
Concept explainers
Exercise 19-3
Analysis of cost flows
C2
As of the end of June, the job cost sheets at Racing Wheels, Inc., show the following total costs accumulated on three custom jobs.
Job 102 was started in production in May, and the Mowing costs were assigned to it in May: direct materials, $6,000; direct labor, $1,800; and
1. What was the cost of the raw materials requisitioned in June for each of the three jobs?
2. How much direct labor cost was incurred during June for each of the three jobs?
3. What predetermined overhead rate is used during June?
4. How much total cost is transferred to finished goods during June?
Check (4) $81,300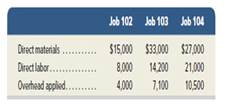
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 19 Solutions
Connect Access Card For Fundamental Accounting Principles
- I want to correct answer general accounting questionarrow_forwardKindly help me with accounting questionsarrow_forwardDuo Corporation is evaluating a project with the following cash flows: Year 0 1 2 3 Cash Flow -$ 30,000 12,200 14,900 16,800 4 5 13,900 -10,400 The company uses an interest rate of 8 percent on all of its projects. a. Calculate the MIRR of the project using the discounting approach. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations and enter your answer as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16. b. Calculate the MIRR of the project using the reinvestment approach. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations and enter your answer as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16. c. Calculate the MIRR of the project using the combination approach. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations and enter your answer as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16. a. Discounting approach MIRR b. Reinvestment approach MIRR c. Combination approach MIRR % % %arrow_forward
- Provide correct answer general accounting questionarrow_forwardNeed help with this question solution general accountingarrow_forwardConsider a four-year project with the following information: Initial fixed asset investment = $555,000; straight-line depreciation to zero over the four-year life; zero salvage value; price = $37; variable costs = $25; fixed costs = $230,000; quantity sold = 79,000 units; tax rate = 24 percent. How sensitive is OCF to changes in quantity sold?arrow_forward
- Light emitting diodes (LED) light bulbs have become required in recent years, but do they make financial sense? Suppose a typical 60-watt incandescent light bulb costs $.39 and lasts 1,000 hours. A 15-watt LED, which provides the same light, costs $3.10 and lasts for 12,000 hours. A kilowatt-hour of electricity costs $.115. A kilowatt-hour is 1,000 watts for 1 hour. If you require a return of 11 percent and use a light fixture 500 hours per year, what is the equivalent annual cost of each light bulb? Note: A negative answer should be indicated by a minus sign. Do not round intermediate calculations and round your answers to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16.arrow_forwardRecently, Abercrombie & Fitch has been implementing a turnaround strategy since its sales had been falling for the past few years (11% decrease in 2014, 8% in 2015, and just 3% in 2016.) One part of Abercrombie's new strategy has been to abandon its logo-adorned merchandise, replacing it with a subtler look. Abercrombie wrote down $20.6 million of inventory, including logo-adorned merchandise, during the year ending January 30, 2016. Some of this inventory dated back to late 2013. The write-down was net of the amount it would be able to recover selling the inventory at a discount. The write-down is significant; Abercrombie's reported net income after this write-down was $35.6 million. Interestingly, Abercrombie excluded the inventory write-down from its non-GAAP income measures presented to investors; GAAP earnings were also included in the same report. Question: From an investor standpoint, do you think that the effect of the inventory write-down should be considered when…arrow_forwardFinancial accountingarrow_forward
 Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting, Chapters 1-27 (New in Account...AccountingISBN:9781305666160Author:James A. Heintz, Robert W. ParryPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27 (New in Account...AccountingISBN:9781305666160Author:James A. Heintz, Robert W. ParryPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning





