
Explain why each is an incorrect IUPAC name and write the correct IUPAC name for the intended compound.
- (a) 1,3-Dimethylbutane
- (b) 4-Methylpentane
- (c) 2,2-Diethylbutane
- (d) 2-Ethyl-3-methylpentane
- (e) 2-Propylpentane
- (f) 2,2-Diethylheptane
- (g) 2,2-Dimethylcyclopropane
- (h) 1-Ethyl-5-methylcyclohexane
(a)
Interpretation:
The reason for the incorrect IUPAC name of the given compound has to be explained also the correct IUPAC name for the intended compound has to be given.
Concept Introduction:
IUPAC nomenclature:
The rules for writing IUPAC system of names is as follows,
- 1) For an alkane with unbranched chain of carbon atoms, prefix the root word showing the number of carbon atoms ad end the name with –ane.
- 2) For branched chain alkane, select the longest chain of carbon atoms as the parent chain, its name becomes the root name.
- 3) Number all the carbon atoms in the parent chain. When a substituent is attached to the chain, the number shows the carbon atom to which the substituent is attached. Use a hyphen in the name to connect the number to the substituent name.
- 4) Always number the parent chain in such a way that the carbon bearing substituent gets the lower number.
- 5) If a same substituent is present more than one time, then number the parent chain in such a way that the first encountered substituent gets the lowest number. Prefix di-, tri-, tetra-, penta- and so on to indicate the number of times the substituent occurs. A comma is used to separate position numbers.
- 6) If there are two or more different substituents, list them in alphabetical order and number the chain from the end that gives the lower number to the substituent encountered first. If there are different substituents in equivalent positions on opposite ends of the parent chain, give the substituent of lower alphabetical order the lower number.
- 7) Alphabetize the names of the substituents first and then insert these prefixes.
- 8) Where two or more parent chains of identical lengths are present, the chain with greater number of substituent must be chosen as parent chain.
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
1,3-Dimethylbutane
Correct IUPAC name:
The structure of 1,3-Dimethylbutane is,
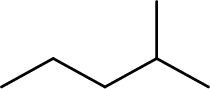
The given IUPAC name is incorrect because in the above structure, the longest chain is pentane.
The main carbon chain has five carbon atoms and one methyl group at the second position
Hence, the correct IUPAC name is 2-methylpentane.
(b)
Interpretation:
The reason for the incorrect IUPAC name of the given compound has to be explained also the correct IUPAC name for the intended compound has to be given.
Concept Introduction:
IUPAC nomenclature:
The rules for writing IUPAC system of names is as follows,
- 1) For an alkane with unbranched chain of carbon atoms, prefix the root word showing the number of carbon atoms ad end the name with –ane.
- 2) For branched chain alkane, select the longest chain of carbon atoms as the parent chain, its name becomes the root name.
- 3) Number all the carbon atoms in the parent chain. When a substituent is attached to the chain, the number shows the carbon atom to which the substituent is attached. Use a hyphen in the name to connect the number to the substituent name.
- 4) Always number the parent chain in such a way that the carbon bearing substituent gets the lower number.
- 5) If a same substituent is present more than one time, then number the parent chain in such a way that the first encountered substituent gets the lowest number. Prefix di-, tri-, tetra-, penta- and so on to indicate the number of times the substituent occurs. A comma is used to separate position numbers.
- 6) If there are two or more different substituents, list them in alphabetical order and number the chain from the end that gives the lower number to the substituent encountered first. If there are different substituents in equivalent positions on opposite ends of the parent chain, give the substituent of lower alphabetical order the lower number.
- 7) Alphabetize the names of the substituents first and then insert these prefixes.
- 8) Where two or more parent chains of identical lengths are present, the chain with greater number of substituent must be chosen as parent chain.
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
4-Methylpentane
Correct IUPAC name:
The structure of 4-Methylpentane is,
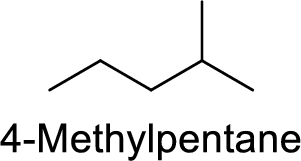
The given IUPAC name is incorrect because in the above structure, the pentane is numbered wrongly.
The main carbon chain has five carbon atoms and one methyl group at the second position
Hence, the correct IUPAC name is 2-methylpentane.
(c)
Interpretation:
The reason for the incorrect IUPAC name of the given compound has to be explained also the correct IUPAC name for the intended compound has to be given.
Concept Introduction:
IUPAC nomenclature:
The rules for writing IUPAC system of names is as follows,
- 1) For an alkane with unbranched chain of carbon atoms, prefix the root word showing the number of carbon atoms ad end the name with –ane.
- 2) For branched chain alkane, select the longest chain of carbon atoms as the parent chain, its name becomes the root name.
- 3) Number all the carbon atoms in the parent chain. When a substituent is attached to the chain, the number shows the carbon atom to which the substituent is attached. Use a hyphen in the name to connect the number to the substituent name.
- 4) Always number the parent chain in such a way that the carbon bearing substituent gets the lower number.
- 5) If a same substituent is present more than one time, then number the parent chain in such a way that the first encountered substituent gets the lowest number. Prefix di-, tri-, tetra-, penta- and so on to indicate the number of times the substituent occurs. A comma is used to separate position numbers.
- 6) If there are two or more different substituents, list them in alphabetical order and number the chain from the end that gives the lower number to the substituent encountered first. If there are different substituents in equivalent positions on opposite ends of the parent chain, give the substituent of lower alphabetical order the lower number.
- 7) Alphabetize the names of the substituents first and then insert these prefixes.
- 8) Where two or more parent chains of identical lengths are present, the chain with greater number of substituent must be chosen as parent chain.
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
2,2-Diethylbutane
Correct IUPAC name:
The structure of 2,2-Diethylbutane is,
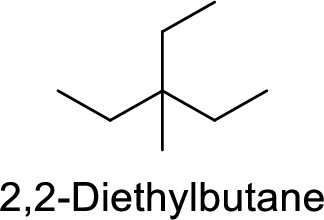
The given IUPAC name is incorrect because in the above structure, the longest chain is pentane.
The main carbon chain has five carbon atoms and one methyl group and one ethyl group at the third position
Hence, the correct IUPAC name is 3-ethyl-3-methylpentane.
(d)
Interpretation:
The reason for the incorrect IUPAC name of the given compound has to be explained also the correct IUPAC name for the intended compound has to be given.
Concept Introduction:
IUPAC nomenclature:
The rules for writing IUPAC system of names is as follows,
- 1) For an alkane with unbranched chain of carbon atoms, prefix the root word showing the number of carbon atoms ad end the name with –ane.
- 2) For branched chain alkane, select the longest chain of carbon atoms as the parent chain, its name becomes the root name.
- 3) Number all the carbon atoms in the parent chain. When a substituent is attached to the chain, the number shows the carbon atom to which the substituent is attached. Use a hyphen in the name to connect the number to the substituent name.
- 4) Always number the parent chain in such a way that the carbon bearing substituent gets the lower number.
- 5) If a same substituent is present more than one time, then number the parent chain in such a way that the first encountered substituent gets the lowest number. Prefix di-, tri-, tetra-, penta- and so on to indicate the number of times the substituent occurs. A comma is used to separate position numbers.
- 6) If there are two or more different substituents, list them in alphabetical order and number the chain from the end that gives the lower number to the substituent encountered first. If there are different substituents in equivalent positions on opposite ends of the parent chain, give the substituent of lower alphabetical order the lower number.
- 7) Alphabetize the names of the substituents first and then insert these prefixes.
- 8) Where two or more parent chains of identical lengths are present, the chain with greater number of substituent must be chosen as parent chain.
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
2-Ethyl-3-methylpentane
Correct IUPAC name:
The structure of 2-Ethyl-3-methylpentane is,
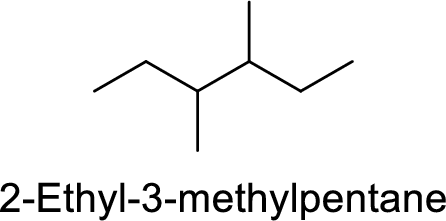
The given IUPAC name is incorrect because in the above structure, the longest chain is hexane.
The main carbon chain has six carbon atoms and two methyl group at the third and fourth position
Hence, the correct IUPAC name is 3,4-dimethylhexane.
(e)
Interpretation:
The reason for the incorrect IUPAC name of the given compound has to be explained also the correct IUPAC name for the intended compound has to be given.
Concept Introduction:
IUPAC nomenclature:
The rules for writing IUPAC system of names is as follows,
- 1) For an alkane with unbranched chain of carbon atoms, prefix the root word showing the number of carbon atoms ad end the name with –ane.
- 2) For branched chain alkane, select the longest chain of carbon atoms as the parent chain, its name becomes the root name.
- 3) Number all the carbon atoms in the parent chain. When a substituent is attached to the chain, the number shows the carbon atom to which the substituent is attached. Use a hyphen in the name to connect the number to the substituent name.
- 4) Always number the parent chain in such a way that the carbon bearing substituent gets the lower number.
- 5) If a same substituent is present more than one time, then number the parent chain in such a way that the first encountered substituent gets the lowest number. Prefix di-, tri-, tetra-, penta- and so on to indicate the number of times the substituent occurs. A comma is used to separate position numbers.
- 6) If there are two or more different substituents, list them in alphabetical order and number the chain from the end that gives the lower number to the substituent encountered first. If there are different substituents in equivalent positions on opposite ends of the parent chain, give the substituent of lower alphabetical order the lower number.
- 7) Alphabetize the names of the substituents first and then insert these prefixes.
- 8) Where two or more parent chains of identical lengths are present, the chain with greater number of substituents must be chosen as parent chain.
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
2-Propylpentane
Correct IUPAC name:
The structure of 2-Propylpentane is,
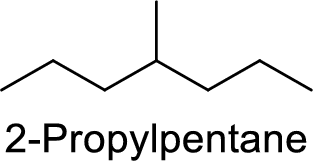
The given IUPAC name is incorrect because in the above structure, the longest chain is heptane.
The main carbon chain has seven carbon atoms and one methyl group at the fourth position
Hence, the correct IUPAC name is 4-methylheptane.
(f)
Interpretation:
The reason for the incorrect IUPAC name of the given compound has to be explained also the correct IUPAC name for the intended compound has to be given.
Concept Introduction:
IUPAC nomenclature:
The rules for writing IUPAC system of names is as follows,
- 1) For an alkane with unbranched chain of carbon atoms, prefix the root word showing the number of carbon atoms ad end the name with –ane.
- 2) For branched chain alkane, select the longest chain of carbon atoms as the parent chain, its name becomes the root name.
- 3) Number all the carbon atoms in the parent chain. When a substituent is attached to the chain, the number shows the carbon atom to which the substituent is attached. Use a hyphen in the name to connect the number to the substituent name.
- 4) Always number the parent chain in such a way that the carbon bearing substituent gets the lower number.
- 5) If a same substituent is present more than one time, then number the parent chain in such a way that the first encountered substituent gets the lowest number. Prefix di-, tri-, tetra-, penta- and so on to indicate the number of times the substituent occurs. A comma is used to separate position numbers.
- 6) If there are two or more different substituents, list them in alphabetical order and number the chain from the end that gives the lower number to the substituent encountered first. If there are different substituents in equivalent positions on opposite ends of the parent chain, give the substituent of lower alphabetical order the lower number.
- 7) Alphabetize the names of the substituents first and then insert these prefixes.
- 8) Where two or more parent chains of identical lengths are present, the chain with greater number of substituent must be chosen as parent chain.
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
2,2-Diethylheptane
Correct IUPAC name:
The structure of 2,2-Diethylheptane is,
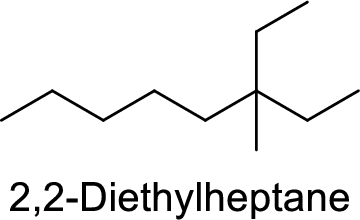
The given IUPAC name is incorrect because in the above structure, the longest chain is octane.
The main carbon chain has eight carbon atoms and one methyl group and one ethyl group are at the second carbon.
Hence, the correct IUPAC name is 3-ethyl-3-methyloctane.
(g)
Interpretation:
The reason for the incorrect IUPAC name of the given compound has to be explained also the correct IUPAC name for the intended compound has to be given.
Concept Introduction:
IUPAC nomenclature:
The rules for writing IUPAC system of names is as follows,
- 1) For an alkane with unbranched chain of carbon atoms, prefix the root word showing the number of carbon atoms ad end the name with –ane.
- 2) For branched chain alkane, select the longest chain of carbon atoms as the parent chain, its name becomes the root name.
- 3) Number all the carbon atoms in the parent chain. When a substituent is attached to the chain, the number shows the carbon atom to which the substituent is attached. Use a hyphen in the name to connect the number to the substituent name.
- 4) Always number the parent chain in such a way that the carbon bearing substituent gets the lower number.
- 5) If a same substituent is present more than one time, then number the parent chain in such a way that the first encountered substituent gets the lowest number. Prefix di-, tri-, tetra-, penta- and so on to indicate the number of times the substituent occurs. A comma is used to separate position numbers.
- 6) If there are two or more different substituents, list them in alphabetical order and number the chain from the end that gives the lower number to the substituent encountered first. If there are different substituents in equivalent positions on opposite ends of the parent chain, give the substituent of lower alphabetical order the lower number.
- 7) Alphabetize the names of the substituents first and then insert these prefixes.
- 8) Where two or more parent chains of identical lengths are present, the chain with greater number of substituent must be chosen as parent chain.
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
2,2-Dimethylcyclopropane
Correct IUPAC name:
The structure of 2,2-Dimethylcyclopropane is,
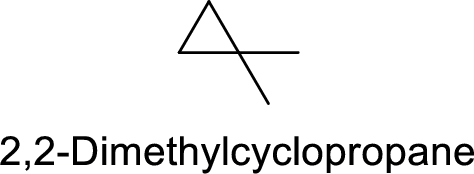
The ring is numbered incorrectly for the above structure.
The main core of the given compound has a cyclic three membered ring with two methyl groups at one carbon.
Hence, the correct IUPAC name is 1,1-dimethylcylcopropane.
(h)
Interpretation:
The reason for the incorrect IUPAC name of the given compound has to be explained also the correct IUPAC name for the intended compound has to be given.
Concept Introduction:
IUPAC nomenclature:
The rules for writing IUPAC system of names is as follows,
- 1) For an alkane with unbranched chain of carbon atoms, prefix the root word showing the number of carbon atoms ad end the name with –ane.
- 2) For branched chain alkane, select the longest chain of carbon atoms as the parent chain, its name becomes the root name.
- 3) Number all the carbon atoms in the parent chain. When a substituent is attached to the chain, the number shows the carbon atom to which the substituent is attached. Use a hyphen in the name to connect the number to the substituent name.
- 4) Always number the parent chain in such a way that the carbon bearing substituent gets the lower number.
- 5) If a same substituent is present more than one time, then number the parent chain in such a way that the first encountered substituent gets the lowest number. Prefix di-, tri-, tetra-, penta- and so on to indicate the number of times the substituent occurs. A comma is used to separate position numbers.
- 6) If there are two or more different substituents, list them in alphabetical order and number the chain from the end that gives the lower number to the substituent encountered first. If there are different substituents in equivalent positions on opposite ends of the parent chain, give the substituent of lower alphabetical order the lower number.
- 7) Alphabetize the names of the substituents first and then insert these prefixes.
- 8) Where two or more parent chains of identical lengths are present, the chain with greater number of substituent must be chosen as parent chain.
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
1-Ethyl-5-methylcyclohexane
Correct IUPAC name:
The structure of 1-Ethyl-5-methylcyclohexane is,
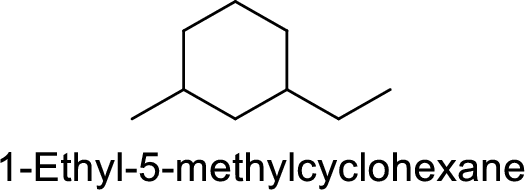
The main core of the given compound has a cyclic six membered ring with one ethyl groups at first carbon and one methyl group at third carbon.
The main carbon chain has six carbon atoms and one methyl group at the second position
Hence, the correct IUPAC name is 1-ethyl-3-methylcyclohexane.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- S: Using a phase diagram leksogi/x/sl.exe/1ou-IgNs kr 7j8P3jH-IQs_pBan HhvTCeeBZbufuBYTI0Hz7m7D3ZdHYU+80XL-5alyVp O States of Matter Using a phase diagram to find a phase transition temperature or pressure se the phase diagram of Substance X below to find the boiling point of X when the pressure on the liquid is 1.6 atm. pressure (atm) 32- 16- solid liquid 0. gas 100 200 temperature (K) 300 Note: your answer must be within 12.5 °C of the exact answer to be graded correct. 10 Explanation Check § Q Search J 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Researrow_forward151.2 254.8 85.9 199.6 241.4 87.6 242.5 186.4 155.8 257.1 242.9 253.3 256.0 216.6 108.7 239.0 149.7 236.4 152.1 222.7 148.7 278.2 268.7 234.4 262.7 283.2 143.6 QUESTION: Using this group of data on salt reduced tomato sauce concentration readings answer the following questions: 1. 95% Cl Confidence Interval (mmol/L) 2. [Na+] (mg/100 mL) 3. 95% Na+ Confidence Interval (mg/100 mL)arrow_forwardResults Search Results Best Free Coursehero Unloc xb Success Confirmation of Q x O Google Pas alekscgi/x/lsl.exe/1o_u-IgNslkr 7j8P3jH-IQs_pBanHhvlTCeeBZbufu BYTI0Hz7m7D3ZcHYUt80XL-5alyVpwDXM TEZayFYCavJ17dZtpxbFD0Qggd1J O States of Matter Using a phase diagram to find a phase transition temperature or pressure Gabr 3/5 he pressure above a pure sample of solid Substance X at 101. °C is lowered. At what pressure will the sample sublime? Use the phase diagram of X below to nd your answer. pressure (atm) 24- 12 solid liquid gas 200 400 temperature (K) 600 ote: your answer must be within 0.15 atm of the exact answer to be graded correct. atm Thanation Check © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center I Q Search L³ ملةarrow_forward
- 301.7 348.9 193.7 308.6 339.5 160.6 337.7 464.7 223.5 370.5 326.6 327.5 336.1 317.9 203.8 329.8 221.9 331.7 211.7 309.6 223.4 353.7 334.6 305.6 340.0 304.3 244.7 QUESTION: Using this group of data on regular tomato sauce concentration readings answer the following questions: 1. 95% Cl Confidence Interval (mmol/L) 2. [Na+] (mg/100 mL) 3. 95% Na+ Confidence Interval (mg/100 mL)arrow_forwardSearch Results Search Results Best Free Coursehero Unlo x b Success Confirmation of Q aleks.com/alekscgi/x/sl.exe/10_u-lgNslkr7j8P3jH-IQs_pBan HhvlTCeeBZbufu BYTIOHz7m7D3ZcHYUt80XL-5alyVpwDXM TEZayFYCav States of Matter Using a phase diagram to find a phase transition temperature or pressure Use the phase diagram of Substance X below to find the temperature at which X turns to a gas, if the pressure above the solid is 3.7 atm. pressure (atm) 0. 32- 16 solid liquid gas 200 temperature (K) Note: your answer must be within 20 °C of the exact answer to be graded correct. Дос Xarrow_forwardConsider the reaction below to answer the following questions: Acetoacetic ester can be prepared by the Claisen self-condensation reaction of ethyl acetate. 1. NaOEt, EtOH H&C OCH CH3 2 H30 H3C CH2 OCH2CH3 A. Write the complete stepwise mechanism for this reaction. Show all electron flow with arrows and draw all intermediate structures. B. Ethyl acetate can be prepared from ethanol as the only organic starting material. Show all reagents and structures for all intermediates in this preparation. C. Give the structures of the ester precursors for the following Claisen condensation product and formulate the reaction. OEtarrow_forward
- Use the phase diagram of Substance X below to find the temperature at which X turns to a gas, if the pressure above the solid is 3.7 atm. pressure (atm) 32 16 solid liquid gas 0 0 200 temperature (K) Note: your answer must be within 20 °C of the exact answer to be graded correct. Шос ☑ كarrow_forwardStarting from bromoethane, how could you prepare the following compounds: a. Ethanol. b. Acetaldehyde f. Acetone. e. 2-Propanol i. Acetoacetic ester. d. 2-Bromoacetic acid. c. Acetic acid g. Acetamide. j. Ethylmalonate k. Gama ketoacid. h. Ethyl magnesium bromide.arrow_forward- The pressure above a pure sample of solid Substance X at 60. °C is raised. At what pressure will the sample melt? Use the phase diagram of X below to find your answer. pressure (atm) 02 0.4 solid Hliquid gas 0 0 200 400 600 temperature (K) Note: your answer must be within 0.025 atm of the exact answer to be graded correct. ☐ atmarrow_forward
- 15. What is the order of decreasing reactivity towards nucleophilic acyl substitution for the carboxylic acid derivatives? (most reactive first) 0 O H3C COC CH3 H₂C C N(CH3)2 H3C C OCH3 A. a. I, 11, 111, b. I, III, IV, II C. II, IV, III, I ° (CH3)2CH C OCH3 IV d. II, I, III, IV B. R COCR 0 0 0 13= RC NH2 RC OR RC CI === IV a. I, III, II, IV b. II, III, I, IV C. III, II, I, IV d. IV, I, III, IIarrow_forwardDraw the formula of the product obtained by reacting D-Tallose with bromine water.arrow_forwardChoose the best reagent(s) for carrying out the following conversions from the list below. Place the letter corresponding to the best choice in the blank to the left of the conversion. a. KMnO4, H3O+ b. Tollens' Reagent [oxidizing reagent] C. NaBH4, ethanol d. 1. BH3 2. H3O+ e. 1. CH3MgBr, ether 2. H3O+ f. CrO3, H2SO4, H₂O g. 1. Mg, ether 2. CO2 3. H3O+ h. 1. NaCN 2. H2SO4, H2, heat i. O3, then Zn and HOAC j. CH₂I A. B. C. CH CH=CHCH2COOH Br CEN CH COOH + HOOCCH COOH COOH 010 CH3arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





