
In addition to the maternal effect genes that establish anterior/posterior polarity in the Drosophila embryo (like bicoid and nanos), other maternal effect genes, including dorsal, pelle, and Toll, independently determine dorsal/ventral polarity. The dorsal gene encodes a transcription factor (Dorsal), originally deposited in the egg cytoplasm, that determines ventralness in a concentration-dependent manner. As shown in the following figure(Wild type), a gradient of Dorsal nuclear localization exists in early embryos: Cells whose nuclei have the highest Dorsal protein concentration become the ventral-most cells, cells whose nuclei have no Dorsal protein aredorsal-most, and lateral cells “learn” their positions and fates through the particular intermediate Dorsal proteinlevels in their nuclei. The figure shows sections through blastoderm embryos, where D = dorsal and V = ventral
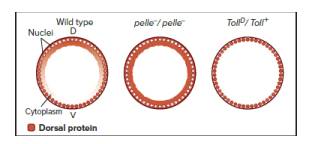
Embryos from mothers homozygous for dorsal null mutations are dorsalized-every cell along the dorsal/ventral axis “thinks” it is the ventral-most cell. Embryos from mothers homozygous for loss-of-function pelle mutations or heterozygous for gain-of-function (constitutively active) TollD> mutations show altered patterns of Dorsal protein localization, as shown in the figure. Pelle and Toll expression are unaltered in dorsal loss-of-function mutants (not shown).
| a. | Describe the alterations in Dorsal protein localization in embryos produced by pelle-/pelle- or TollD/Toll+mutant mothers. |
| b | Based on the information given, order the dorsal, pelle, and Toll genes in a pathway. |
| c. | The two kinds of embryos described in part (a) die just before hatching. Describe their morphological mutant |
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 19 Solutions
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes
- Plating 50 microliters of a sample diluted by a factor of 10-6 produced 91 colonies. What was the originalcell density (CFU/ml) in the sample?arrow_forwardEvery tutor here has got this wrong, don't copy off them.arrow_forwardSuppose that the population from question #1 (data is in table below) is experiencing inbreeding depression (F=.25) (and no longer experiencing natural selection). Calculate the new expected genotype frequencies (f) in this population after one round of inbreeding. Please round to 3 decimal places. Genotype Adh Adh Number of Flies 595 Adh Adh 310 Adhs Adhs 95 Total 1000 fladh Adh- flAdn Adh fAdhs Adharrow_forward
- Which of the following best describes why it is difficult to develop antiviral drugs? Explain why. A. antiviral drugs are very difficult to develop andhave no side effects B. viruses are difficult to target because they usethe host cell’s enzymes and ribosomes tometabolize and replicate C. viruses are too small to be targeted by drugs D. viral infections usually clear up on their ownwith no problemsarrow_forwardThis question has 3 parts (A, B, & C), and is under the subject of Nutrition. Thank you!arrow_forwardThey got this question wrong the 2 previous times I uploaded it here, please make sure it's correvct this time.arrow_forward
- This question has multiple parts (A, B & C), and under the subject of Nutrition. Thank you!arrow_forwardCalculate the CFU/ml of a urine sample if 138 E. coli colonies were counted on a Nutrient Agar Plate when0.5 mls were plated on the NA plate from a 10-9 dilution tube. You must highlight and express your answerin scientific notatioarrow_forwardDon't copy off the other answer if there is anyarrow_forward
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning





