
a.
To determine:
The piece of DNA is cut by EcoRI, the resulting fragments are separated by gel electrophoresis, and the gel is stained with ethidium bromide. Draw a picture of the bands that will appear on the gel.
Introduction:
EcoRI is type II restriction enzyme.
a.
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation: The following gel shows that DNA fragments are present after the EcoRI has cleaved at
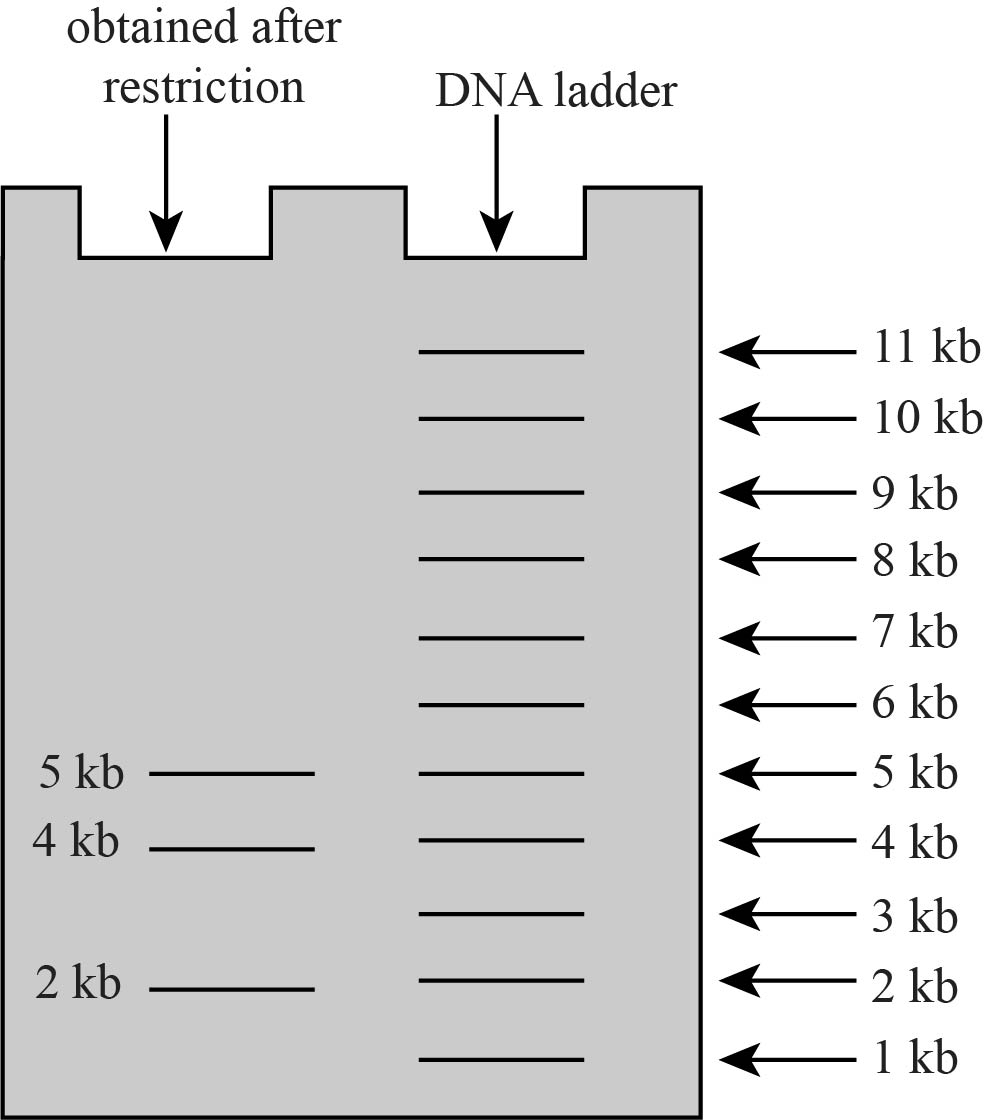
Fig. 1: Gel electrophoresis DNA fragmentation.
After the action of enzyme EcoRI on the DNA, it will produce three fragments of length
b.
To determine:
If a mutation that alters EcoRI site 1 occurs in this piece of DNA, how will the banding pattern on the gel differ from the one that drew in part a?
Introduction:
EcoRI is type II restriction enzyme.
b.
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation: The following gel on that DNA fragments only two fragments of length is obtained
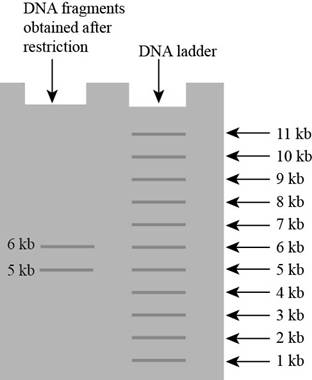
Fig 2 Gel fragmentation
Only two fragments will obtained if the EcoRI site 1 is mutated, two fragments are
c.
To determine:
The difference of banding pattern on the gel that drew in part a if mutations that alter EcoRI sites 1 and 2 occur in this piece of DNA.
Introduction:
EcoRI is type II restriction enzyme.
c.
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation: The gel electrophoresis after the mutation occurs at both sites.
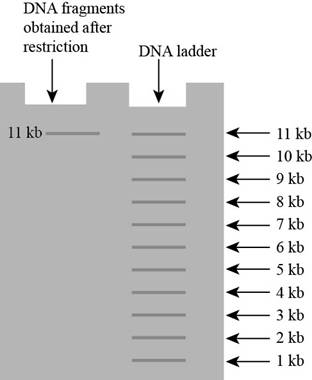
Fig. 3: Gel electrophoresis result
If mutation occur on the both sites, then there will be no cutting and if there will be no cutting then fragment will remain same.
d.
To determine:
The difference of banding pattern on the gel differ from the one that drew in part a if the 1000 bp of DNA were inserted between the two restriction sites.
Introduction:
EcoRI is type II restriction enzyme.
d.
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation: The gel on that DNA fragments only two fragments of length is obtained
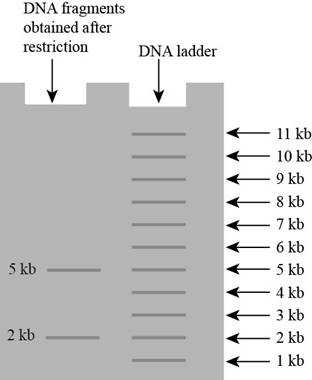
Fig 4: Gel fragmentation
Inserting
e.
To determine:
The difference in the banding pattern on the gel differ from the one that drew in part a if 500 bp of DNA between the two restriction sites were deleted.
Introduction:
EcoRI is type II restriction enzyme.
e.
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation: The gel on that DNA fragments only three fragments of length are obtained
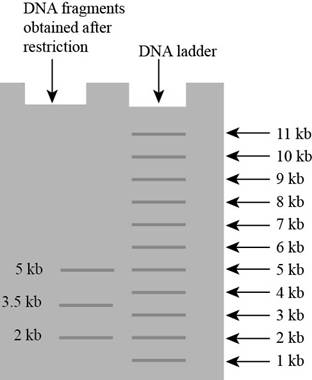
Fig 5 Gel fragmentation
Deleting
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
Genetics
- Molecular Biology Explain/discuss how “slow stop” and “quick/fast stop” mutants wereused to identify different protein involved in DNA replication in E. coli.arrow_forwardMolecular Biology Question A gene that codes for a protein was removed from a eukaryotic cell and inserted into a prokaryotic cell. Although the gene was successfully transcribed and translated, it produced a different protein than it produced in the eukaryotic cell. What is the most likely explanation?arrow_forwardMolecular Biology LIST three characteristics of origins of replicationarrow_forward
- Molecular Biology Question Please help. Thank you For E coli DNA polymerase III, give the structure and function of the b-clamp sub-complex. Describe how the structure of this sub-complex is important for it’s function.arrow_forwardMolecular Biology LIST three characteristics of DNA Polymerasesarrow_forwardMolecular Biology RNA polymerase core enzyme structure contains what subunits? To form holo enzyme, sigma factor is added to core. What is the name of the structure formed? Give the detailed structure of sigma factor and the function of eachdomain. Please help. Thank youarrow_forward
- Molecular Biology You have a single bacterial cell whose DNA is labelled with radioactiveC14. After 5 rounds of cell division, how may cells will contain radioactive DNA? Please help. Thank youarrow_forward1. Explain the structure and properties of atoms and chemical bonds (especially how they relate to DNA and proteins). Also add some pictures.arrow_forward1. In the Sentinel Cell DNA integrity is preserved through nanoscopic helicase-coordinated repair, while lipids in the membrane are fortified to resist environmental mutagens. also provide pictures for this question.arrow_forward
- Explain the structure and properties of atoms and chemical bonds (especially how they relate to DNA and proteins). Also add some pictures.arrow_forwardIn the Sentinel Cell DNA integrity is preserved through nanoscopic helicase-coordinated repair, while lipids in the membrane are fortified to resist environmental mutagens. also provide pictures for this question.arrow_forward1. Explain how genetic information is stored, copied, transferred, and expressed. Also add some pictures for this question.arrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





