
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The given condensed structure has to be classified based on the
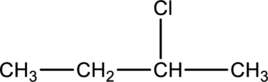
Concept Introduction:
Hydrocarbons:
Only carbon and hydrogen atoms are connected to each other by the strong covalent bonds in any organic molecule is called hydrocarbon.
Alkenes are hydrocarbon that must contain a carbon-carbon double bond in it. The general formula of alkene is drawn here:
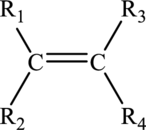
Alkynes are also hydrocarbon that must contain a carbon-carbon triple bond in it. The general formula of alkyne is shown here:

Aromatic compounds are organic molecules that possess the aromatic character similar to benzene.
Alkyl halides are halogenated hydrocarbons with the formula,

Alcohols:
Alcohols are organic compounds whose molecules contains the hydroxyl

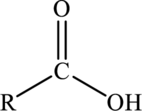
Carboxylic acids:
Carboxylic acids are hydrocarbon derivatives that contains the carboxyl functional group bonded to the alkyl groups. The general formula of carboxylic acids is drawn here:
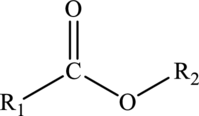
Esters:
Esters are a class of organic compounds that can be derived from the dehydration reaction of carboxylic acids with alcohols. The generalized formula of esters is shown below:
(b)
Interpretation:
The given condensed structure has to be classified based on the functional group or a class of organic compounds.
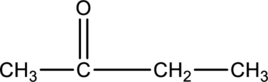
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(c)
Interpretation:
The given condensed structure has to be classified based on the functional group or a class of organic compounds.
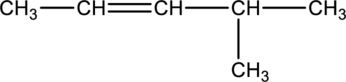
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(d)
Interpretation:
The given condensed structure has to be classified based on the functional group or a class of organic compounds.
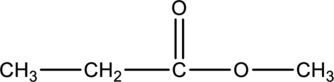
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(e)
Interpretation:
The given condensed structure has to be classified based on the functional group or a class of organic compounds.
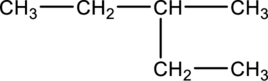
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 19 Solutions
Foundations of College Chemistry 15e Binder Ready Version + WileyPLUS Registration Card
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing 2,2-dimethylpropanal with acetaldehyde and sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardSynthesize 2-Ethyl-3-methyloxirane from dimethyl(propyl)sulfonium iodide using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize 2-Hydroxy-2-phenylacetonitrile from phenylmethanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Synthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIf possible, please provide the formula of the compound 3,3-dimethylbut-2-enal.arrow_forward
- Synthesize 1,4-dibromobenzene from acetanilide (N-phenylacetamide) using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing (3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide with sodium hydride.arrow_forwardWe mix N-ethyl-2-hexanamine with excess methyl iodide and followed by heating with aqueous Ag2O. Indicate the major products obtained.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing acetophenone with iodine and NaOH.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing 2-Propanone and ethyllithium and performing a subsequent acid hydrolysis.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained if (E)-2-butenal and 3-oxo-butanenitrile are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forward

 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,





