
Organic Chemistry
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9781118452288
Author: David R. Klein
Publisher: WILEY
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Chapter 19.13, Problem 36CC
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation:
The synthesis of the following compound has to be illustrated using benzene as the starting compound.
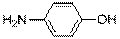
Concept Introduction:
- Electrophilic substitution reactions of
aromatic compounds are known as aromatic electrophilic substitution reactions. An electrophile is a species that is deficient of electrons.
- Benzene is an electron rich Aromatic compound. It undergoes aromatic electrophilic substitution reaction. The delocalized nature of pi electrons in benzene attributes a special property to benzene called resonance.
- The various types of electrophilic substitution reactions in benzene are – Chlorination, Bromination, Nitration, Sulfonation, Friedel Crafts Alkylation/Acylation etc.
- Apart from electrophilic substitution reactions benzene and its derivatives also undergo another special type of reactions namely Aromatic nucleophilic substitution reactions.
- The criteria for aromatic nucleophilic substitution reaction to occur are –
- The aromatic ring must contain a strong electron withdrawing group
- The aromatic ring must contain a leaving group
- The leaving group must be posited either ortho or para position to the strong electron withdrawing group.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
LTS
Solid:
AT=Te-Ti
Trial 1
Trial 2
Trial 3
Average
ΔΗ
Mass water, g
24.096
23.976
23.975
Moles of solid, mol
0.01763
001767
0101781
Temp. change, °C
2.9°C
11700
2.0°C
Heat of reaction, J
-292.37J -170.473
-193.26J
AH, kJ/mole
16.58K 9.647 kJ 10.85 kr
16.58K59.64701
KJ
mol
12.35k
Minimum AS,
J/mol K
41.582
mol-k
Remember: q = mCsAT (m = mass of water, Cs=4.184J/g°C) & qsin =-qrxn &
Show your calculations for:
AH in J and then in kJ/mole for Trial 1:
qa (24.0969)(4.1845/g) (-2.9°C)=-292.37J
qsin =
qrxn =
292.35 292.37J
AH in J = 292.375 0.2923kJ
0.01763m01
=1.65×107
AH in kJ/mol =
=
16.58K
0.01763mol
mol
qrx
Minimum AS in J/mol K (Hint: use the average initial temperature of the three trials, con
Kelvin.)
AS=AHIT
(1.65×10(9.64×103) + (1.0
Jimai
For the compound: C8H17NO2
Use the following information to come up with a plausible structure:
8
This compound has "carboxylic acid amide" and ether functional groups.
The peaks at 1.2ppm are two signals that are overlapping one another.
One of the two signals is a doublet that represents 6 hydrogens; the
other signal is a quartet that represents 3 hydrogens.
Vnk the elements or compounds in the table below in decreasing order of their boiling points. That is, choose 1 next to the substance with the highest bolling
point, choose 2 next to the substance with the next highest boiling point, and so on.
substance
C
D
chemical symbol,
chemical formula
or Lewis structure.
CH,-N-CH,
CH,
H
H 10: H
C-C-H
H H H
Cale
H 10:
H-C-C-N-CH,
Bri
CH,
boiling point
(C)
Сен
(C) B
(Choose
Chapter 19 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Ch. 19.2 - Prob. 1CCCh. 19.3 - Prob. 2CCCh. 19.3 - Prob. 3CCCh. 19.4 - Prob. 4CCCh. 19.5 - Prob. 5CCCh. 19.5 - Prob. 6CCCh. 19.5 - Prob. 7CCCh. 19.6 - Prob. 8CCCh. 19.6 - Prob. 9CCCh. 19.6 - Prob. 10CC
Ch. 19.7 - Prob. 11CCCh. 19.7 - Prob. 12CCCh. 19.8 - Prob. 13CCCh. 19.9 - Prob. 14CCCh. 19.9 - Prob. 15CCCh. 19.10 - Prob. 1LTSCh. 19.10 - Prob. 16PTSCh. 19.10 - Prob. 17ATSCh. 19.10 - Prob. 18ATSCh. 19.11 - Prob. 2LTSCh. 19.11 - Prob. 19PTSCh. 19.11 - Prob. 20ATSCh. 19.11 - Prob. 21ATSCh. 19.11 - Prob. 3LTSCh. 19.11 - Prob. 22PTSCh. 19.11 - Prob. 23ATSCh. 19.11 - Prob. 24ATSCh. 19.11 - Prob. 4LTSCh. 19.11 - Prob. 25PTSCh. 19.11 - Prob. 26ATSCh. 19.11 - Prob. 27ATSCh. 19.12 - Prob. 28CCCh. 19.12 - Prob. 29CCCh. 19.12 - Prob. 5LTSCh. 19.12 - Prob. 30PTSCh. 19.12 - Prob. 31ATSCh. 19.12 - Prob. 32ATSCh. 19.12 - Prob. 6LTSCh. 19.12 - Prob. 33PTSCh. 19.12 - Prob. 34ATSCh. 19.13 - Prob. 35CCCh. 19.13 - Prob. 36CCCh. 19.13 - Prob. 37CCCh. 19.14 - Prob. 38CCCh. 19.14 - Prob. 39CCCh. 19.15 - Prob. 7LTSCh. 19.15 - Prob. 40PTSCh. 19.15 - Prob. 41PTSCh. 19.15 - Prob. 42ATSCh. 19 - Prob. 43PPCh. 19 - Prob. 44PPCh. 19 - Prob. 45PPCh. 19 - Prob. 46PPCh. 19 - Prob. 47PPCh. 19 - Prob. 48PPCh. 19 - Prob. 49PPCh. 19 - Prob. 50PPCh. 19 - Prob. 51PPCh. 19 - Prob. 52PPCh. 19 - Prob. 53PPCh. 19 - Prob. 54PPCh. 19 - Prob. 55PPCh. 19 - Prob. 56PPCh. 19 - Prob. 57PPCh. 19 - Prob. 58PPCh. 19 - Prob. 59PPCh. 19 - Prob. 60PPCh. 19 - Prob. 61PPCh. 19 - Prob. 62PPCh. 19 - Prob. 63PPCh. 19 - Prob. 64PPCh. 19 - Prob. 65PPCh. 19 - Prob. 66PPCh. 19 - Prob. 67PPCh. 19 - Prob. 68PPCh. 19 - Prob. 69PPCh. 19 - Prob. 70PPCh. 19 - Prob. 71PPCh. 19 - Prob. 72PPCh. 19 - Prob. 73PPCh. 19 - Prob. 74IPCh. 19 - Prob. 75IPCh. 19 - Prob. 76IPCh. 19 - Prob. 77IPCh. 19 - Prob. 78IPCh. 19 - Prob. 79IPCh. 19 - Prob. 80IPCh. 19 - Prob. 81IPCh. 19 - Prob. 82IPCh. 19 - Prob. 83IP
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Please help me find the 1/Time, Log [I^-] Log [S2O8^2-], Log(time) on the data table. With calculation steps. And the average for runs 1a-1b. Please help me thanks in advance. Will up vote!arrow_forwardQ1: Answer the questions for the reaction below: ..!! Br OH a) Predict the product(s) of the reaction. b) Is the substrate optically active? Are the product(s) optically active as a mix? c) Draw the curved arrow mechanism for the reaction. d) What happens to the SN1 reaction rate in each of these instances: 1. Change the substrate to Br "CI 2. Change the substrate to 3. Change the solvent from 100% CH3CH2OH to 10% CH3CH2OH + 90% DMF 4. Increase the substrate concentration by 3-fold.arrow_forwardExperiment 27 hates & Mechanisms of Reations Method I visual Clock Reaction A. Concentration effects on reaction Rates Iodine Run [I] mol/L [S₂082] | Time mo/L (SCC) 0.04 54.7 Log 1/ Time Temp Log [ ] 13,20] (time) / [I] 199 20.06 23.0 30.04 0.04 0.04 80.0 22.8 45 40.02 0.04 79.0 21.6 50.08 0.03 51.0 22.4 60-080-02 95.0 23.4 7 0.08 0-01 1970 23.4 8 0.08 0.04 16.1 22.6arrow_forward
- (15 pts) Consider the molecule B2H6. Generate a molecular orbital diagram but this time using a different approach that draws on your knowledge and ability to put concepts together. First use VSEPR or some other method to make sure you know the ground state structure of the molecule. Next, generate an MO diagram for BH2. Sketch the highest occupied and lowest unoccupied MOs of the BH2 fragment. These are called frontier orbitals. Now use these frontier orbitals as your basis set for producing LGO's for B2H6. Since the BH2 frontier orbitals become the LGOS, you will have to think about what is in the middle of the molecule and treat its basis as well. Do you arrive at the same qualitative MO diagram as is discussed in the book? Sketch the new highest occupied and lowest unoccupied MOs for the molecule (B2H6).arrow_forwardQ8: Propose an efficient synthesis of cyclopentene from cyclopentane.arrow_forwardQ7: Use compound A-D, design two different ways to synthesize E. Which way is preferred? Please explain. CH3I ONa NaOCH 3 A B C D E OCH3arrow_forward
- Predict major product(s) for the following reactions. Note the mechanism(s) of the reactions (SN1, E1, SN2 or E2).arrow_forward(10 pts) The density of metallic copper is 8.92 g cm³. The structure of this metal is cubic close-packed. What is the atomic radius of copper in copper metal?arrow_forwardPredict major product(s) for the following reactions. Note the mechanism(s) of the reactions (SN1, E1, SN2 or E2).arrow_forward
- Predict major product(s) for the following reactions. Note the mechanism(s) of the reactions (SN1, E1, SN2 or E2).arrow_forwardQ3: Rank the following compounds in increasing reactivity of E1 and E2 eliminations, respectively. Br ca. go do A CI CI B C CI Darrow_forwardQ5: Predict major product(s) for the following reactions. Note the mechanism(s) of the reactions (SN1, E1, SN2 or E2). H₂O דיי "Br KN3 CH3CH2OH NaNH2 NH3 Page 3 of 6 Chem 0310 Organic Chemistry 1 HW Problem Sets CI Br excess NaOCH 3 CH3OH Br KOC(CH3)3 DuckDuckGarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY