
<LCPO> VECTOR MECH,STAT+DYNAMICS
12th Edition
ISBN: 9781265566296
Author: BEER
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 19.4, Problem 19.101P
A collar with mass m that slides on a frictionless horizontal rod is attached to a spring with constant k and is acted upon by a periodic force with a magnitude of P = Pm sin ωft. Determine the range of values of ωf for which the amplitude of the vibration exceeds three times the static deflection caused by a constant force with a magnitude of Pm.
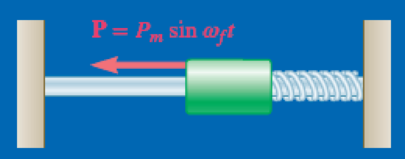
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
oyfr
3. The figure shows a frame under the
influence of an external loading made up
of five forces and two moments. Use the
scalar method to calculate moments.
a. Write the resultant force of the
external loading in Cartesian vector
form.
b. Determine the
& direction
of the resultant moment of the
external loading about A.
15 cm
18 cm
2.2 N-m
B
50 N
45°
10 cm
48 N.m
250 N
60 N
20
21
50 N
25 cm
100 N
A
118,
27cm 5, 4:1
The 2-mass system shown below depicts a disk which rotates about its center and has rotational
moment of inertia Jo and radius r. The angular displacement of the disk is given by 0. The spring
with constant k₂ is attached to the disk at a distance from the center. The mass m has linear
displacement & and is subject to an external force u. When the system is at equilibrium, the spring
forces due to k₁ and k₂ are zero. Neglect gravity and aerodynamic drag in this problem. You may
assume the small angle approximation which implies (i) that the springs and dampers remain in
their horizontal / vertical configurations and (ii) that the linear displacement d of a point on the
edge of the disk can be approximated by d≈re.
Ө
K2
www
m
4
Cz
777777
Jo
Make the following assumptions when analyzing the forces and torques:
тв
2
0>0, 0>0, x> > 0, >0
Derive the differential equations of motion for this dynamic system. Start by sketching
LARGE and carefully drawn free-body-diagrams for the disk and the…
A linear system is one that satisfies the principle of superposition. In other words, if an input u₁
yields the output y₁, and an input u2 yields the output y2, the system is said to be linear if a com-
bination of the inputs u = u₁ + u2 yield the sum of the outputs y = y1 + y2.
Using this fact, determine the output y(t) of the following linear system:
given the input:
P(s) =
=
Y(s)
U(s)
=
s+1
s+10
u(t) = e−2+ sin(t)
=e
Chapter 19 Solutions
<LCPO> VECTOR MECH,STAT+DYNAMICS
Ch. 19.1 - A particle moves in simple harmonic motion....Ch. 19.1 - A particle moves in simple harmonic motion....Ch. 19.1 - Prob. 19.3PCh. 19.1 - Prob. 19.4PCh. 19.1 - Prob. 19.5PCh. 19.1 - Prob. 19.6PCh. 19.1 - Prob. 19.7PCh. 19.1 - A simple pendulum consisting of a bob attached to...Ch. 19.1 - Prob. 19.9PCh. 19.1 - Prob. 19.10P
Ch. 19.1 - Prob. 19.11PCh. 19.1 - Prob. 19.12PCh. 19.1 - Prob. 19.13PCh. 19.1 - Prob. 19.14PCh. 19.1 - A 5-kg collar C is released from rest in the...Ch. 19.1 - Prob. 19.16PCh. 19.1 - Prob. 19.17PCh. 19.1 - An 11-lb block is attached to the lower end of a...Ch. 19.1 - Block A has a mass m and is supported by the...Ch. 19.1 - A 13.6-kg block is supported by the spring...Ch. 19.1 - Prob. 19.21PCh. 19.1 - 19.21 and 19.22A 50-kg block is supported by the...Ch. 19.1 - Prob. 19.23PCh. 19.1 - The period of vibration of the system shown is...Ch. 19.1 - Prob. 19.25PCh. 19.1 - Prob. 19.26PCh. 19.1 - From mechanics of materials, it is known that for...Ch. 19.1 - From mechanics of materials it is known that when...Ch. 19.1 - Prob. 19.29PCh. 19.1 - Prob. 19.30PCh. 19.1 - If h = 700 mm and d = 500 mm and each spring has a...Ch. 19.1 - Prob. 19.32PCh. 19.1 - Prob. 19.33PCh. 19.1 - Prob. 19.34PCh. 19.1 - Prob. 19.35PCh. 19.1 - Prob. 19.36PCh. 19.2 - The 9-kg uniform rod AB is attached to springs at...Ch. 19.2 - Prob. 19.38PCh. 19.2 - Prob. 19.39PCh. 19.2 - Prob. 19.40PCh. 19.2 - A 15-lb slender rod AB is riveted to a 12-lb...Ch. 19.2 - A 20-lb uniform cylinder can roll without sliding...Ch. 19.2 - A square plate of mass m is held by eight springs,...Ch. 19.2 - Prob. 19.44PCh. 19.2 - Prob. 19.45PCh. 19.2 - A three-blade wind turbine used for research is...Ch. 19.2 - A connecting rod is supported by a knife-edge at...Ch. 19.2 - A semicircular hole is cut in a uniform square...Ch. 19.2 - A uniform disk of radius r = 250 mm is attached at...Ch. 19.2 - A small collar of mass 1 kg is rigidly attached to...Ch. 19.2 - Prob. 19.51PCh. 19.2 - Prob. 19.52PCh. 19.2 - Prob. 19.53PCh. 19.2 - Prob. 19.54PCh. 19.2 - The 8-kg uniform bar AB is hinged at C and is...Ch. 19.2 - Prob. 19.56PCh. 19.2 - Prob. 19.57PCh. 19.2 - Prob. 19.58PCh. 19.2 - Prob. 19.59PCh. 19.2 - Prob. 19.60PCh. 19.2 - Two uniform rods, each of weight W = 24 lb and...Ch. 19.2 - A homogeneous rod of mass per unit length equal to...Ch. 19.2 - Prob. 19.63PCh. 19.2 - Prob. 19.64PCh. 19.2 - A 60-kg uniform circular plate is welded to two...Ch. 19.2 - Prob. 19.66PCh. 19.2 - Prob. 19.67PCh. 19.2 - The centroidal radius of gyration ky of an...Ch. 19.3 - Two blocks each have a mass 1.5 kg and are...Ch. 19.3 - Prob. 19.70PCh. 19.3 - Prob. 19.71PCh. 19.3 - Prob. 19.72PCh. 19.3 - Prob. 19.73PCh. 19.3 - Prob. 19.74PCh. 19.3 - Prob. 19.75PCh. 19.3 - Prob. 19.76PCh. 19.3 - Prob. 19.77PCh. 19.3 - Blade AB of the experimental wind-turbine...Ch. 19.3 - A 15-lb uniform cylinder can roll without sliding...Ch. 19.3 - Prob. 19.80PCh. 19.3 - Prob. 19.81PCh. 19.3 - Prob. 19.82PCh. 19.3 - Prob. 19.83PCh. 19.3 - Prob. 19.84PCh. 19.3 - A homogeneous rod of weight W and length 2l is...Ch. 19.3 - A 10-lb uniform rod CD is welded at C to a shaft...Ch. 19.3 - Prob. 19.87PCh. 19.3 - Prob. 19.88PCh. 19.3 - Prob. 19.89PCh. 19.3 - Prob. 19.90PCh. 19.3 - Prob. 19.91PCh. 19.3 - Prob. 19.92PCh. 19.3 - Prob. 19.93PCh. 19.3 - A uniform rod of length L is supported by a...Ch. 19.3 - Prob. 19.95PCh. 19.3 - Three collars each have a mass m and are connected...Ch. 19.3 - Prob. 19.97PCh. 19.3 - As a submerged body moves through a fluid, the...Ch. 19.4 - A 4-kg collar can slide on a frictionless...Ch. 19.4 - Prob. 19.100PCh. 19.4 - A collar with mass m that slides on a frictionless...Ch. 19.4 - Prob. 19.102PCh. 19.4 - The 1.2-kg bob of a simple pendulum of length l =...Ch. 19.4 - Prob. 19.104PCh. 19.4 - A precision experiment sits on an optical table...Ch. 19.4 - Prob. 19.106PCh. 19.4 - Prob. 19.107PCh. 19.4 - The crude-oil pumping rig shown is driven at 20...Ch. 19.4 - Prob. 19.109PCh. 19.4 - Prob. 19.110PCh. 19.4 - Prob. 19.111PCh. 19.4 - Rod AB is rigidly attached to the frame of a motor...Ch. 19.4 - Prob. 19.113PCh. 19.4 - Prob. 19.114PCh. 19.4 - A motor of weight 100 lb is supported by four...Ch. 19.4 - Prob. 19.116PCh. 19.4 - Prob. 19.117PCh. 19.4 - Prob. 19.118PCh. 19.4 - Prob. 19.119PCh. 19.4 - One of the tail rotor blades of a helicopter has...Ch. 19.4 - Prob. 19.121PCh. 19.4 - Prob. 19.122PCh. 19.4 - Prob. 19.123PCh. 19.4 - Prob. 19.124PCh. 19.4 - A 60-lb disk is attached with an eccentricity e =...Ch. 19.4 - A small trailer and its load have a total mass of...Ch. 19.5 - Prob. 19.127PCh. 19.5 - Prob. 19.128PCh. 19.5 - Prob. 19.129PCh. 19.5 - Prob. 19.130PCh. 19.5 - Prob. 19.131PCh. 19.5 - Prob. 19.132PCh. 19.5 - Prob. 19.133PCh. 19.5 - Prob. 19.134PCh. 19.5 - Prob. 19.135PCh. 19.5 - Prob. 19.136PCh. 19.5 - Prob. 19.137PCh. 19.5 - Prob. 19.138PCh. 19.5 - A machine element weighing 500 lb is supported by...Ch. 19.5 - Prob. 19.140PCh. 19.5 - Prob. 19.141PCh. 19.5 - Prob. 19.142PCh. 19.5 - Prob. 19.143PCh. 19.5 - A 36-lb motor is bolted to a light horizontal beam...Ch. 19.5 - One of the tail rotor blades of a helicopter has...Ch. 19.5 - Prob. 19.146PCh. 19.5 - Prob. 19.147PCh. 19.5 - Prob. 19.148PCh. 19.5 - Prob. 19.149PCh. 19.5 - Prob. 19.150PCh. 19.5 - The suspension of an automobile can be...Ch. 19.5 - Prob. 19.152PCh. 19.5 - Prob. 19.153PCh. 19.5 - Prob. 19.154PCh. 19.5 - 19.155 and 19.156 Draw the electrical analog of...Ch. 19.5 - Prob. 19.156PCh. 19.5 - 19.157 and 19.158Write the differential equations...Ch. 19.5 - 19.157 and 19.158Write the differential equations...Ch. 19 - An automobile wheel-and-tire assembly of total...Ch. 19 - Prob. 19.160RPCh. 19 - Disks A and B weigh 30 lb and 12 lb, respectively,...Ch. 19 - A small trailer and its load have a total mass of...Ch. 19 - A 0.8-lb ball is connected to a paddle by means of...Ch. 19 - Prob. 19.164RPCh. 19 - A 4-lb uniform rod is supported by a pin at O and...Ch. 19 - Prob. 19.166RPCh. 19 - Prob. 19.167RPCh. 19 - A small ball of mass m attached at the midpoint of...Ch. 19 - Prob. 19.169RPCh. 19 - If either a simple or a compound pendulum is used...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The manometer fluid in the figure given below is mercury where D = 3 in and h = 1 in. Estimate the volume flow in the tube (ft3/s) if the flowing fluid is gasoline at 20°C and 1 atm. The density of mercury and gasoline are 26.34 slug/ft3 and 1.32 slug/ft3 respectively. The gravitational force is 32.2 ft/s2.arrow_forwardUsing the Bernoulli equation to find the general solution. If an initial condition is given, find the particular solution. y' + xy = xy¯¹, y(0) = 3arrow_forwardTest for exactness. If exact, solve. If not, use an integrating factor as given or obtained by inspection or by the theorems in the text. a. 2xydx+x²dy = 0 b. (x2+y2)dx-2xydy = 0 c. 6xydx+5(y + x2)dy = 0arrow_forward
