
Concept explainers
a. Which compounds are Bronsted-Lowry acids:
b. Which compounds are Bronsted-Lowry bases:
c. Classify each compound as an acid, a base, or both:
(a)
Interpretation: Among the given compounds, Bronsted-Lowry acids are to be identified.
Concept introduction: Bronsted-Lowry acids are those species which donate proton. They are also known as proton donor. The net charge on Bronsted-Lowry acids can be zero or negative or positive.
Answer to Problem 2.1P
The Bronsted-Lowry acid is
Explanation of Solution
All Bronsted-Lowry acids donate proton.
Hydrogen bromide contain hydrogen atom. Hence, it is a Bronsted-Lowry acid.
Ammonia contains a lone pair of electrons which can be easily donated to form a new bond. Hence, it is a Bronsted-Lowry base.
No hydrogen is present in the
In the given set of compounds, Bronsted-Lowry acid is
(b)
Interpretation: Among the given compounds, Bronsted-Lowry bases are to be identified.
Concept introduction: Bronsted-Lowry bases are those species which can accept a proton. The Base must contain a lone pair or pi bond that could be easily donated to an acid to form a new bond. Bronsted-Lowry base are proton acceptor. The net charge on Bronsted-Lowry base can be zero and negative.
Answer to Problem 2.1P
The Bronsted-Lowry acids are
Explanation of Solution
All Bronsted-lowry bases contain lone pair of electrons or pi bond. In
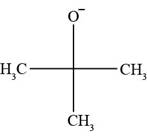
Figure 1
The molecule
![]()
Figure 2
There is neither a pi bond nor a negative charge present in
In the given set of compounds, Bronsted-Lowry acids are
(c)
Interpretation: Among the given compounds, Bronsted-lowry bases are to be identified.
Concept introduction: Bronsted-Lowry bases are those species which can accept a proton. The Base must contain a lone pair or pi bond that could be easily donated to an acid to form a new bond. Bronsted-Lowry base are proton acceptor. The net charge on Bronsted-Lowry base can be zero and negative.
Answer to Problem 2.1P
The Bronsted-Lowry acids are
Explanation of Solution
All Bronsted-Lowry bases contain lone pairs of electrons or pi bond. Bronsted-Lowry acids contain proton.
Ethanol contains hydrogen atom and lone pairs on oxygen atom. Hence, it is a Bronsted-Lowry base as well as a Bronsted-Lowry acid.
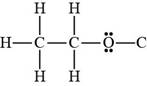
Figure 3
Propane contains only hydrogen atoms. Hence, it is a Bronsted-Lowry acid.
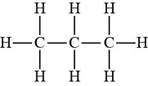
Figure 4
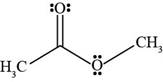
Figure 5
The Bronsted-Lowry acids are
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Find the pH of a 0.120 M solution of HNO2. Find the pH ignoring activity effects (i.e., the normal way). Find the pH in a solution of 0.050 M NaCl, including activityarrow_forwardPlease help me answer these three questions. Required info should be in data table.arrow_forwardDraw the major organic substitution product or products for (2R,3S)-2-bromo-3-methylpentane reacting with the given nucleophile. Clearly drawn the stereochemistry, including a wedged bond, a dashed bond and two in-plane bonds at each stereogenic center. Omit any byproducts. Bri CH3CH2O- (conc.) Draw the major organic product or products.arrow_forward
- Tartaric acid (C4H6O6) is a diprotic weak acid. A sample of 875 mg tartaric acid are dissolved in 100 mL water and titrated with 0.994 M NaOH. How many mL of NaOH are needed to reach the first equivalence point? How many mL of NaOH are needed to reach the second equivalence point?arrow_forwardIncluding activity, calculate the solubility of Pb(IO3)2 in a matrix of 0.020 M Mg(NO3)2.arrow_forwardIncluding activity coefficients, find [Hg22+] in saturated Hg2Br2 in 0.00100 M KBr.arrow_forward
- Including activity, calculate the pH of a 0.010 M HCl solution with an ionic strength of 0.10 M.arrow_forwardCan I please get the graph 1: Concentration vs. Density?arrow_forwardOrder the following series of compounds from highest to lowest reactivity to electrophilic aromatic substitution, explaining your answer: 2-nitrophenol, p-Toluidine, N-(4-methylphenyl)acetamide, 4-methylbenzonitrile, 4-(trifluoromethyl)benzonitrile.arrow_forward
- Ordene la siguiente serie de compuestos de mayor a menor reactividad a la sustitución aromática electrofílica, explicando su respuesta: ácido bencenosulfónico, fluorobenceno, etilbenceno, clorobenceno, terc-butilbenceno, acetofenona.arrow_forwardCan I please get all final concentrations please!arrow_forwardState the detailed mechanism of the reaction of benzene with isopropanol in sulfuric acid.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





