membered cyclic ring. The name ends with suffix –ol which indicates that there will be an alcoholic
The structural formula and line–angle formula for Cyclopentanol is drawn below.
(j)
Interpretation:
For the given IUPAC name, the corresponding structural formula and line–angle formula has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Condensed structural formula:
Structural formula in which grouping of atoms are done and in which the central atoms along with the other atoms are connected to them are treated as group is known as Condensed structural formula.
Line–angle formula:
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula. This is a shorthand representation of an organic molecule with lines which represents its molecular bonding. In line–angle formula, hydrogen atoms are not shown.
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Cyclopentanone
Structural formula and line–angle formula:
From the name it is known that the main core of the compound has five membered cyclic ring structure. The name ends with suffix –one which indicates that there will be a ketone
The structural formula and line–angle formula for Cyclopentanone is drawn below.
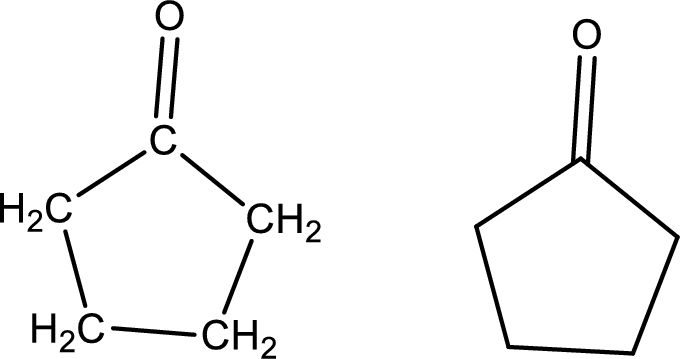
(k)
Interpretation:
For the given IUPAC name, the corresponding structural formula and line–angle formula has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Condensed structural formula:
Structural formula in which grouping of atoms are done and in which the central atoms along with the other atoms are connected to them are treated as group is known as Condensed structural formula.
Line–angle formula:
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula. This is a shorthand representation of an organic molecule with lines which represents its molecular bonding. In line–angle formula, hydrogen atoms are not shown.
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Cyclohexanol
Structural formula and line–angle formula:
From the name it is known that the main core of the compound has six membered cyclic ring structure. The name ends with suffix –ol which indicates that there will be an alcoholic
The structural formula and line–angle formula for Cyclohexanol is drawn below.
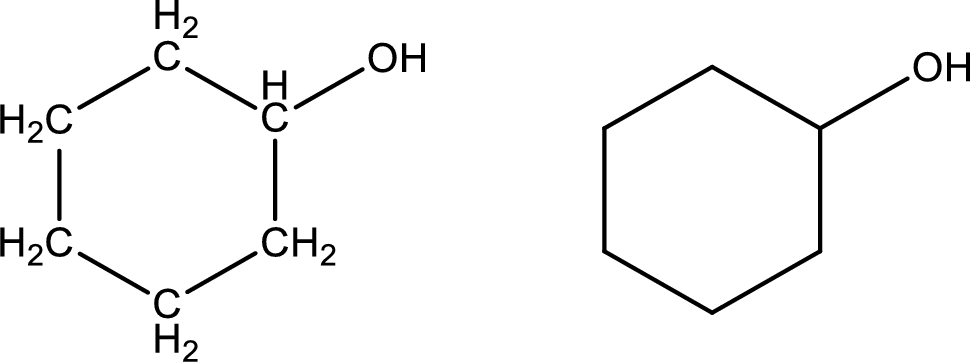
(l)
Interpretation:
For the given IUPAC name, the corresponding structural formula and line–angle formula has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Condensed structural formula:
Structural formula in which grouping of atoms are done and in which the central atoms along with the other atoms are connected to them are treated as group is known as Condensed structural formula.
Line–angle formula:
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula. This is a shorthand representation of an organic molecule with lines which represents its molecular bonding. In line–angle formula, hydrogen atoms are not shown.
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Propanone
Structural formula and line–angle formula:
From the name it is known that the longest chain has three carbon atoms. The name ends with suffix –one which indicates that there will be a ketone
The structural formula and line–angle formula for Propanone is drawn below.
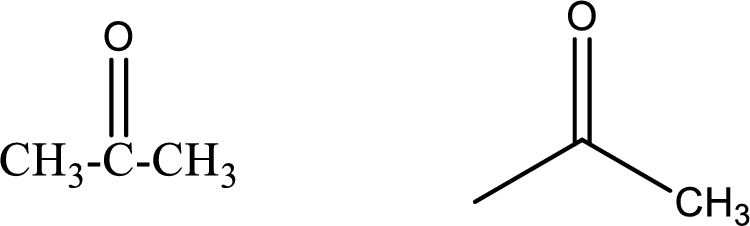
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- helparrow_forwardThe temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forwardQUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forward
- pressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forwarder your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward5.arrow_forward
- 6.arrow_forward0/5 alekscgi/x/sl.exe/1o_u-IgNglkr7j8P3jH-IQs_pBaHhvlTCeeBZbufuBYTi0Hz7m7D3ZcSLEFovsXaorzoFtUs | AbtAURtkqzol 1HRAS286, O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 3 pressure (atm) + 0- 0 5+ 200 temperature (K) 400 Explanation Check X 0+ F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 S 2025 McGraw Hill LLC All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Center Accessibility Q Search LUCR + F8 F9 F10 F11 F12 * % & ( 5 6 7 8 9 Y'S Dele Insert PrtSc + Backsarrow_forward5.arrow_forward
- 9arrow_forwardalekscgi/x/lsl.exe/1o_u-IgNslkr7j8P3jH-IQs_pBanHhvlTCeeBZbufu BYTI0Hz7m7D3ZS18w-nDB10538ZsAtmorZoFusYj2Xu9b78gZo- O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 3- 200 temperature (K) Explanation Chick Q Sowncharrow_forward0+ aleksog/x/lsl.exe/1ou-lgNgkr7j8P3H-IQs pBaHhviTCeeBZbufuBYTOHz7m7D3ZStEPTBSB3u9bsp3Da pl19qomOXLhvWbH9wmXW5zm O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 Gab The temperature on a sample of pure X held at 0.75 atm and -229. °C is increased until the sample sublimes. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.50 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. F3 pressure (atm) 0- 0 200 Explanation temperature (K) Check F4 F5 ☀+ Q Search Chill Will an 9 ENG F6 F7 F8 F9 8 Delete F10 F11 F12 Insert PrtSc 114 d Ararrow_forward
