
Concept explainers
Antibiotic Effects on Mitochondria Tetracyclines are antibiotics that inactivate bacterial ribosomes. Knowing that mitochondria evolved from bacteria, researchers suspected tetracyclines might affect mitochondria by harming their ribosomes. FIGURE 19. 11 shows the effects of an experiment in which mice were given either tetracycline or a control antibiotic that affects cell wall production. After 10 days of treatment, the function of mitochondria in the mice was assessed.
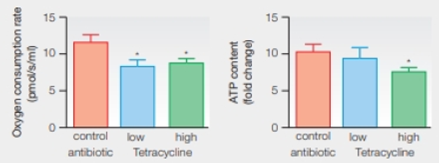
FIGURE 19.11 Effects of tetracycline on mitochondria. Mice received low-dose tetracycline, high-dose tetracycline, or a control antibiotic that targets bacterial cell walls. Mitochondrial function was assessed by looking at oxygen consumption rate and ATP content in homogenized mouse livers. Bar graphs show means with standard error. An * indicates a statistically significant difference between the experimental and the control treatments.
Do these results support the hypothesis that tetracyclines impair mitochondrial function?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 19 Solutions
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes
- 1. In the following illustration of a phospholipid... (Chemistry Primer and Video 2-2, 2-3 and 2-5) a. Label which chains contain saturated fatty acids and non-saturated fatty acids. b. Label all the areas where the following bonds could form with other molecules which are not shown. i. Hydrogen bonds ii. Ionic Bonds iii. Hydrophobic Interactions 12-6 HICIH HICIH HICHH HICHH HICIH OHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHH C-C-C-C-C-c-c-c-c-c-c-c-c-c-c-c-C-C-H HH H H H H H H H H H H H H H H H H H HO H-C-O H-C-O- O O-P-O-C-H H T HICIH HICIH HICIH HICIH HHHHHHH HICIH HICIH HICIH 0=C HIC -C-C-C-C-C-C-C-C-CC-C-C-C-C-C-C-C-C-H HHHHHHHHH IIIIIIII HHHHHHHH (e-osbiv)arrow_forwardAnswer this as a dental assistant studentarrow_forwardbuatkan judul skripsi tentang parasitologi yang sedang trendinharrow_forward
- Dental assistantarrow_forwardO Macmillan Learning Glu-His-Trp-Ser-Gly-Leu-Arg-Pro-Gly The pKa values for the peptide's side chains, terminal amino groups, and carboxyl groups are provided in the table. Amino acid Amino pKa Carboxyl pKa Side-chain pKa glutamate 9.60 2.34 histidine 9.17 1.82 4.25 6.00 tryptophan 9.39 2.38 serine 9.15 2.21 glycine 9.60 2.34 leucine 9.60 2.36 arginine 9.04 2.17 12.48 proline 10.96 1.99 Calculate the net charge of the molecule at pH 3. net charge at pH 3: Calculate the net charge of the molecule at pH 8. net charge at pH 8: Calculate the net charge of the molecule at pH 11. net charge at pH 11: Estimate the isoelectric point (pl) for this peptide. pl:arrow_forwardBiology Questionarrow_forward
- This entire structure (Pinus pollen cone) using lifecycle terminology is called what?arrow_forwardThis entire structure using lifecycle terminology is called what? megastrobilus microstrobilus megasporophyll microsporophyll microsporangium megasporangium none of thesearrow_forwardHow much protein should Sarah add to her diet if she gets pregnant? Sarah's protein requirements during pregnancy would be higher. See Hint B2. During calculations, use numbers rounded to the first decimal place. In your answer, round the number of grams to the nearest whole number. _______ g ?arrow_forward
- C MasteringHealth MasteringNu X session.healthandnutrition-mastering.pearson.com/myct/itemView?assignment ProblemID=17396422&attemptNo=1&offset=prevarrow_forwardMost people, even those who exercise regularly at low to average intensity (1 hour at the gym or a 2- to 3-mile walk several times per week), do not need an increased protein intake. What would be the protein needs of a man named Josh who exercises moderately and is the same age and size as Wayne? Josh is 5 ft, 8 in tall and weighs 183 lb. Round the number of grams to the nearest whole number. During calculations, use numbers rounded to the first decimal place. Because protein requirement is a range, please enter two numbers: lower and upper range values, respectively. Separate the lower and upper range values, in that order, by a comma. ___, ___ g ?arrow_forwardC MasteringHealth MasteringNu X session.healthandnutrition-mastering.pearson.com/myct/itemView?assignment ProblemID=17396422&attemptNo=1&offset=prevarrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_iosRecommended textbooks for you
 Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
