
(a)
Interpretation:
IUPAC name of given compound has to be given.
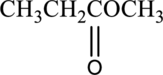
Concept introduction:
IUAC gives rules for the naming of chemical compounds. These rules are,
Carboxylic ester is the one of the types of organic compound with general structure of
Ester contains two parts,
In the nomenclature of Carboxylic ester, find the longest chain of the compound first then remaining groups and atoms are consider as substituent.
First write the alcohol part of the compound then write the acid parte with the –ate suffix.
Find the parent chin first then number the carbon atoms in the parent chain by giving lowest number Carboxylic group followed by designate the other substituent in its position in parent chain.
If more than one same substituent or Carboxylic groups were occurs, add a prefix (di-, tri-, tetra-, ect..) in front of parent chain name.
Finally the systematic name was written as, alcohol part followed acid part name with ate suffix.
(b)
Interpretation:
IUPAC name of given compound has to be given.
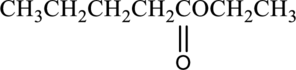
Concept introduction:
IUPAC Nomenclature:
IUAC gives rules for the naming of chemical compounds. These rules are,
Carboxylic ester is the one of the types of organic compound with general structure of
Ester contains two parts,
In the nomenclature of Carboxylic ester, find the longest chain of the compound first then remaining groups and atoms are consider as substituent.
First write the alcohol part of the compound then write the acid parte with the –ate suffix.
Find the parent chin first then number the carbon atoms in the parent chain by giving lowest number Carboxylic group followed by designate the other substituent in its position in parent chain.
If more than one same substituent or Carboxylic groups were occurs, add a prefix (di-, tri-, tetra-, ect..) in front of parent chain name.
Finally the systematic name was written as, alcohol part followed acid part name with ate suffix.
(c)
Interpretation:
IUPAC name of given compound has to be given.
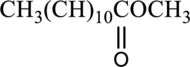
Concept introduction:
IUPAC Nomenclature:
IUAC gives rules for the naming of chemical compounds. These rules are,
Carboxylic ester is the one of the types of organic compound with general structure of
Ester contains two parts,
In the nomenclature of Carboxylic ester, find the longest chain of the compound first then remaining groups and atoms are consider as substituent.
First write the alcohol part of the compound then write the acid parte with the –ate suffix.
Find the parent chin first then number the carbon atoms in the parent chain by giving lowest number Carboxylic group followed by designate the other substituent in its position in parent chain.
If more than one same substituent or Carboxylic groups were occurs, add a prefix (di-, tri-, tetra-, ect..) in front of parent chain name.
Finally the systematic name was written as, alcohol part followed acid part name with ate suffix.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 19 Solutions
Foundations of College Chemistry 15e Binder Ready Version + WileyPLUS Registration Card
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing 2,2-dimethylpropanal with acetaldehyde and sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardSynthesize 2-Ethyl-3-methyloxirane from dimethyl(propyl)sulfonium iodide using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize 2-Hydroxy-2-phenylacetonitrile from phenylmethanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Synthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIf possible, please provide the formula of the compound 3,3-dimethylbut-2-enal.arrow_forward
- Synthesize 1,4-dibromobenzene from acetanilide (N-phenylacetamide) using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing (3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide with sodium hydride.arrow_forwardWe mix N-ethyl-2-hexanamine with excess methyl iodide and followed by heating with aqueous Ag2O. Indicate the major products obtained.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing acetophenone with iodine and NaOH.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing 2-Propanone and ethyllithium and performing a subsequent acid hydrolysis.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained if (E)-2-butenal and 3-oxo-butanenitrile are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forward
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning



