
Concept explainers
A temperature-sensitive allele of the gene encoding the Notch protein (Nts) helped researchers understand the many roles of this protein in fly eye development. Notch is a transmembrane receptor that, when bound to a ligand, relays a signal to the nucleus. In one experiment, wild-type and Nts homozygous developing eyes were allowed to grow in larvae for several hours at permissive temperature, and then the temperature was shifted to the restrictive temperature. After 4 hours, the eyes were dissected from the larvae and the photoreceptors were labeled with an antibody to a protein expressed in all photoreceptors (blue cells in the figure that follows are labeled with antibody). The black dots represent ommatidia at more advanced stages of development that are not shown in the figure.
Eye development occurs in a structure called the eye imaginal disc present in the larva.
Ommatidia develop behind an indentation called the morphogenetic furrow (mf in the diagram). The furrow forms at the posterior of the disc and moves anteriorly; every 2 hours, a new row of ommatidia initiates development posterior to the furrow, while the rows behind that row mature successively to the next stages of assembly. (Only one ommatidium is shown in the diagram, rather than an entire row.) Therefore, in a single eye disc, ommatidia at all stages of development are present. As you saw in Fig. 19.3, the first cells to join the ommatidium are the photoreceptors, R1–R8, and they do so in a particular order.
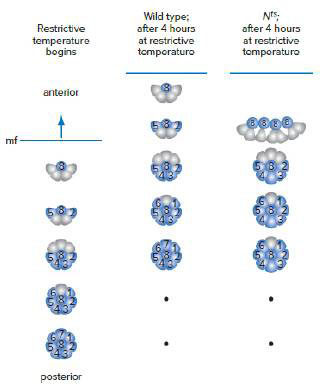
Describe the different roles of the Notch protein at different stages of ommatidial assembly.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 19 Solutions
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes
- Molecular Biology Question Please help. Thank you Explain what is meant by the term “defective virus.” Explain how a defective virus is able to replicate.arrow_forwardMolecular Biology Explain why changing the codon GGG to GGA should not be harmful. Please help . Thank youarrow_forwardStage Percent Time in Hours Interphase .60 14.4 Prophase .20 4.8 Metaphase .10 2.4 Anaphase .06 1.44 Telophase .03 .72 Cytukinesis .01 .24 Can you summarize the results in the chart and explain which phases are faster and why the slower ones are slow?arrow_forward
- Can you circle a cell in the different stages of mitosis? 1.prophase 2.metaphase 3.anaphase 4.telophase 5.cytokinesisarrow_forwardWhich microbe does not live part of its lifecycle outside humans? A. Toxoplasma gondii B. Cytomegalovirus C. Francisella tularensis D. Plasmodium falciparum explain your answer thoroughly.arrow_forwardSelect all of the following that the ablation (knockout) or ectopoic expression (gain of function) of Hox can contribute to. Another set of wings in the fruit fly, duplication of fingernails, ectopic ears in mice, excess feathers in duck/quail chimeras, and homeosis of segment 2 to jaw in Hox2a mutantsarrow_forward
- Select all of the following that changes in the MC1R gene can lead to: Changes in spots/stripes in lizards, changes in coat coloration in mice, ectopic ear formation in Siberian hamsters, and red hair in humansarrow_forwardPleiotropic genes are genes that (blank) Cause a swapping of organs/structures, are the result of duplicated sets of chromosomes, never produce protein products, and have more than one purpose/functionarrow_forwardA loss of function mutation in Pitx1 enhancers can cause (blank) Removal of Pitx1 exons and growth of ectopic hindlimbs, growth of extra ectopic forelimbs, loss of forelimb specification and development, and loss of hindlimb specification and developmentarrow_forward
- Hox1a most likely contributes to (blank) patterning in the developing embryo? Ventral, posterior, limb or anteriorarrow_forwardSelect all of the following that can help establish Hox gene expression boundaries (things that affect Hox and not things that Hox affects). Retinoic acid, anterior/posterior axis, fibroblast growth factors, vagal neural crest, and enhancersarrow_forwardEctopic expression of Hox often results in (blank) phenotypes. (Blank) transformations are characterized by the replacement of one body part/structure with another. Hoxeotic, homealoneotic, joexotic, or homeoticarrow_forward
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College





