
Concept explainers
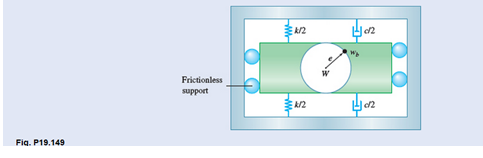
A simplified model of a washing machine is shown. A bundle of wet clothes forms a weight
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 19 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics
- assuming that mass = 2150 kg K = 80.98 N/mm C =21.19 N/mm Please answer correctly please.arrow_forwardA single-cylinder compressor with a mass of 150 kg is mounted on rubber wedges.Compressor rubber wedgesit has been observed that the wedges collapsed by 2mm when placed on it Damped free on wedges without starting the compressorwhen released into vibration, it completed 100 full oscillations in 10 seconds. The stroke of compressor is 100mm a-)Calculate the spring constant (k) of the wedges. b-) Calculate the degree of damping (c) of the wedges. c-)The vibration amplitude of the regular regime was measured as 1mm when the compressor was operated at a speed of 1000rpm In the compressorcalculate the amount of moving masses.arrow_forwardWhich of the following statements are valid for the rod below that is undergoing fixed axis rotation about pin O, where the spring constant is k = 115 N/m and the damping coefficient is c = 302 N.s/m? The slender rod has mass m = 17 kg and length L = 0.6 m. The differential equation governing the motion of the rod is given below. (In the statements below, wn denotes the natural frequency ωn, while wd denotes the damped frequency ωd.) a) Damped vibration, wn and wd not applicable b) Underdamped, wn = 2.60 rad/s, wd = 17.57 rad/s c) Overdamped, wn = 2.25 rad/s, wd not applicable d) Overdamped, wn = 2.60 rad/s, wd not applicable e) Underdamped, wn = 2.25 rad/s, wd = 26.55 rad/sarrow_forward
- The maximum permissible recoil distance of a gun is specified as 0.5 m. If the initial recoil velocity is to be between 8 m/s and 10 m/s, find the mass of the gun and the spring stiffness of the recoil mechanism. Assume that a critically damped dashpot is used in the recoil mechanism and the mass of the gun has to be at least 500 kg.arrow_forwardAn electric motor and its base have a combined mass of M = 12 kg. Each of the four springs attached to the base has a stiffness k =480 kN/m and a viscous damping coefficient c. The unbalance of the motor is equivalent to a mass m =0.005 kg located at the distance e=90mm from the center of the shaft.When the motor is running at ω = 400 rad/s, its steady-state amplitude is 1.8 mm.Determine (a) the damping coefficient of each spring; and (b) the phase anglebetween the displacement of the motor and ωt.arrow_forwardA 7-kg block is suspended by three identical springs, each with k = 200 N/m. The bottom of the block is attached to a dashpot that provides a damping force of F= 50|M N, where v is in m/s. At t = 0 s, the block is given an initial velocity upward of 0.6 m/s from its equilibrium position. (a) What is the natural frequency of the system? (b) Show whether this is an underdamped, a critically damped, or an overdamped system. (c) What is the frequency of the damped system? (d) What is the amplitude of the damped oscillation?arrow_forward
- A loaded railroad car weighing 30,000 lb is rolling at a constant velocity v0 when it couples with a spring and dashpot bumper system (Fig. 1). The recorded displacement–time curve of the loaded railroad car after coupling is as shown (Fig. 2). Determine (a) the damping constant, (b) the spring constant. (Hint: Use the definition of logarithmic decrement given in 19.129.)arrow_forward6. A spring with a spring constant of k = 2 is placed in a medium with a damping force numerically equal to 4 times the instantaneous velocity. If an object of mass m is suspended from the spring, determine all values of m for which the subsequent free motion will be non-oscillatory.arrow_forwardA rotating machine of 400 kg is similar to the system shown below. It operates at 3600 rpm (note: 1 rpm = 2π/60 rad/s). The machine is unbalanced such that its effect is equivalent to a 4 kg mass located 20 cm from the axis of rotation. An isolator with a spring stiffness of 8x106 N/m and a damping constant of 2x104 Ns/m is placed between the machine and the foundation. Determine the steady state response of the system. Find the force transmitted to the foundation and transmissibility of the isolator. Find the damping ratio of the system ζ . Find the transmissibility of the system, Tf. Find the frequency ratio of the system, β. Find the amplitude of the harmonic excitation force of the system, Fo in Newton (N). Find the displacement amplitude of the steady state response of the system, X in millimeters (mm). Find the damped frequency of the system, ωd in rad/s. Find the force transmitted to the foundation, FT in Newton (N). Find the frequency of the harmonic…arrow_forward
- A rotating machine of 400 kg is similar to the system shown below. It operates at 3600 rpm (note: 1 rpm = 2π/60 rad/s). The machine is unbalanced such that its effect is equivalent to a 4 kg mass located 20 cm from the axis of rotation. An isolator with a spring stiffness of 8x106 N/m and a damping constant of 2x104 Ns/m is placed between the machine and the foundation. Determine the steady state response of the system. Find the force transmitted to the foundation and transmissibility of the isolator. Find the damping ratio of the system ζ . Find the transmissibility of the system, Tf. Find the frequency ratio of the system, β. Find the amplitude of the harmonic excitation force of the system, Fo in Newton (N). Find the displacement amplitude of the steady state response of the system, X in millimeters (mm). Find the damped frequency of the system, ωd in rad/s. Find the force transmitted to the foundation, FT in Newton (N). Find the frequency of the harmonic…arrow_forwardA weight of 32 pounds is suspended from a spring with a modulus of 5 lb/ft. From equilibrium position, the weight is pulled down 4 inches below and then released. Given that the damping force in pounds is numerically equal to four times the instantaneous velocity, what is the position of the weight after sec.arrow_forwardNote: End of the question answers also given.. Read the question carefully and give me right solutions with clear calculationsarrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





