
Concept explainers
Still referring to Problem 1, what will be the possible genotypes of offspring from the following matings? With what frequency will each genotype show up?
- a. AABB × aaBB
- b. AaBB × AABb
- c. AaBb × aabb
- d. AaBb × AaBb
a.
To predict: The predicted genotype frequencies among the offspring for the mating AABB × aaBB.
Introduction: The law of independent assortment and law of segregation are the laws proposed by Gregor Johann Mendel, a geneticist. Mendel proposed the law of independent assortment based on the results of monohybrid cross that “two alleles at any locus tend to separate from each other during meiosis, so they end up in different gametes”. Mendel proposed the law of independent assortment based on the results of dihybrid cross that “alleles at one locus tend to assort into gametes independently of alleles at other loci”. The number of possible allele combination for the given genotype is given by the formula 2n where “n” is the number of heterozygous alleles that are present.
Explanation of Solution
A monohybrid cross is constructed with Punnett square for the parents having the genotype AABB and aaBB.
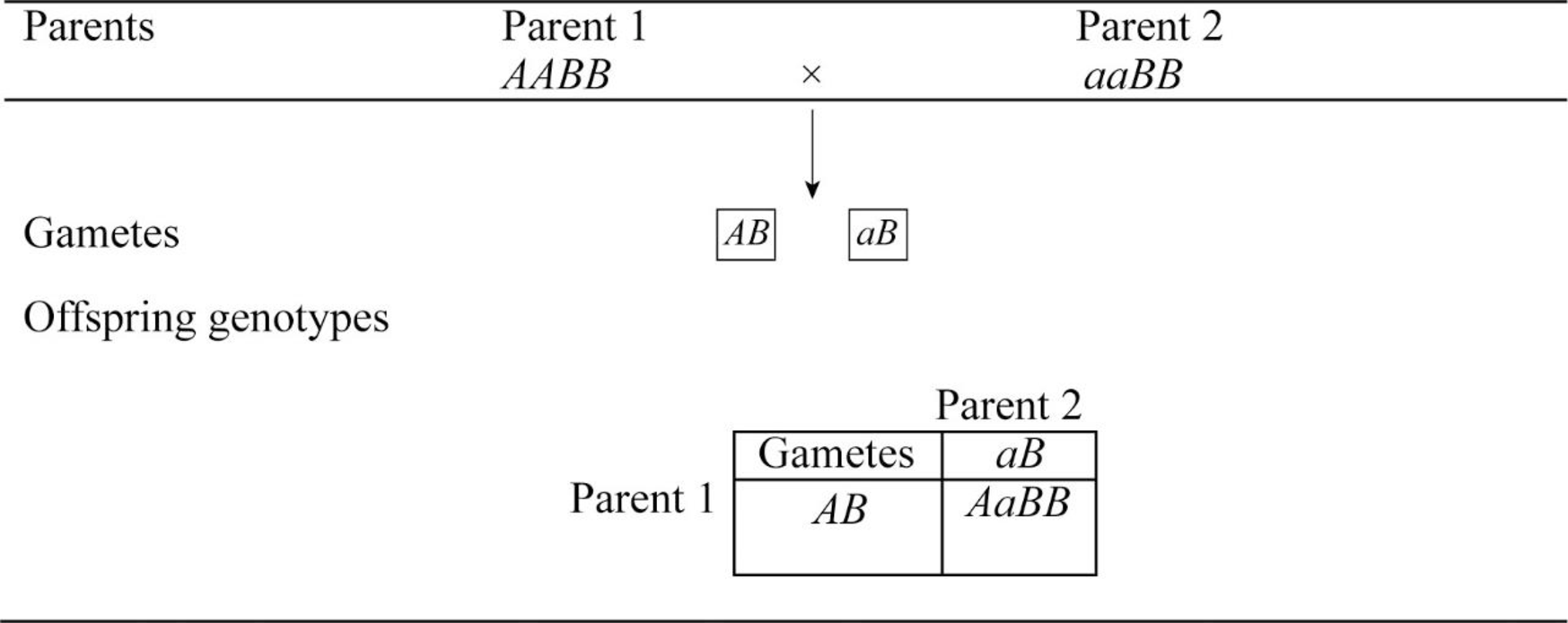
All the offspring have the same genotype AaBB. Therefore, there is no genotype frequency.
b.