- Newton's law of cooling. A thermometer, reading 5°C, is brought into a room whose temperature is 22°C. One minute later the thermometer reading is 12°C. How long does it take until the reading is practically 22°C, say, 21.9°C?arrow_forwardSolve a. y' + 2xy = ex-x² b. y' + y sin x = ecosx, y(0) = −1 y(0) = −2.5arrow_forward= MMB 241 Tutorial 3.pdf 2/6 90% + + 5. The boat is traveling along the circular path with a speed of v = (0.0625t²) m/s, where t is in seconds. Determine the magnitude of its acceleration when t = 10 s. 40 m v = 0.0625² 6. If the motorcycle has a deceleration of at = (0.001s) m/s² and its speed at position A is 25 m/s, determine the magnitude of its acceleration when it passes point B. .A 90° 300 m n B 2arrow_forward
- = MMB 241 Tutorial 3.pdf 4/6 67% + 9. The car is traveling along the road with a speed of v = (2 s) m/s, where s is in meters. Determine the magnitude of its acceleration when s = 10 m. v = (2s) m/s 50 m 10. The platform is rotating about the vertical axis such that at any instant its angular position is u = (4t 3/2) rad, where t is in seconds. A ball rolls outward along the radial groove so that its position is r = (0.1+³) m, where t is in seconds. Determine the magnitudes of the velocity and acceleration of the ball when t = 1.5s.arrow_forwardThe population of a certain country is known to increase at a rate proportional to the number of people presently living in the country. If after two years the population has doubled, and after three years the population is 20,000, estimate the number of people initially living in the country.arrow_forward= MMB 241 Tutorial 3.pdf 6/6 100% + | 日 13. The slotted link is pinned at O, and as a result of the constant angular velocity *= 3 rad/s it drives the peg P for a short distance along the spiral guide r = (0.40) m, where 0 is in radians. Determine the radial and transverse components of the velocity and acceleration of P at the instant = 1/3 rad. 0.5 m P r = 0.40 =3 rad/sarrow_forward
- = MMB 241 Tutorial 3.pdf 1/6 90% + DYNAMICS OF PARTICLES (MMB 241) Tutorial 3 Topic: Kinematics of Particles:- Path and Polar coordinate systems and general curvilinear QUESTIONS motion. 1. Determine the acceleration at s = 2 m if v = (2 s) m/s², where s is in meters. At s = 0, v = 1 m/s. 3 m 2. Determine the acceleration when t=1s if v = (4t2+2) m/s, where t is in seconds. v=(4²+2) m/s 6 marrow_forward5.112 A mounting bracket for electronic components is formed from sheet metal with a uniform thickness. Locate the center of gravity of the bracket. 0.75 in. 3 in. ༧ Fig. P5.112 1.25 in. 0.75 in. y r = 0.625 in. 2.5 in. 1 in. 6 in. xarrow_forward4-105. Replace the force system acting on the beam by an equivalent resultant force and couple moment at point B. A 30 in. 4 in. 12 in. 16 in. B 30% 3 in. 10 in. 250 lb 260 lb 13 5 12 300 lbarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Ch 2 - 2.2.2 Forced Undamped Oscillation; Author: Benjamin Drew;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6Tb7Rx-bCWE;License: Standard youtube license