
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The skeletal structure of the given fatty acid should be drawn and cis-double bond is to be indicated.
Concept Introduction:
Fatty acids are long-chain
Unsaturated fatty acids can be defined as the long-chain fatty acids which have a long hydrocarbon chain with −COOH group. In unsaturated fatty acids, the carbon chain must have at least one double bond.
Answer to Problem 33P
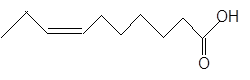
Explanation of Solution
Given:
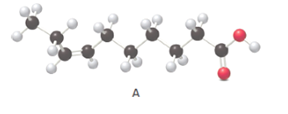
Fatty acids are long-chain carboxylic acids, which consist of two parts; long hydrocarbon chains and polar −COOH group. The long hydrocarbon chain consists of carbon and H atoms, so it has C-C and C-H bonds only, whereas, the polar −COOH group has polar C=O and C-O bonds. The unsaturated fatty acids have cis and trans-double bonds in the hydrocarbon chain.
In the ball-and-stick model, the red ball represents O atom, black ball represents C atom and white ball represents H atoms. Thus, the skeletal structure is:
(b)
Interpretation:
The omega-n designation for the
Concept Introduction:
Fatty acids are long-chain carboxylic acid, which may or may not have unsaturation in the molecule. They react with glycerol to form triglycerides. The reaction is called esterification as a carboxylic acid group reacts with the alcoholic group to form an ester group.
Unsaturated fatty acids can be defined as the long-chain fatty acids which have a long hydrocarbon chain with −COOH group. In unsaturated fatty acids, the carbon chain must have at least one double bond.
Answer to Problem 33P
The
Explanation of Solution
Fatty acids are long-chain carboxylic acids, which consist of two parts; long hydrocarbon chains and polar −COOH group. If there is at least one double bond in the long hydrocarbon chain of the fatty acid it is said to be an unsaturated fatty acid.
The unsaturated fatty acids can also classify as omega-n acids. Here, 'n' represents the position of the first
In the given fatty acid, the first
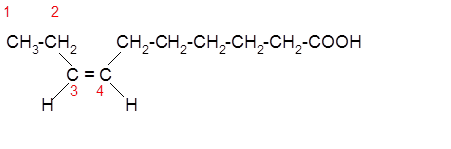
(c)
Interpretation:
The stereoisomer of the
Concept Introduction:
Fatty acids are long-chain carboxylic acid, which may or may not have unsaturation in the molecule. They react with glycerol to form triglycerides. The reaction is called esterification as a carboxylic acid group reacts with the alcoholic group to form an ester group.
Unsaturated fatty acids can be defined as the long-chain fatty acids which have a long hydrocarbon chain with −COOH group. In unsaturated fatty acids, the carbon chain must have at least one double bond.
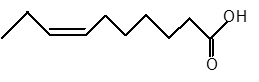
Answer to Problem 33P
The stereoisomer of cis-fatty acid must be trans-isomer as given below;
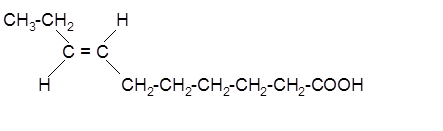
Explanation of Solution
Fatty acids are long-chain carboxylic acids, which consist of two parts; long hydrocarbon chains and polar −COOH group. The double bond can arrange in two ways, i.e., cis and trans in the hydrocarbon chain of the fatty acid molecule. Hence, the stereoisomer of cis-fatty acid
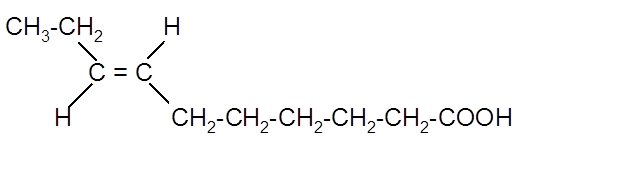
(d)
Interpretation:
The structure of wax formed by the reaction of
Concept Introduction:
Fatty acids are long-chain carboxylic acid, which may or may not have unsaturation in the molecule. They react with glycerol to form triglycerides. The reaction is called esterification as a carboxylic acid group reacts with the alcoholic group to form an ester group.
Unsaturated fatty acids can be defined as the long-chain fatty acids which have a long hydrocarbon chain with −COOH group. In unsaturated fatty acids, the carbon chain must have at least one double bond.
Answer to Problem 33P
The skeleton formula of wax formed by the reaction of
Explanation of Solution
Fatty acids are long-chain carboxylic acids, which consist of two parts; long hydrocarbon chains and polar −COOH group. Waxes are a good example of hydrolyzable lipids, which are composed of fatty acid and higher alcohols. They have an ester
Hence, the reaction of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
CONNECT IA GENERAL ORGANIC&BIO CHEMISTRY
- Epoxides can be opened in aqueous acid or aqueous base to produce diols (molecules with two OH groups). In this question, you'll explore the mechanism of epoxide opening in aqueous acid. 2nd attempt Be sure to show all four bonds at stereocenters using hash and wedge lines. 0 0 Draw curved arrows to show how the epoxide reacts with hydronium ion. 100 +1: 1st attempt Feedback Be sure to show all four bonds at stereocenters using hash and wedge lines. See Periodic Table See Hint H A 5 F F Hr See Periodic Table See Hintarrow_forward03 Question (1 point) For the reaction below, draw both of the major organic products. Be sure to consider stereochemistry. > 1. CH₂CH₂MgBr 2. H₂O 3rd attempt Draw all four bonds at chiral centers. Draw all stereoisomers formed. Draw the structures here. e 130 AN H See Periodic Table See Hint P C Brarrow_forwardYou may wish to address the following issues in your response if they are pertinent to the reaction(s) you propose to employ:1) Chemoselectivity (why this functional group and not another?) 2) Regioselectivity (why here and not there?) 3) Stereoselectivity (why this stereoisomer?) 4) Changes in oxidation state. Please make it in detail and draw it out too in what step what happens. Thank you for helping me!arrow_forward
- 1) Chemoselectivity (why this functional group and not another?) 2) Regioselectivity (why here and not there?) 3) Stereoselectivity (why this stereoisomer?) 4) Changes in oxidation state. Everything in detail and draw out and write it.arrow_forwardCalculating the pH at equivalence of a titration 3/5 Izabella A chemist titrates 120.0 mL of a 0.7191M dimethylamine ((CH3)2NH) solution with 0.5501 M HBr solution at 25 °C. Calculate the pH at equivalence. The pk of dimethylamine is 3.27. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. Note for advanced students: you may assume the total volume of the solution equals the initial volume plus the volume of HBr solution added. pH = ☐ ✓ 18 Ar Boarrow_forwardAlcohols can be synthesized using an acid-catalyzed hydration of an alkene. An alkene is combined with aqueous acid (e.. sulfuric acid in water). The reaction mechanism typically involves a carbocation intermediate. > 3rd attempt 3343 10 8 Draw arrows to show the reaction between the alkene and hydronium ion. that 2nd attempt Feedback 1st attempt تعمال Ju See Periodic Table See Hint F D Ju See Periodic Table See Hintarrow_forward
- Draw the simplified curved arrow mechanism for the reaction of acetone and CHgLi to give the major product. 4th attempt Π Draw the simplified curved arrow mechanism T 3rd attempt Feedback Ju See Periodic Table See Hint H -H H -I H F See Periodic Table See Hintarrow_forwardSelect the correct reagent to accomplish the first step of this reaction. Then draw a mechanism on the Grignard reagent using curved arrow notation to show how it is converted to the final product. 4th attempt Part 1 (0.5 point) Select the correct reagent to accomplish the first step of this reaction. Choose one: OA Mg in ethanol (EtOH) OB. 2 Li in THF O C. Li in THF D. Mg in THF O E Mg in H2O Part 2 (0.5 point) Br Part 1 Bri Mg CH B CH, 1 Draw intermediate here, but no arrows. © TE See Periodic Table See Hint See Hint ין Harrow_forwardSelect the product for the following reaction. HO HO PCC OH ○ OH O HO ○ HO HO HOarrow_forward
- 5:45 Х Select the final product for the following reaction sequence. O O 1. Mg. ether 2.D.Oarrow_forwardBased on the chart Two similarities between the molecule with alpha glycosidic linkages. Two similarities between the molecules with beta glycosidtic linkages. Two differences between the alpha and beta glycosidic linkages.arrow_forwardplease help fill in the tablearrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