To predict: The predicted genotype frequencies among the offspring for the mating AaBB × AABb.
Introduction: The law of independent assortment and law of segregation are the laws proposed by Gregor Johann Mendel, a geneticist. Mendel proposed the law of independent assortment based on the results of monohybrid cross that “two alleles at any locus tend to separate from each other during meiosis, so they end up in different gametes”. Mendel proposed the law of independent assortment based on the results of dihybrid cross that “alleles at one locus tend to assort into gametes independently of alleles at other loci”. The number of possible allele combination for the given genotype is given by the formula 2n where “n” is the number of heterozygous alleles that are present.
Explanation of Solution
A monohybrid cross is constructed with Punnett square for the parents having the genotype AaBB and AABb.
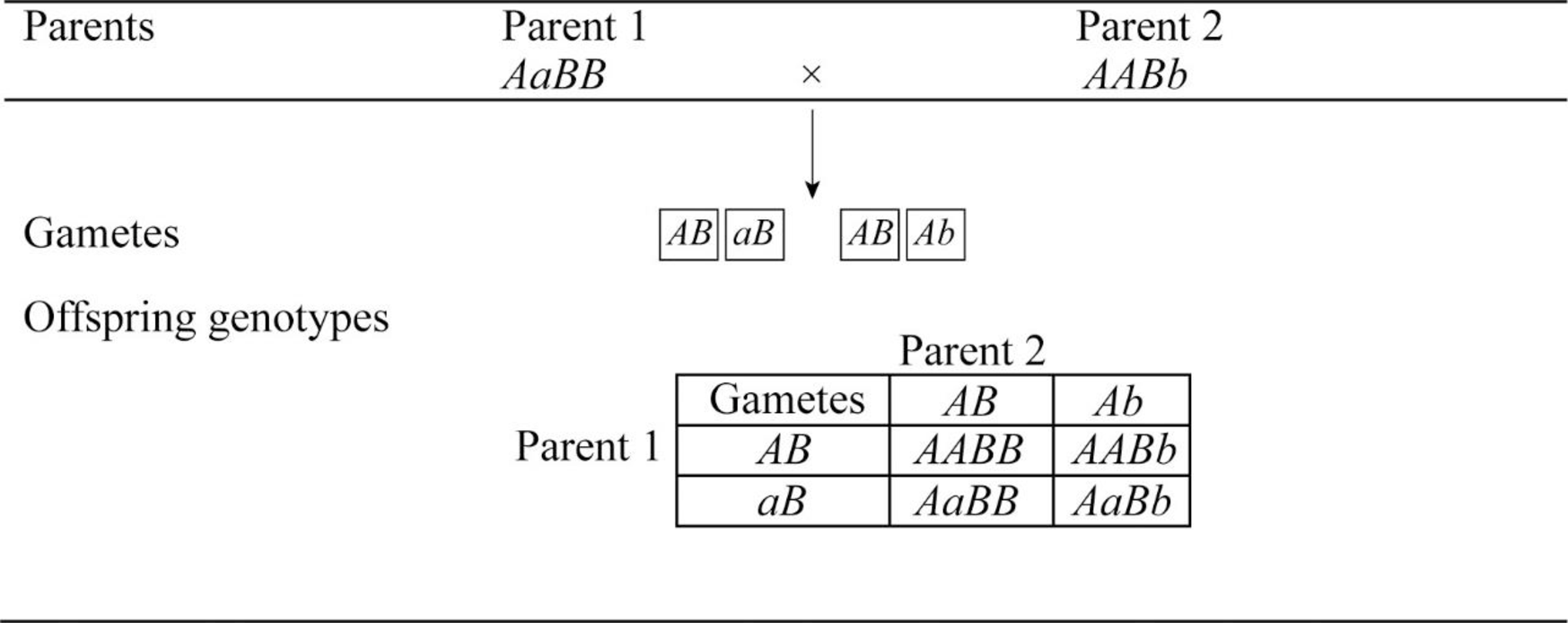
The following is the frequency of genotypes.
Total number of possible genotypes = 4.
AABB=
AABb=
AaBB=
AaBb =
The frequency of all four genotypes is 25%.
c.
To predict: The predicted genotype frequencies among the offspring for the mating AaBb × aabb.
Introduction: The law of independent assortment and law of segregation are the laws proposed by Gregor Johann Mendel, a geneticist. Mendel proposed the law of independent assortment based on the results of monohybrid cross that “two alleles at any locus tend to separate from each other during meiosis, so they end up in different gametes”. Mendel proposed the law of independent assortment based on the results of dihybrid cross that “alleles at one locus tend to assort into gametes independently of alleles at other loci”. The number of possible allele combination for the given genotype is given by the formula 2n where “n” is the number of heterozygous alleles that are present.
Explanation of Solution
A monohybrid cross is constructed with Punnett square for the parents having the genotype AaBb and aabb
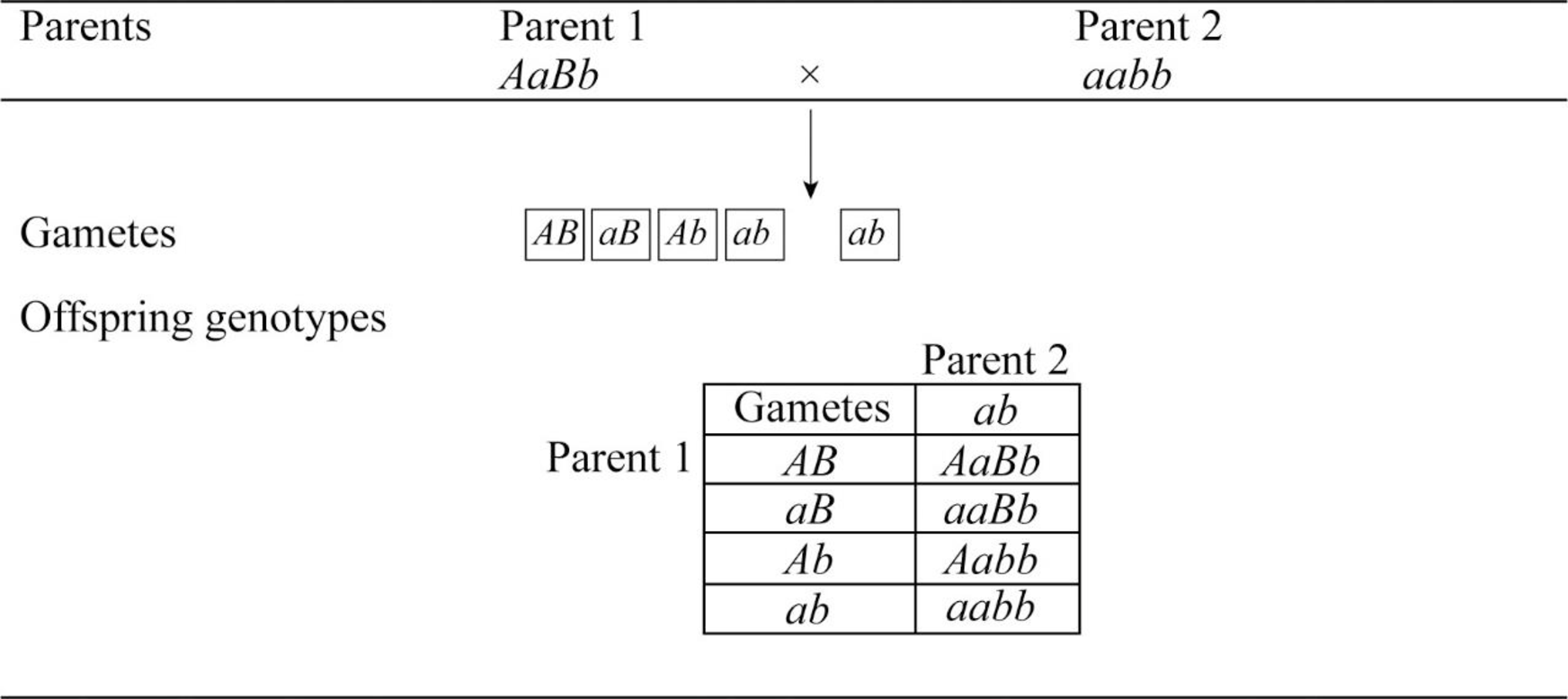
The following is the frequency of genotypes.
Total number of possible genotypes = 4.
AABB=
aaBB=
Aabb=
aabb =
The frequency of all four genotypes is 25%.
d.
To predict: The predicted genotype frequencies among the offspring for the mating AaBb × AaBb.
Introduction: The law of independent assortment and law of segregation are the laws proposed by Gregor Johann Mendel, a geneticist. Mendel proposed the law of independent assortment based on the results of monohybrid cross that “two alleles at any locus tend to separate from each other during meiosis, so they end up in different gametes”. Mendel proposed the law of independent assortment based on the results of dihybrid cross that “alleles at one locus tend to assort into gametes independently of alleles at other loci”. The number of possible allele combination for the given genotype is given by the formula 2n where “n” is the number of heterozygous alleles that are present.
Explanation of Solution
A monohybrid cross is constructed with Punnett square for the parents having the genotype AaBb and AaBb.
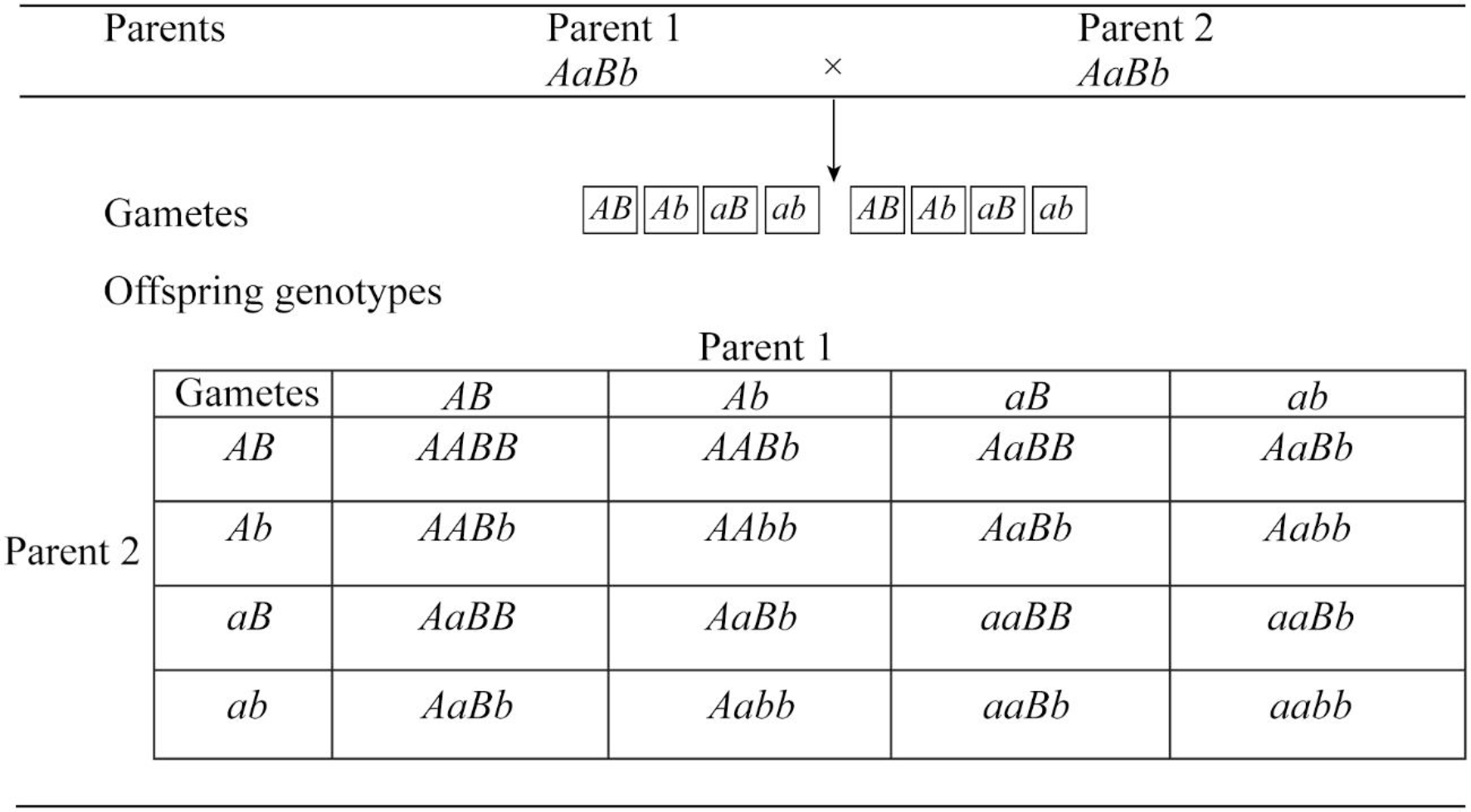
The following is the frequency of genotypes.
Total number of possible genotypes = 16.
AABB=
AABb=
AaBB=
AaBb=
AAbb=
Aabb=
aaBB=
aaBb=
aabb=
The frequency of genotypes AABB, aaBB , AAbb and aabb is 6.25%.
The frequency of genotypes AaBB, AABb, aaBb and Aabb is 12.5%.
The frequency of genotypes AaBb is 25%.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)
- Can I please get this answered with the colors and how the R group is suppose to be set up. Thanksarrow_forwardfa How many different gametes, f₂ phenotypes and f₂ genotypes can potentially be produced from individuals of the following genotypes? 1) AaBb i) AaBB 11) AABSC- AA Bb Cc Dd EE Cal bsm nortubaarrow_forwardC MasteringHealth MasteringNu × session.healthandnutrition-mastering.pearson.com/myct/itemView?assignment ProblemID=17396416&attemptNo=1&offset=prevarrow_forward10. Your instructor will give you 2 amino acids during the activity session (video 2-7. A. First color all the polar and non-polar covalent bonds in the R groups of your 2 amino acids using the same colors as in #7. Do not color the bonds in the backbone of each amino acid. B. Next, color where all the hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic interactions and ionic bonds could occur in the R group of each amino acid. Use the same colors as in #7. Do not color the bonds in the backbone of each amino acid. C. Position the two amino acids on the page below in an orientation where the two R groups could bond together. Once you are satisfied, staple or tape the amino acids in place and label the bond that you formed between the two R groups. - Polar covalent Bond - Red - Non polar Covalent boND- yellow - Ionic BonD - PINK Hydrogen Bonn - Purple Hydrophobic interaction-green O=C-N H I. H HO H =O CH2 C-C-N HICK H HO H CH2 OH H₂N C = Oarrow_forwardFind the dental formula and enter it in the following format: I3/3 C1/1 P4/4 M2/3 = 42 (this is not the correct number, just the correct format) Please be aware: the upper jaw is intact (all teeth are present). The bottom jaw/mandible is not intact. The front teeth should include 6 total rectangular teeth (3 on each side) and 2 total large triangular teeth (1 on each side).arrow_forward12. Calculate the area of a circle which has a radius of 1200 μm. Give your answer in mm² in scientific notation with the correct number of significant figures.arrow_forwardDescribe the image quality of the B.megaterium at 1000X before adding oil? What does adding oil do to the quality of the image?arrow_forwardWhich of the follwowing cells from this lab do you expect to have a nucleus and why or why not? Ceratium, Bacillus megaterium and Cheek epithelial cells?arrow_forward14. If you determine there to be debris on your ocular lens, explain what is the best way to clean it off without damaging the lens?arrow_forward11. Write a simple formula for converting mm to μm when the number of mm's is known. Use the variable X to represent the number of mm's in your formula.arrow_forward13. When a smear containing cells is dried, the cells shrink due to the loss of water. What technique could you use to visualize and measure living cells without heat-fixing them? Hint: you did this technique in part I.arrow_forward10. Write a simple formula for converting μm to mm when the number of μm's are known. Use the variable X to represent the number of um's in your formula.arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning





