
(a)
Interpretation:
The dynamic model of the given process is to be described along with the degree of freedom analysis.
Concept introduction:
For chemical processes, dynamic models consisting of ordinary differential equations are derived through unsteady-state conservation laws. These laws generally include mass and energy balances.
The process models generally include algebraic relationships which commence from
The degree of freedom analysis of a process model ensures that its model equations are solvable. The expression to calculate the degree of freedom is:
Here,
Answer to Problem 2.1E
The dynamic model for the given process is:
Degree of analysis results in 4 degrees of freedom for the given process.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
A process model containing two input streams of the same liquid is stirred perfectly in a constant-volume tank. For each of the streams, the temperature and flowrate vary with time.
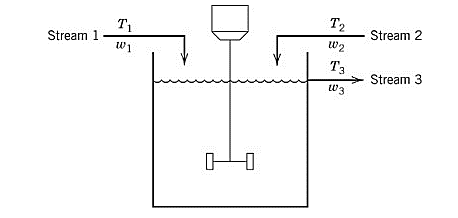
Assume that both the input streams come from the upstream units and their flowrates and temperature are known as the function of time.
For the given tank, apply the degree of freedom analysis. The parameters taken for the given process are the density
Variables taken for the given process model are
For the given process model, there will be 1 independent equation for the energy balance. Thus,
Use equation (1) to calculate the degree of freedom as:
Therefore, the degree of freedom analysis results in 4 degree of freedom for the given process model.
For the tank system given, write the overall mass balance equation as:
Here,
Substitute above equation in equation (2) as:
It is assumed that the tank is a constant-volume system and its density does not vary with time and temperature, thus,
Therefore, the mass balance on the given process model gives,
Now, apply energy balance and write its equation as the total energy of the tank is conserved.
Substitute equation (3) in above equation and simplify as:
Substitute equation (4) in the above equation and simplify the expression to get the dynamic model of the given process as:
(b)
Interpretation:
The derived dynamic model of the system is to be simplified by eliminating any algebraic equations.
Concept introduction:
For chemical processes, dynamic models consisting of ordinary differential equations are derived through unsteady-state conservation laws. These laws generally include mass and energy balances.
The process models generally include algebraic relationships which commence from thermodynamics, transport phenomena, chemical kinetics, and physical properties of the processes.
Answer to Problem 2.1E
The simplified dynamic model of the given system is:
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
A process model containing two input streams of the same liquid is stirred perfectly in a constant-volume tank. For each of the streams, the temperature and flowrate vary with time.
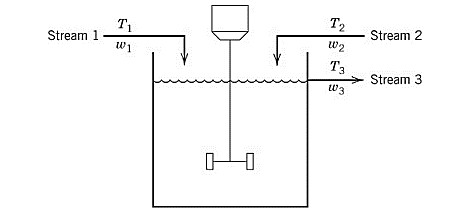
Assume that both the input streams come from the upstream units and their flowrates and temperature are known as the function of time.
From part (a), the dynamic model of the given process is derived as:
Now, let the reference temperature for the system is kept constant. So,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Process Dynamics and Control, 4e
- 1) Indicate whether each statement below is True or False: a) In extractions, small proteins usually end up in the heavy phase. b) In extractions, large proteins usually end up in the heavy phase. c) Tie line length on a phase diagram has no effect on protein partitioning. d) For extraction, we assume that each stage reaches equilibrium. e) Isotherms that are concave down lead to self-sharpening solute fronts in adsorption. f) When scaling up an adsorption unit, the LUB scales proportionally with adsorber length. g) For chromatography, separation efficiency increases when HETP increases. h) In size exclusion chromatography, smaller molecules elute from the column first. i) In hydrophobic interaction chromatography, very hydrophobic proteins elute in water. j) Molecules at very high concentrations elute from the column as a perfect Gaussian peak. k) In chromatography scale-up, resolution will increase as column diameter increases. 1) A good adsorbent typically has no porosity. m)…arrow_forwardChemical Engineering Use the psychrometric chart and demonstrate the linear interpolation method to obtain -0.52 KJ/KgDA. This is the enthalpy deviation. The exercise is uploaded below.arrow_forwardChemical Engineering Use the psychrometric chart. The remaining curves on the psychrometric chart are almost vertical and convex to the left, with labeled values (on Figure 8.4-1) of 0.05, 0.1, 0.2, and so on. (The units of these numbers arekJ/kg DA). Thesecurves are usedto determine theenthalpyof humid air that is not saturated. The procedure is as follows: (a) locate the point on the chart corresponding to air at its specified condition; (b) interpolate to estimate the enthalpy deviation at this point; (c) follow the constant wet-bulb temperature line to the enthalpy scale above the saturation curve, read the value on that scale, and add the enthalpy deviation to it. Also, you will see the exercise on the piece of paper.arrow_forward
- Calculate the permeability of the bed of ion-exchange particles in Example 11.1.arrow_forwardchemical engineering problemarrow_forwardA nozzle is attached to a fire hose by a bolted flange as shown below. What is the force tending to tear apart that flange when the valve in the nozzle is closed?arrow_forward
- the answer should be: V2= -(P0-PL/2μL)(dx-x^)+Ux/darrow_forwardFor spherical sand particles with Dp = 0.03 and ρparticles = 150 lbm / ft3 estimate the minimum fluidizing velocity for air and for water. Assume ε = 0.3. In the case of the water we must rederive Eq. 11.42, taking into account the buoyant force on the particles. Below are the provide answers. Please show all work to get to the correct answers.arrow_forwardPlease show all workarrow_forward
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The





